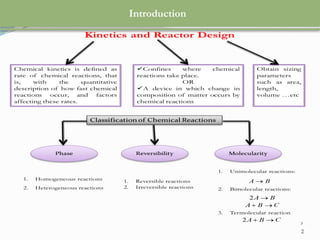
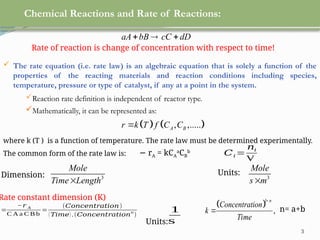
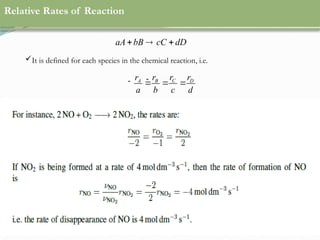
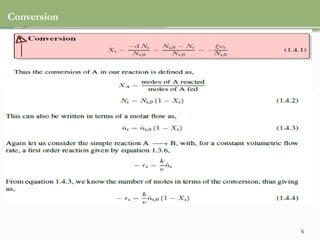
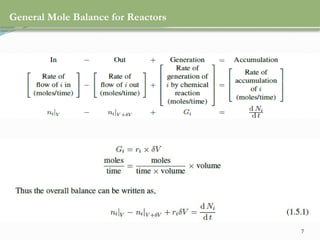
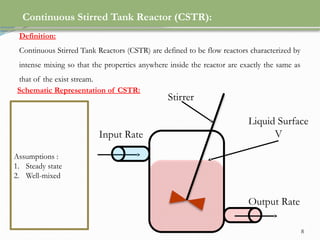
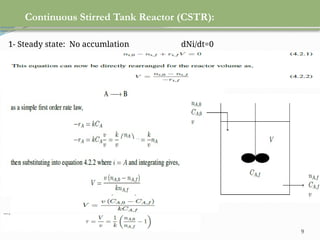
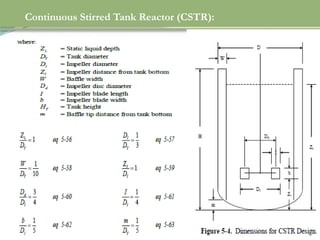
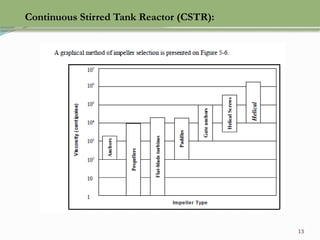
This document discusses chemical reactions, their rates, and the design and operation of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors (CSTRs). It outlines key concepts including rate equations, reaction rates, and the importance of steady-state conditions in CSTRs. The document emphasizes the need for experimental determination of rate laws and describes the ideal behavior of CSTRs as being well-mixed with consistent properties throughout.