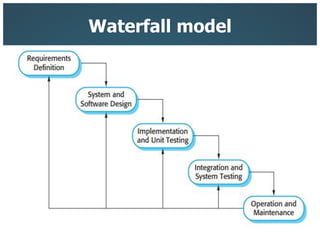
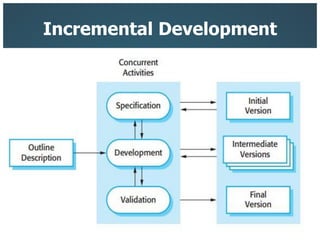
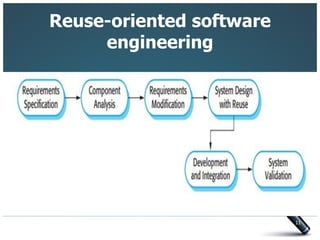
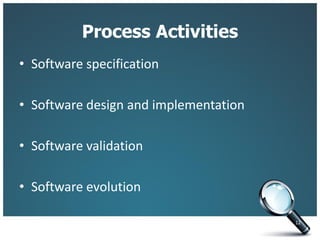
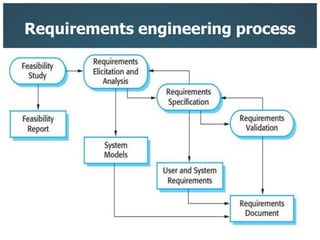
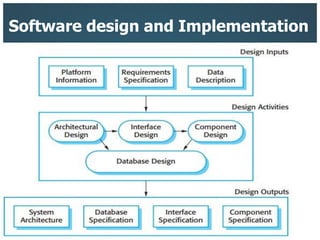
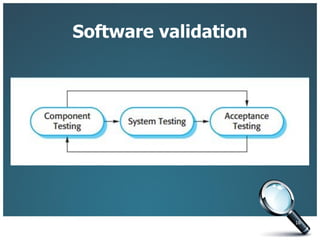
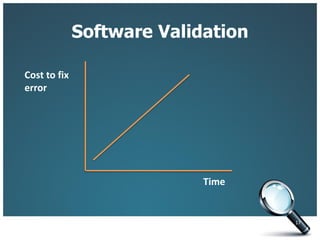
This document introduces three generic software process models: the waterfall model, incremental development, and reuse-oriented software engineering. The waterfall model involves separate, sequential phases from specification to development. Incremental development interleaves specification and development in iterations. Reuse-oriented engineering assembles systems from existing software components. The document also discusses the benefits, disadvantages, and applicability of each model as well as key activities in software processes like specification, design, implementation, validation, and evolution.