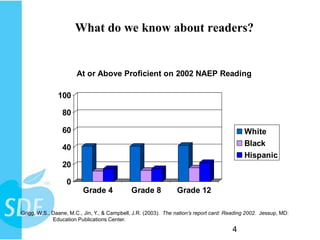
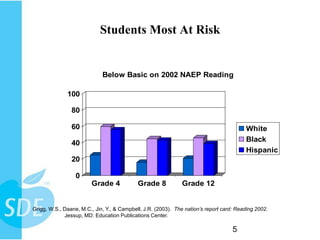
This document discusses strategies for helping reluctant readers. It shows that minority students and those in lower grades struggle most with reading proficiency. Differentiation strategies are recommended like allowing extra time or using audio books. Getting books into students' hands is important, with choices that have appealing covers, characters, and plots. Reluctant readers prefer books with role models, problem solving, and realistic themes. Providing choice and discussing books can help motivate reluctant readers.