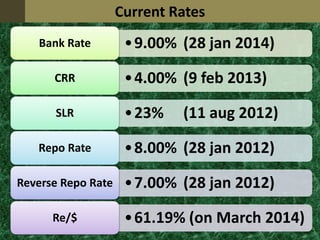
This document discusses monetary policy in India and the tools used by the Reserve Bank of India to regulate monetary policy. It provides background on the governor of RBI and defines monetary policy. It then outlines the objectives of monetary policy in India and describes various quantitative and qualitative measures used by RBI to achieve its objectives, including repo rate, reverse repo rate, bank rate, open market operations, cash reserve ratio, statutory liquidity ratio, moral suasion, direct action, and regulation of consumer credit. It provides current rates for some of these measures and discusses corrective steps taken by RBI to stabilize the exchange rate of the Indian rupee.