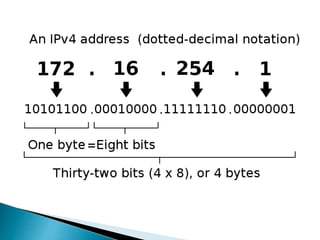
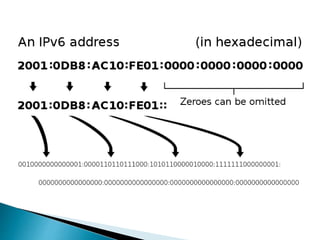
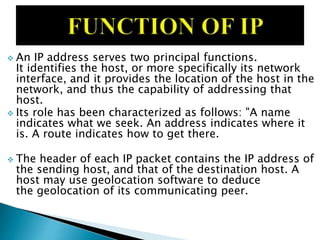
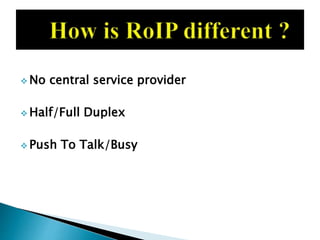
This document discusses Internet Protocol (IP) and Radio over Internet Protocol (RoIP). It defines IP and describes the two main versions, IPv4 and IPv6. It then explains that RoIP uses IP to transmit radio communication signals over networks like the Internet. It provides details on how RoIP can connect radios, phones, and other devices using IP networks and discusses common RoIP applications and uses.