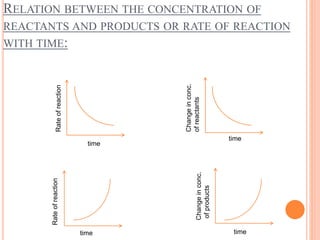
Chemical Reaction Engineering studies how reaction rates are affected by temperature, pressure, and reactant concentration. It provides information about reaction mechanisms, speeds, and types that can be used in bioreactor design. Fundamental concepts include reaction rates, rate laws, and rate constants. Reaction rates are defined as changes in molar concentration over time and can be positive for products or negative for reactants. Rate laws relate reaction rates to reactant concentrations and rate constants measure reaction rates when reactants are at unit concentration.







![RATE LAW OR RATE EQUATION OR KINETIC LAW
The equation which relates the rate of
reaction and the concentration of reactants in a
reaction is called rate law or rate equation .
Consider an equation:
xA+yB product
Rate α [A]x [B]y
Rate=k[A]x [B]y
This equation is called rate equation where x,y
are powers of the concentration of reactants.
‘k’ is rate constant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalreaction2316-151029150326-lva1-app6892/85/Chemical-reaction-2316-9-320.jpg)
![RATE CONSTANT
Rate constant of a chemical reaction is a measure of
rate of reaction, when all reactants are unit conc.
Rate constant = Rate of reaction
[reactants]n
Rate= Rate concentration
Rate constant depends on temperature
Rate constant α temperature](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalreaction2316-151029150326-lva1-app6892/85/Chemical-reaction-2316-10-320.jpg)
![UNITS
Rate constant (k) = Rate of reaction
[reactants]n
k = mol.lit-1.sec-1
[mol]n.[lit]-n
=[mol]1-n.[lit]n-1.sec-1
=[conc.]1-n. sec-1
These two equations are called general nth order
equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalreaction2316-151029150326-lva1-app6892/85/Chemical-reaction-2316-11-320.jpg)

