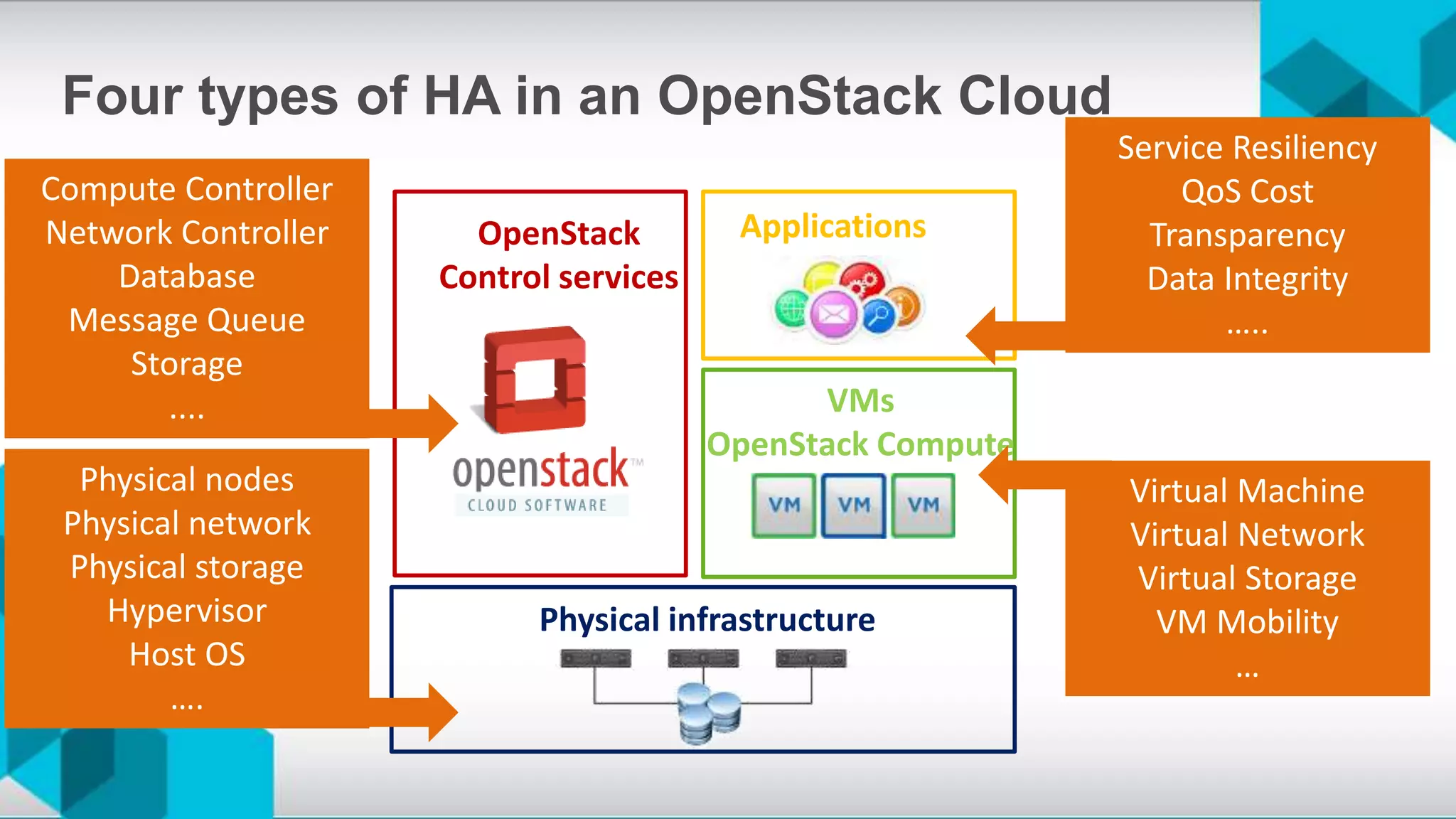
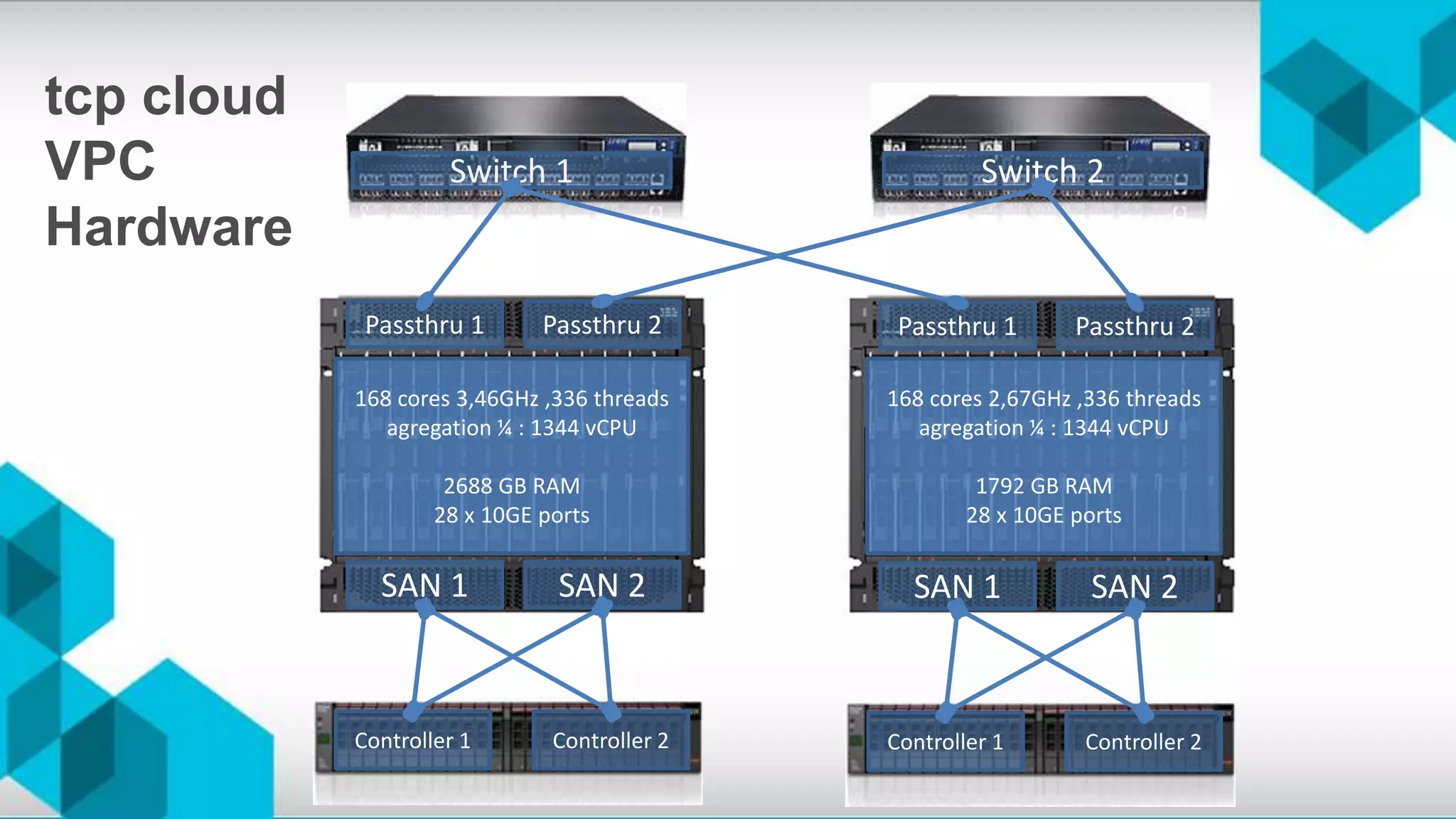
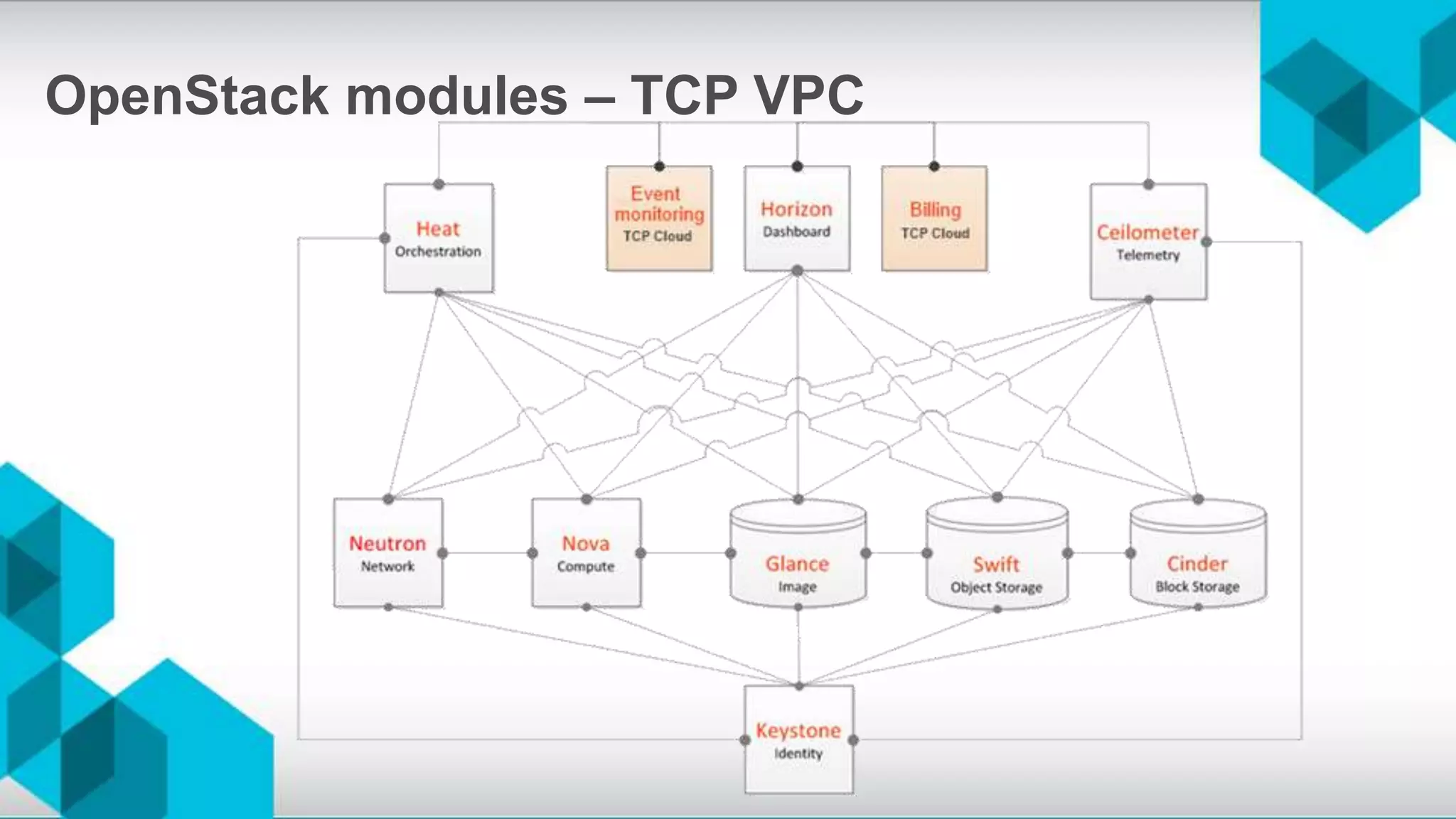
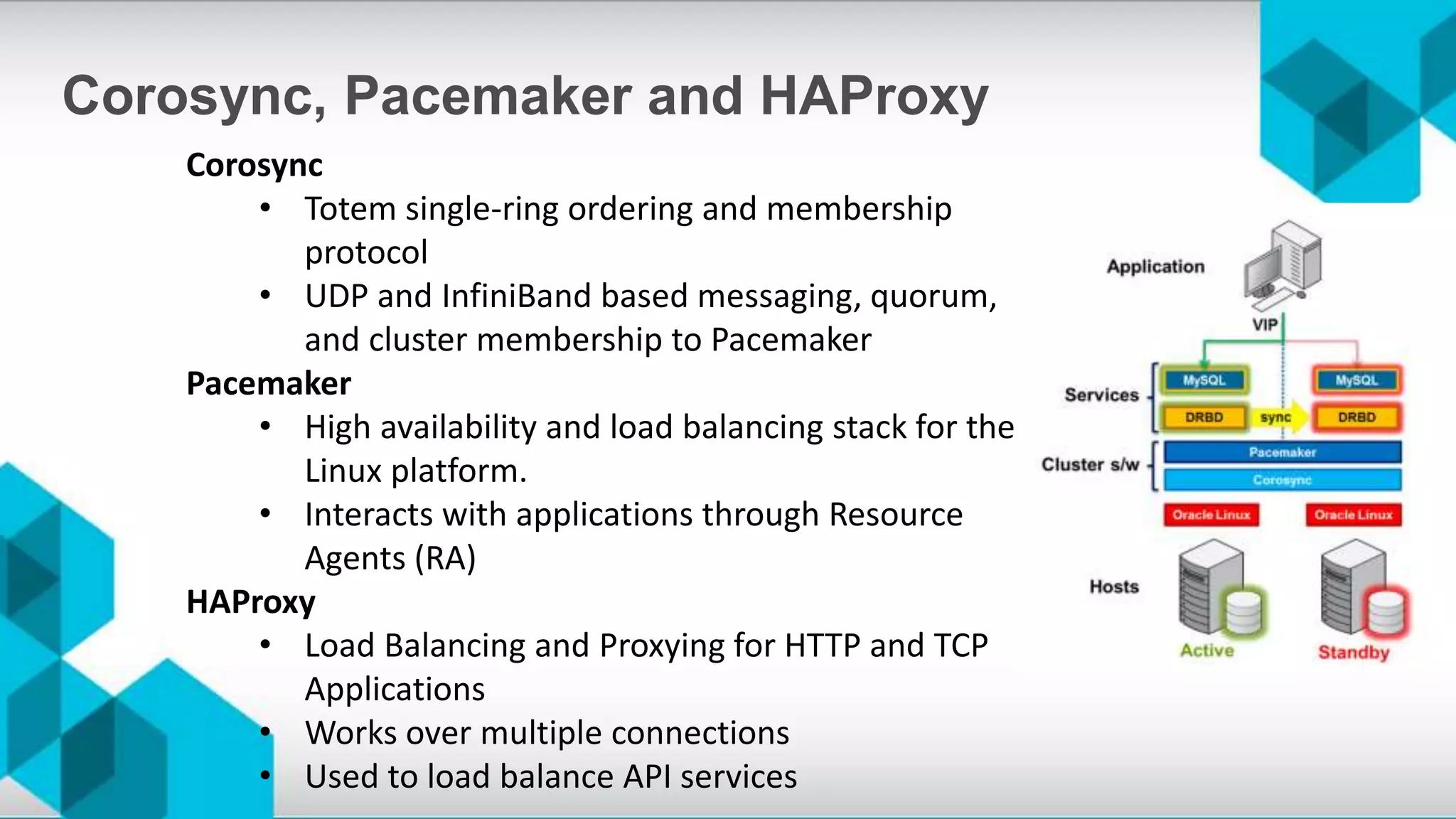
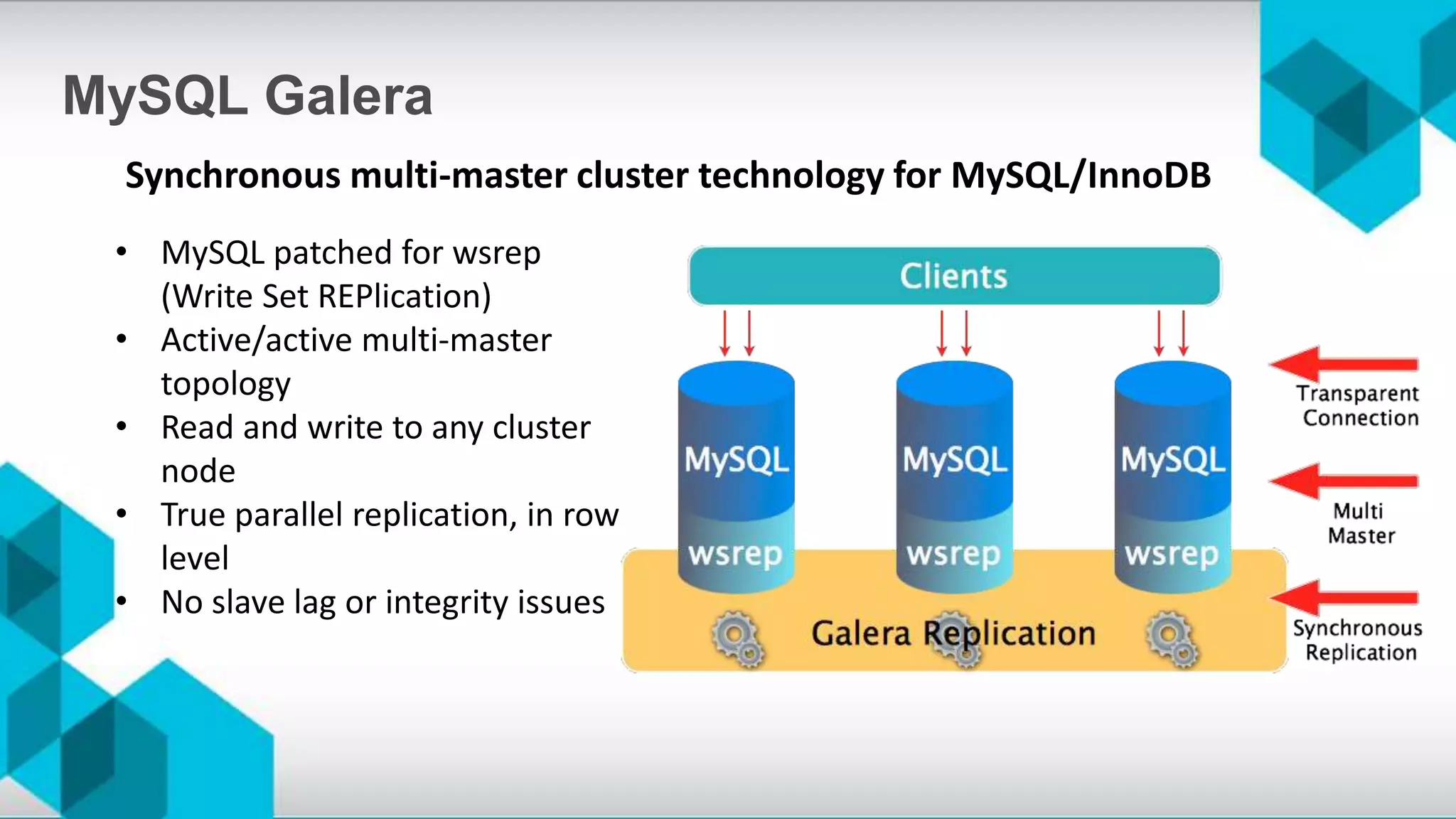
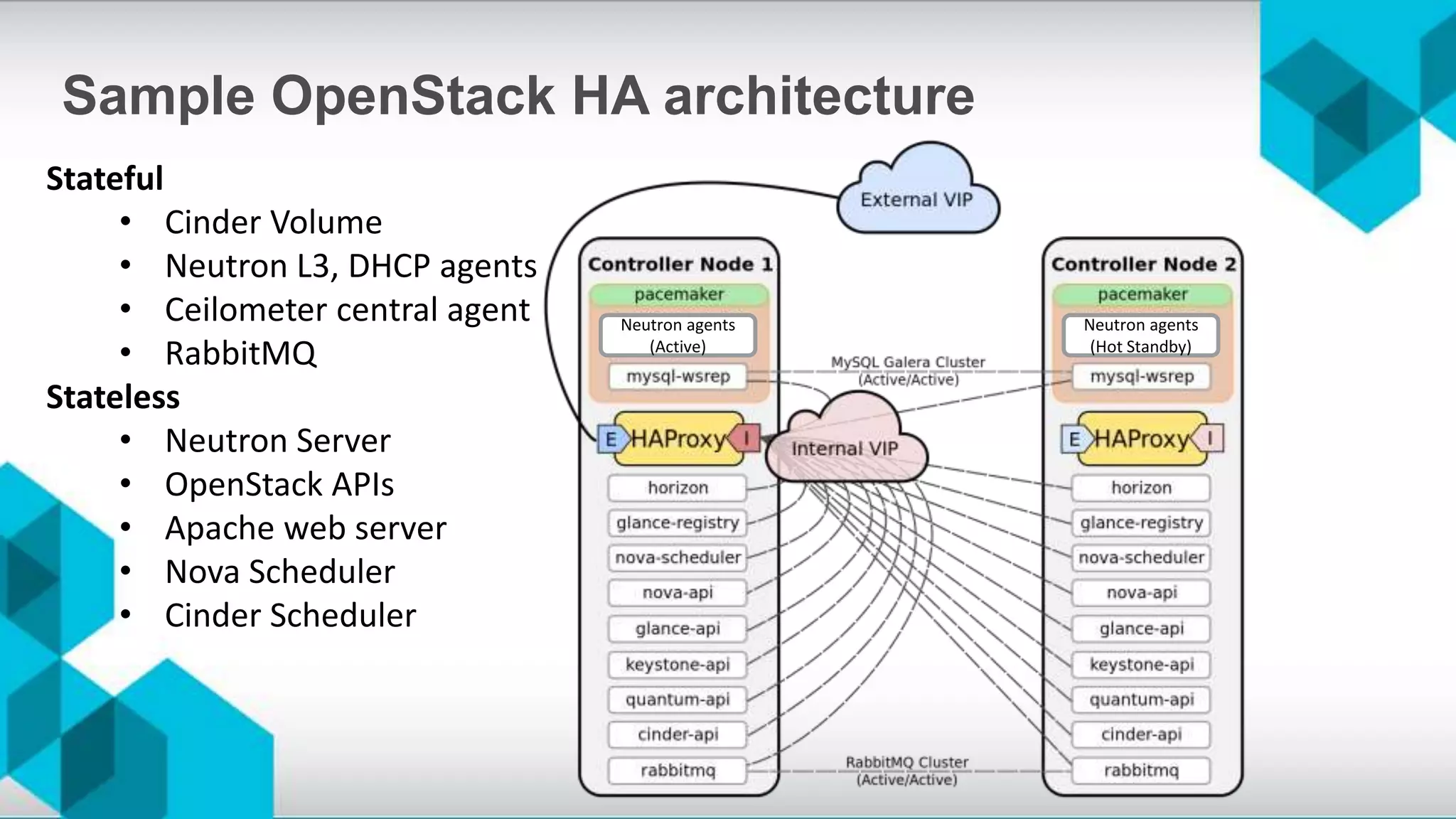
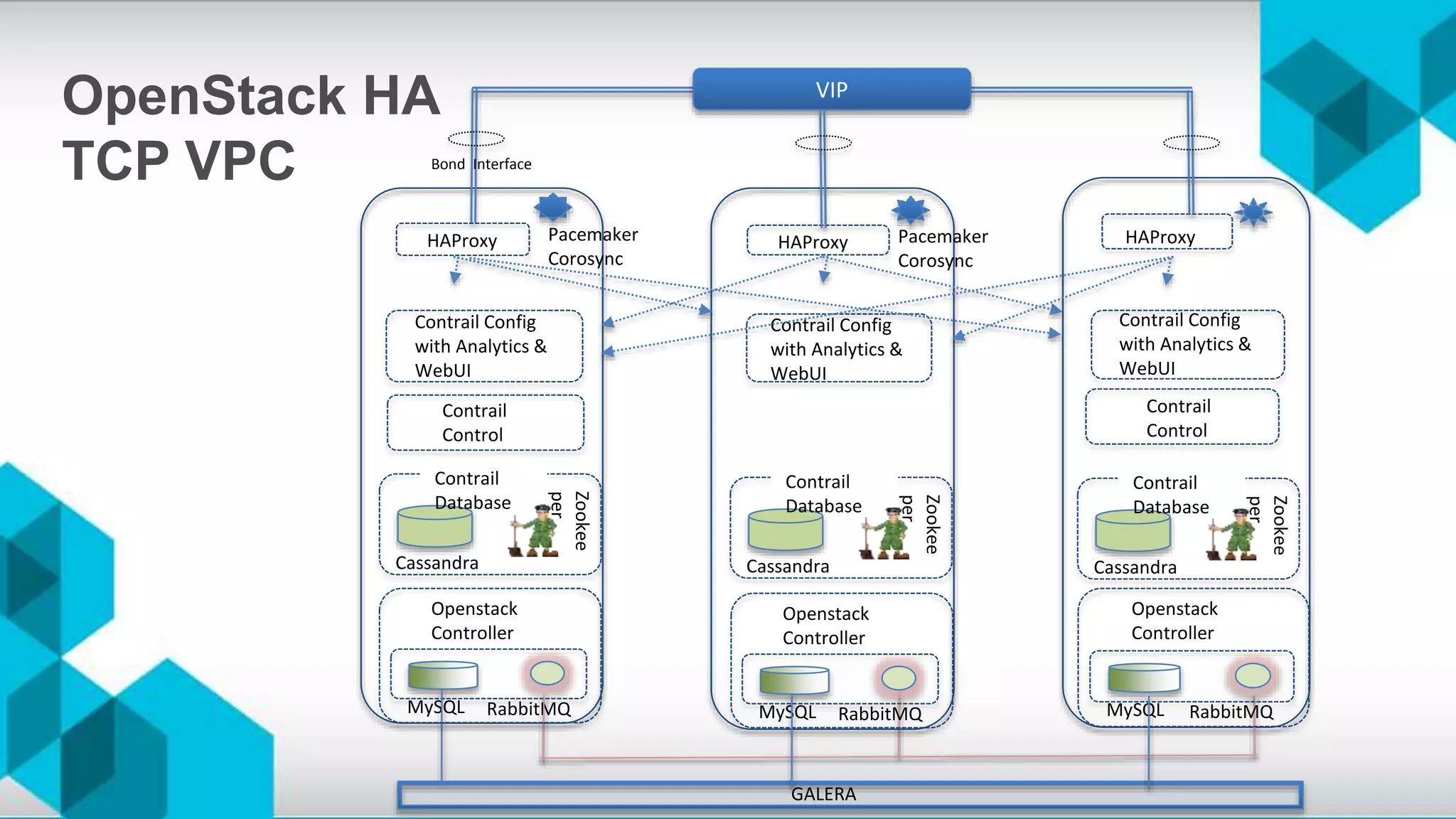
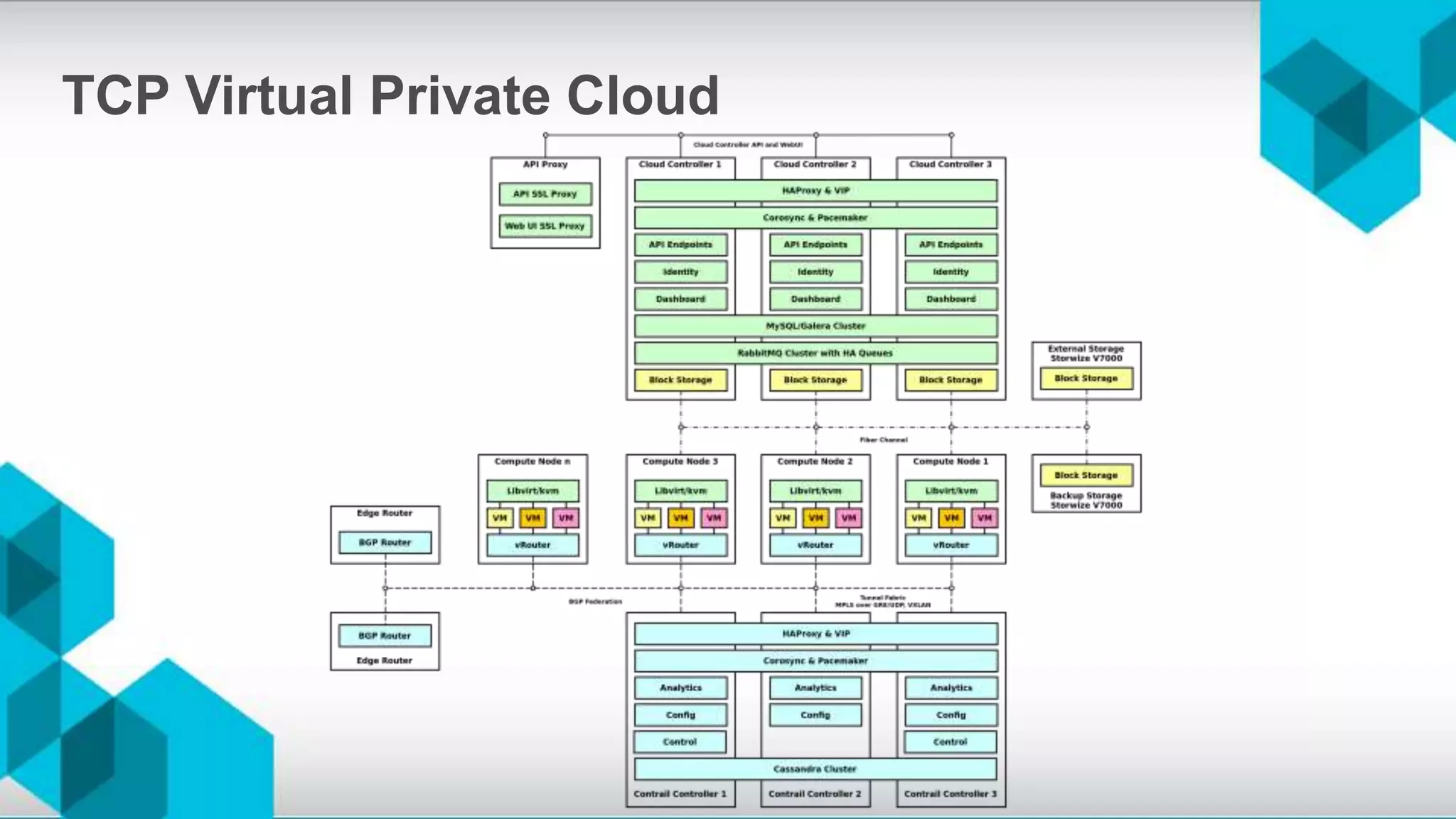
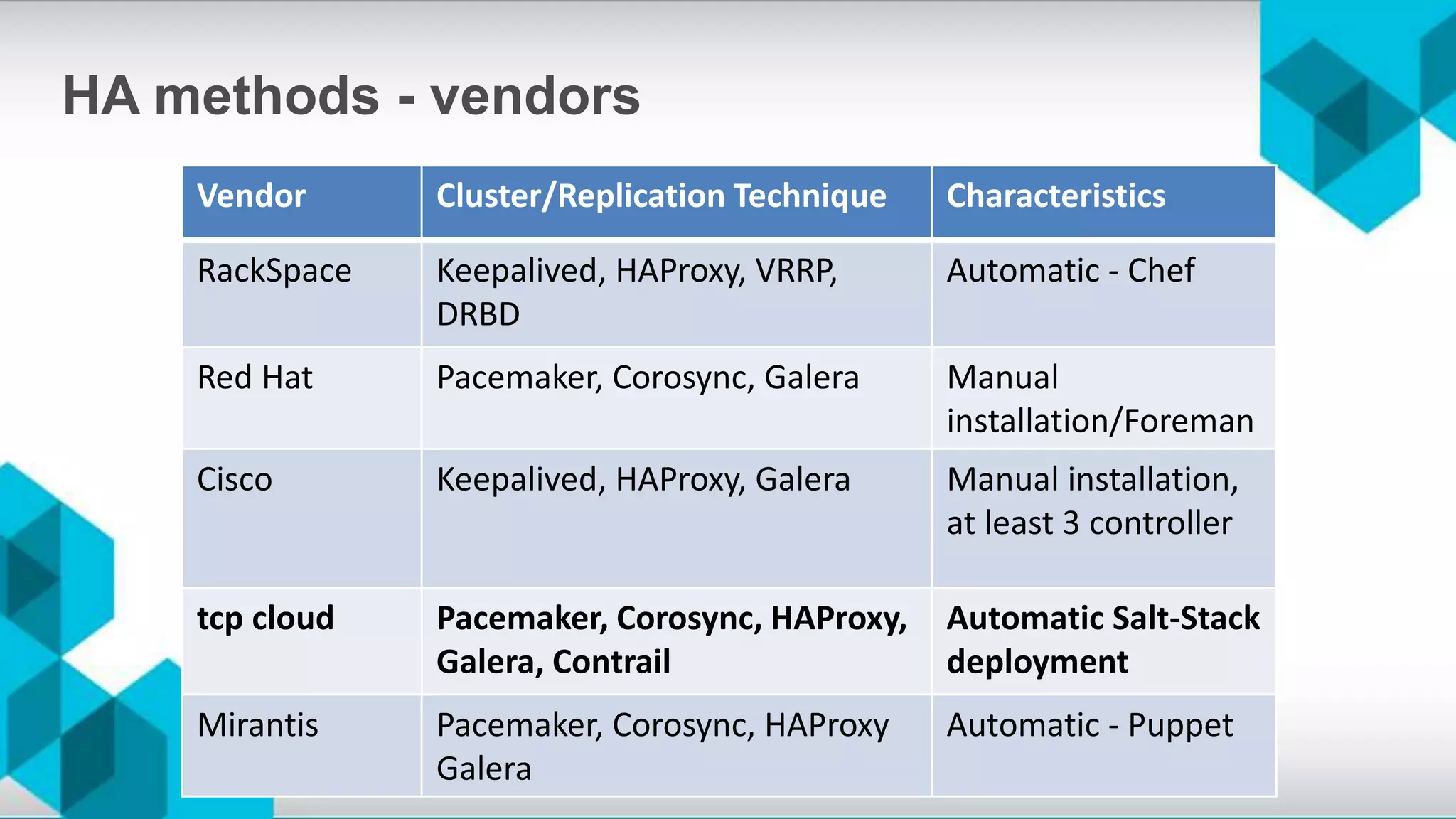
The document discusses high availability (HA) and disaster recovery in OpenStack, outlining the differences between the two while focusing on HA techniques applicable to various components of the OpenStack infrastructure. It elaborates on HA concepts such as active/passive and active/active configurations, and highlights essential technologies like Corosync, Pacemaker, and HAProxy used for maintaining service continuity. Additionally, it addresses the architectural considerations for both stateful and stateless services as well as the challenges associated with implementing HA in OpenStack environments.