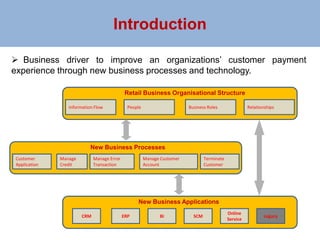
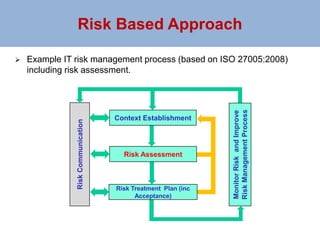
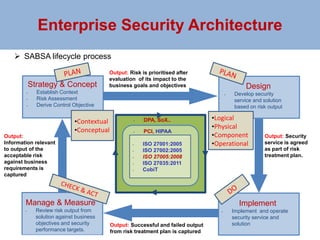
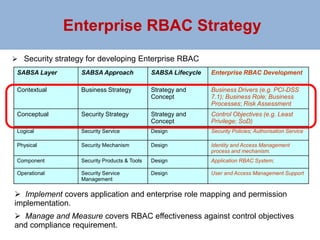
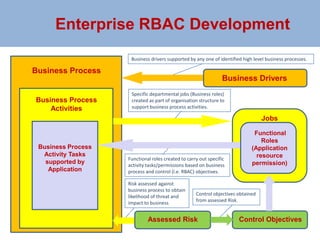
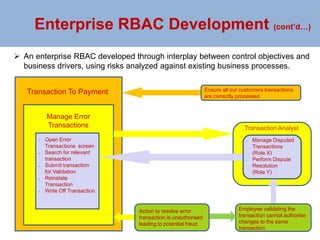
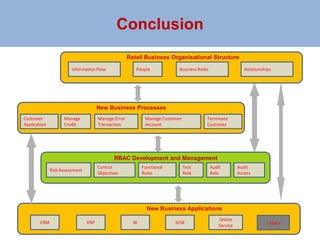
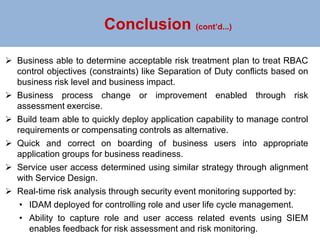
The document outlines a risk-based security architecture for developing enterprise role-based access control (RBAC) to enhance customer payment experiences and manage data privacy laws. It details a strategic approach using the SABSA framework to align security requirements with business objectives, including risk assessment and control objectives. The architecture aims to improve operational effectiveness and compliance while ensuring data integrity and minimizing operational risks in new business processes.