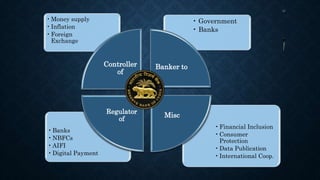
The document outlines the historical development and regulatory framework of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), established in 1935 following a banking crisis that led to extensive reforms. It describes the RBI's monetary policy tools, such as cash reserve ratio and repo rates, aimed at controlling inflation and managing money supply, as well as its regulatory powers over commercial banks. Additionally, it highlights the RBI's initiatives for financial inclusion and consumer protection as part of its broader economic objectives.