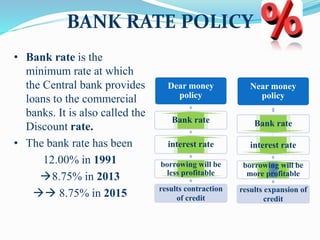
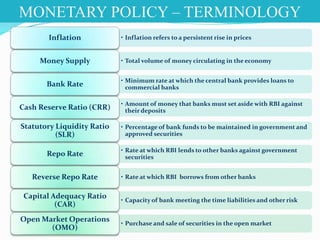
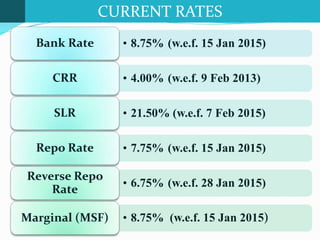
The document discusses monetary policy and fiscal policy in India. It defines monetary policy as the regulation of money supply and credit availability by the Reserve Bank of India. The key tools of monetary policy mentioned are interest rates, cash reserve ratio, statutory liquidity ratio, open market operations, and moral suasion. Fiscal policy is defined as the use of government spending and taxation to influence economic activity. The goal of both policies is to promote economic growth and stability while maintaining price stability and low unemployment. The document provides details on the current rates and targets of various monetary policy tools in India.