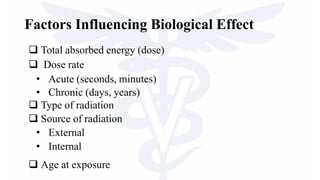
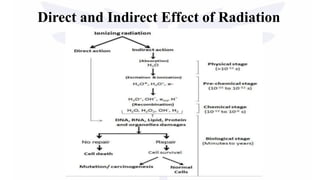
X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation that can pass through materials and damage living cells. Ionizing radiation deposits energy in cells which can cause biological damage at the sub-cellular, cellular, organ and whole organism levels. The most sensitive cells to radiation damage are growth, gonadal, neoplastic and metabolically active cells. Acute radiation exposure over a short time can cause hematopoietic, gastrointestinal and cerebral effects, while long-term low-dose chronic exposure is linked to increased risk of cancer, cataracts and life shortening. Both direct and indirect ionization can damage cells through excitation or alteration of atoms and molecules.