This document provides a summary of a lecture on sorting algorithms:
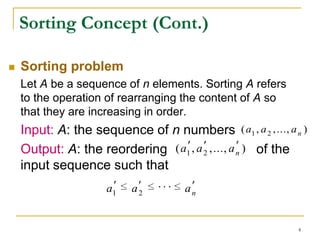
1) It introduces sorting concepts and sorting problems. Common sorting algorithms discussed include selection sort, insertion sort, merge sort, and quick sort.
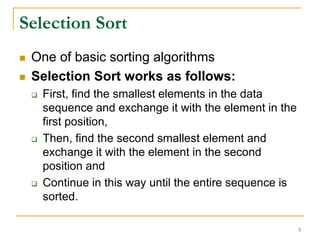
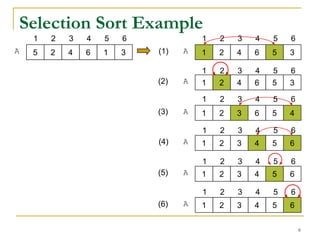
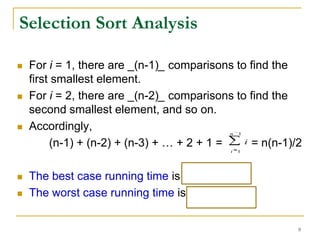
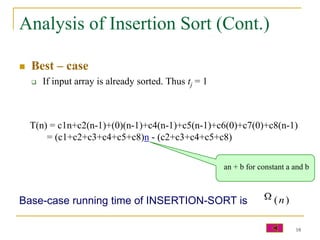
2) Selection sort and insertion sort algorithms are explained in detail with examples. Selection sort has a running time of O(n^2) in all cases.
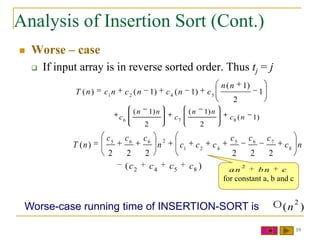
3) Insertion sort's running time depends on how sorted the input array is - it is O(n) for a presorted array but O(n^2) for a reverse sorted array.
4) The time complexity of both algorithms is analyzed mathematically. Selection sort is always O(n^2) while



![Selection Sort Algorithm
Algorithm SelectionSort(A,n)
Input: A: a sequence of n elements
n: the size of A
Output: A: a sorted sequence in ascending order
for i = 1 to n
min = i
for j = i+1 to n
if A[j] < A[min] then
min = j
Swap(A,min,i)
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-7-320.jpg)
![Selection Sort Algorithm (Cont.)
Algorithm: Swap(A,min,i)
Input: A : a sequence of n elements
min: the position of the minimum value of A
while considers at index i of A
i: the considered index of A
Output: exchange A[i] and A[min]
temp = a[min]
a[min] = a[i]
a[i] = temp
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-8-320.jpg)

![Insertion Sort (Cont.)
Insertion sort uses an incremental approach:
having the sorted subarray A[1…j-1], we
insert the single element A[ j ] into its proper
place and then we will get the sorted
subarray A[ 1…j ]
pick up
Sorted order Unsorted order
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-11-320.jpg)
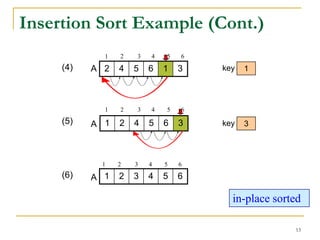
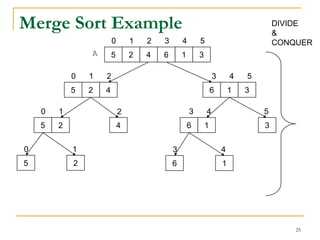
![Insertion Sort Example
1 2 3 4 5 6
5 2 4 6 1 3
key = A[j]
1 2 3 4 5 6
(1) A 5 2 4 6 1 3 key 2
1 2 3 4 5 6
(2) A 2 5 4 6 1 3 key 4
1 2 3 4 5 6
(3) A 2 4 5 6 1 3 key 6
in-place sorted
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-12-320.jpg)
![Insertion Sort Algorithm
Algorithm: INSERTION-SORT(A)
Input: A : A sequence of n numbers
Output: A : A sorted sequence in increasing order of array A
for j = 2 to length(A)
key = A[j]
//Insert A[j] into the sorted sequence A[1…j-1]
i = j-1
while i > 0 and A[i] > key
A[i+1] = A[i]
i = i-1
A[i+1] = key
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-14-320.jpg)

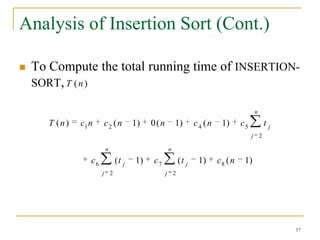
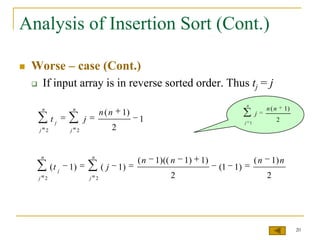
![Insertion Sort Analysis (cont.)
INSERTION-SORT(A) cost times
1. for j = 2 to length(A) c1 n
2. key = A[j] c2 n-1
3. //Insert A[j] into the sorted sequence A[1…j-1] 0 n-1
4. i = j-1 c4 n-1
n
5. while i > 0 and A[i] > key c5 tj
j 2
n
6. A[i+1] = A[i] c6 (t j 1)
j 2
n
7. i = i-1 c7 (t j 1)
j 2
8. A[i+1] = key c8 n-1
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-16-320.jpg)




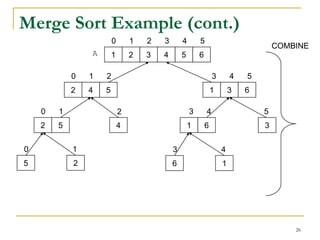
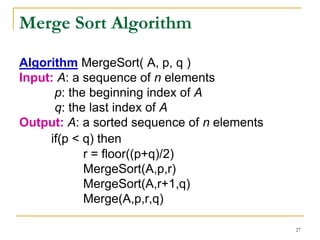
![Algo Merge(A,p,r,q)
Input: A, p, r, q : a sorted subsequences A[p…r] and
A[r+1…q]
Output: A: a sorted sequence A[p…q]
let i=p, k=p, j=r+1
while (i ≤ r) and (j ≤ q)
if (A[i] ≤ A[j]) then
B[k] = A[i]
k++
i++
else
B[k] = A[j]
k=k+1
j=j+1
if (i>r) then /* If the maximum value of left subsequence is less than the right subsequence */
while(j ≤ q)
B[k] = A[j]
k++
j++
else if(j > q) then /* If the maximum value of left subsequence is gather than the right subsequence */
while(i ≤ r)
B[k] = A[i]
k++
i++
for k = p to q
A[k] = b[k]
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-28-320.jpg)

![Quick Sort
Quick Sort, likes merge sort, is based on the
divide-and-conquer approach.
To sort an array A[p…r]
Divide: Partition (rearrange) the array A[p…r] into
two subarray A[p…q -1] and subarray A[q+1…r]
such that:
Each element of A[p…q -1] is less than or equal to A[q]
Each element of A[q+1…r] is greater than A[q]
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-30-320.jpg)
![Quick Sort (Cont.)
To sort sorting an array A[p…r] (cont.)
Conquer: Sort the two subarray A[p…q -1] and
A[q+1…r] by recursive calls to QuickSort.
Combine: Since the subarrays are sorted in place, no
work is needed to combine them: the entire array
A[p…r] is now sorted.
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-31-320.jpg)

![Quick Sort Algorithm
Algo QuickSort(A, p, r)
Input: A: A sequence of n numbers
p: The first index of A
r: The last index of A
Output: A: A sorted sequence in increasing order of array A
• Rearrange the subarray
if (p < r) then A[p…r] in place.
• The elements that is less
q = Partition(A,p,r) than A[q] are placed at the
left side of A[q] and
QuickSort(A,p,q-1) • The elements that is
greater than A[q] are placed
QuickSort(A,q+1,r) at the right side of A[q].
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-33-320.jpg)
![Quick Sort Algorithm (Cont.)
Algo Partition(A, p, r)
Input: A: A sequence of n numbers
p: The first index of A
r: The last index of A
Output: A: The rearranged subarray A[p…r]
key = A[r]
i=p–1
for j = p to r -1
if A[ j ] ≤ key then
i = i+1
exchange A[i] and A[j]
exchange A[i+1] and key
return i+1 34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect11sorting-100228120017-phpapp02/85/Lect11-Sorting-34-320.jpg)

