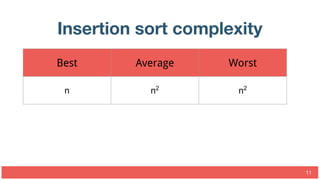
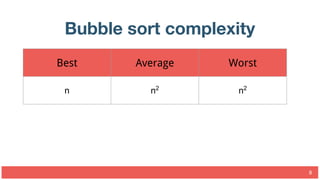
This document discusses different sorting algorithms and their complexities. It covers slow sorts like bubble sort and insertion sort which have quadratic time complexity, as well as medium sorts like merge sort which has linearithmic time complexity. Merge sort works by dividing the array into sublists of one element and then merging the sublists together until the entire list is sorted. The document provides pseudocode examples and analyses the time complexities of various sorting algorithms.






![Pseudocode
7
procedure bubbleSort( A : list of sortable items )
n = length(A)
repeat
swapped = false
for i = 1 to n-1 inclusive do
/* if this pair is out of order */
if A[i-1] > A[i] then
/* swap them and remember something changed */
swap( A[i-1], A[i] )
swapped = true
end if
end for
until not swapped
end procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresandalgorithms-sortingalgorithms-150621094037-lva1-app6892/85/Data-structures-and-algorithms-sorting-algorithms-7-320.jpg)

![Pseudocode
10
for i ← 1 to length(A) - 1
j ← i
while j > 0 and A[j-1] > A[j]
swap A[j] and A[j-1]
j ← j - 1
end while
end for](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructuresandalgorithms-sortingalgorithms-150621094037-lva1-app6892/85/Data-structures-and-algorithms-sorting-algorithms-10-320.jpg)