The document presents an overview of various sorting algorithms, including insertion sort, selection sort, bubble sort, and merge sort. It details each algorithm's methodology, advantages, disadvantages, and complexity in terms of best and worst-case scenarios. The content also includes code examples for implementing these sorting algorithms.



![sortingsorting
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 4
Sorting refers to the process of arranging the elements of
an Array in increasing
order or decreasing order.
i.e., A[0]< A[1]< A[2]<………< A[N-1] or
A[0]> A[1]> A[2]>………> A[N-1]
SORTING ELEMENTS OF AN ARRAY:
Here N is the number of elements in the Array.
Eg: If Array A is
After sorting array A becomes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-4-320.jpg)



![insertion sortinsertion sort
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 8
Insertion Sort
◦ An insertion sort starts by considering the first two
elements of array data[0] and data[1].
◦ If they are out of order, i.e., if data [1] < data [0], change
their positions.
◦ Then the third element, data [2], is considered and
compared with the previous data elements in positions 1
and 0.
if data [2] < data [1] and data[0],
change the positions of](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-8-320.jpg)
![insertion sortinsertion sort
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 9
Insertion Sort
data [1] to position 2 and
data[0] to position 1 and
insert data[2] to position 0.
◦ if data [2] < data [1] only,
◦ change the positions of
data[1] to position 2 and
insert data[2] to position 1.
◦ if data[2]> data [1] and data [0]
◦ do not change the position of data[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-9-320.jpg)
![illustration oF insertionillustration oF insertion
sortsort
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 10
Each element in data[i] is inserted is inserted in proper position j
such that 0 <= j <= i and all elements greater than data [i] are
moved by one position.
Illustration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-10-320.jpg)
![InsertIon sort algorIthmInsertIon sort algorIthm
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 11
Algorithm to sort elements of an array A using Insertion Sort
whose number of elements is len.
◦ Step:1 Set i=1
◦ Step:2 Repeat 3 to 9 until i<len
◦ Step:3 Copy the content of array A in position i to a
variable copy
◦ Step:4 Set j=i
◦ Step:5 Repeat 6 and 7 until j>0 and while A[j-1]> copy.
◦ Step:6 A[j]=A[j-1]
◦ Step:7 Decrement j
◦ Step:8 A[j]=copy
◦ Step:9 Increment i
◦ Step:10 Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-11-320.jpg)
![code forcode for InsertIon sortInsertIon sort
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 12
Code for Insertion Sort whose number of elements is len.
public void insertionsort()
{
int i, j;
for(i=1; i<arr.length; i++)
{
int copy = arr[i];
for(j=i; j>0 && copy < arr[j-1]; j--)
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
arr[j] = copy;
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-12-320.jpg)

![best case and worst case ofbest case and worst case of
InsertIon sortInsertIon sort
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 14
BEST CASE:
◦ best case is when the data are already in order.
◦ only one comparison is to be made for each position.
◦ so there are n-1 comparisons. (n=len in previous
algorithm)
◦ The best time is of the order of n
WORST CASE:
◦ The worst case is when the data are in reverse order.
◦ For each i, the item data[i] is less than every item data
[0] … data[i-1] and each of them is moved by one
position.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-14-320.jpg)

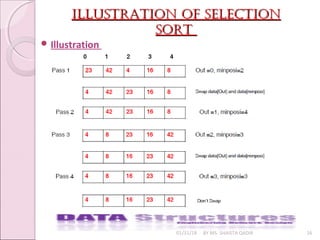
![selectIon sort algorIthmselectIon sort algorIthm
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 17
Algorithm to sort elements of an array A using Selection
Sort whose number of elements is len.
◦ Step:1 Set out=0
◦ Step:2 Repeat 3 to 5 until out<len-1
◦ Step:3 Find position, minposi of minimum element from
the elements A[out],….., A[len-1]
◦ Step:4 Swap A[out] and A[minposi]
◦ Step:5 Increment out
◦ Step:6 Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-17-320.jpg)
![code forcode for selectIon sortselectIon sort
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 18
Code for Insertion Sort whose number of elements is len.
public void selectionsort()
{
int out, in, minposi;
for(out=0; out<arr.length-1; out++)
{
minposi = out;
for(in=out+1; in<arr.length; in++)
if(arr[in] < arr[minposi] )
minposi = in;
swap(out, minposi);
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-18-320.jpg)

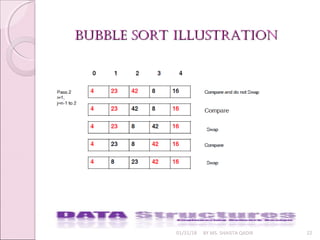
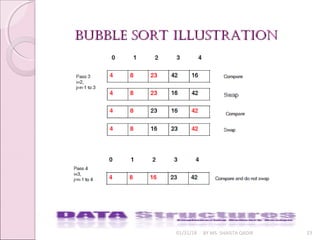
![bubble sortbubble sort
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 20
A Bubble sort bubbles the smallest element to the top.
It compares data[N-1] and data[N-2] and arrange them in
order such that data[N-2]< data[N-1].
Then compare data[N-3] and data[N-2] and arrange such
that data [N-3]< data [N-2].
Continue this until data [0]<data[1]. This pass bubbles out
the smallest number in position 0.
Repeat this comparison with the elements from data[N-1]
to data [1] and so on](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-20-320.jpg)

![bubble Sort algorithmbubble Sort algorithm
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 24
Algorithm to sort elements of an array A using Bubble Sort
whose number of elements is n.
◦ Step:1 Set i=0
◦ Step:2 Repeat 3 to 7 until i<n-1
◦ Step:3 Set j=n-1
◦ Step:4 Repeat 5 to 6 until j>i
◦ Step:5 If data[j]<data[j-1], swap (data[j], data[j-1])
◦ Step:6 Decrement j
◦ Step: 7Increment i
◦ Step:8 Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-24-320.jpg)
![bubble Sort algorithmbubble Sort algorithm
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 25
Algorithm to sort elements of an array A using Bubble Sort
whose number of elements is n.
◦ Step:1 Set i=0
◦ Step:2 Repeat 3 to 7 until i<n-1
◦ Step:3 Set j=n-1
◦ Step:4 Repeat 5 to 6 until j>i
◦ Step:5 If data[j]<data[j-1], swap (data[j], data[j-1])
◦ Step:6 Decrement j
◦ Step: 7Increment i
◦ Step:8 Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-25-320.jpg)
![code Segment forcode Segment for bubblebubble
SortSort
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 26
Code for Bubble Sort
public void bubblesort()
{
int i,n,j;
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
for(j=n-1;j>i;--j)
if(data[j] < data[j-1])
swap(j,j-1);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-26-320.jpg)



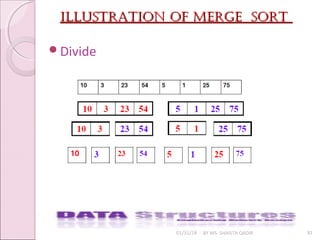

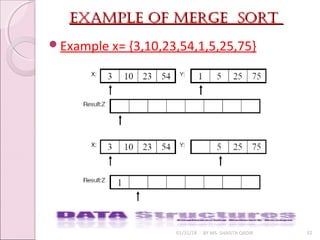
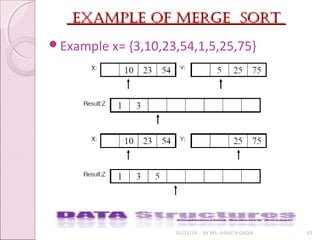
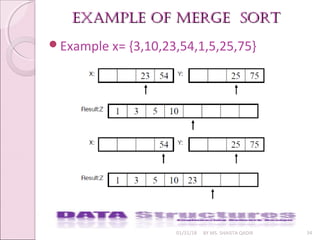
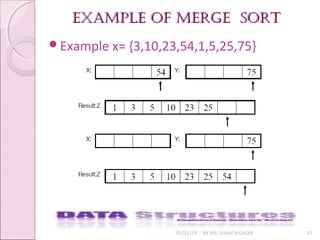
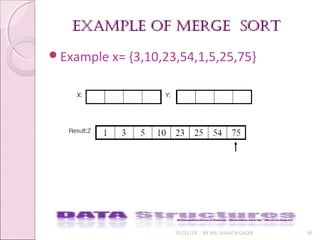
![merge sort algorithmmerge sort algorithm
01/31/18 BY MS. SHAISTA QADIR 37
Algorithm to sort elements of sorted arrays X of size m and Y of
size n using Merge Sort in to another array of size m+n.
◦ Step:1 Set i=0, j=0,k=0
◦ Step:2 If x[i]<=y[j] Go to Step:3 else Go to Step:5
◦ Step:3 Set z[k]=x[i], k=k+1, i=i+1, if i<=m, Go to Step:2
◦ Step:4 Set z[k],……,z[m+n]=y[j],….y[n]
◦ Step:5 Set z[k]=y[j], k=k+1, j=j=j+1, if j<=n, Go to Step:2
◦ Step:6 Set z[k],……,z[m+n]=x[i],….x[m]
◦ Step:7 Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture7-180131101055/85/Sorting-37-320.jpg)
