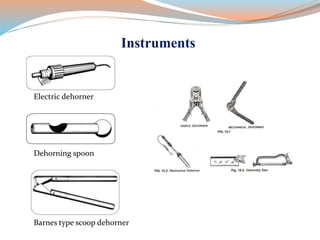
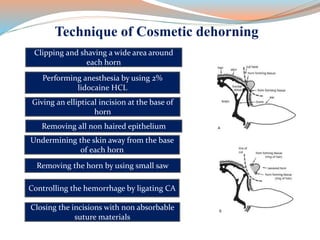
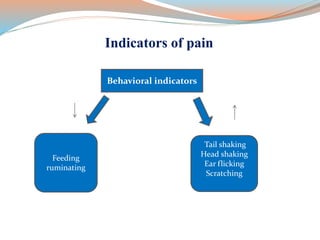
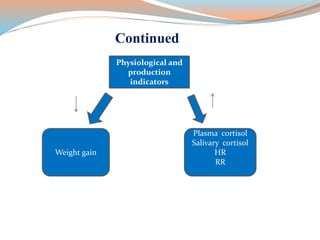
This document discusses dehorning and disbudding cattle. Dehorning removes horns that have already grown, while disbudding destroys horn-producing cells to prevent horn growth. It should be done at a young age using anesthesia and pain relief to reduce stress and risk of injury to the cattle and humans. The proper timing, methods, and post-operative care can help ensure animal welfare.