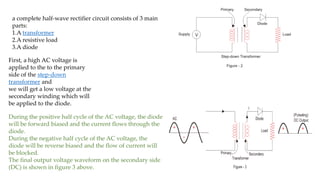
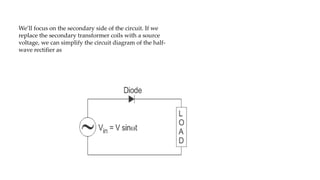
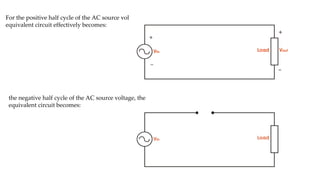
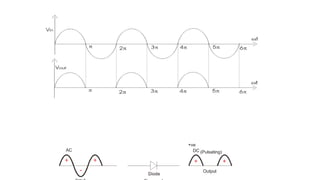
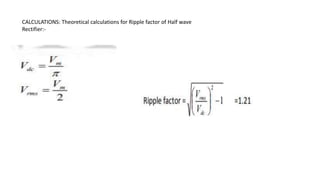
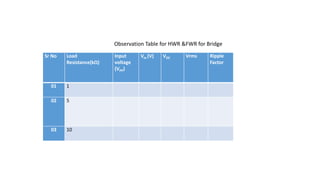
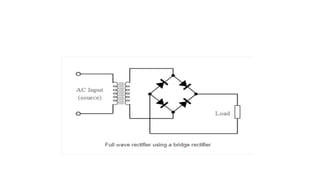
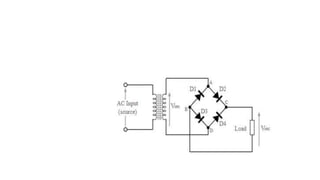
Half wave and full wave rectifiers are used to convert AC to DC voltage. A half wave rectifier only allows one half of the AC cycle to pass through the diode, resulting in a pulsing DC output. It requires only one diode. A full wave bridge rectifier eliminates the pulsing by using four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, resulting in a lower ripple factor and a smoother DC output. The document provides circuit diagrams and calculations to analyze and compare the performance of half wave and full wave rectifiers in terms of their ripple factor.