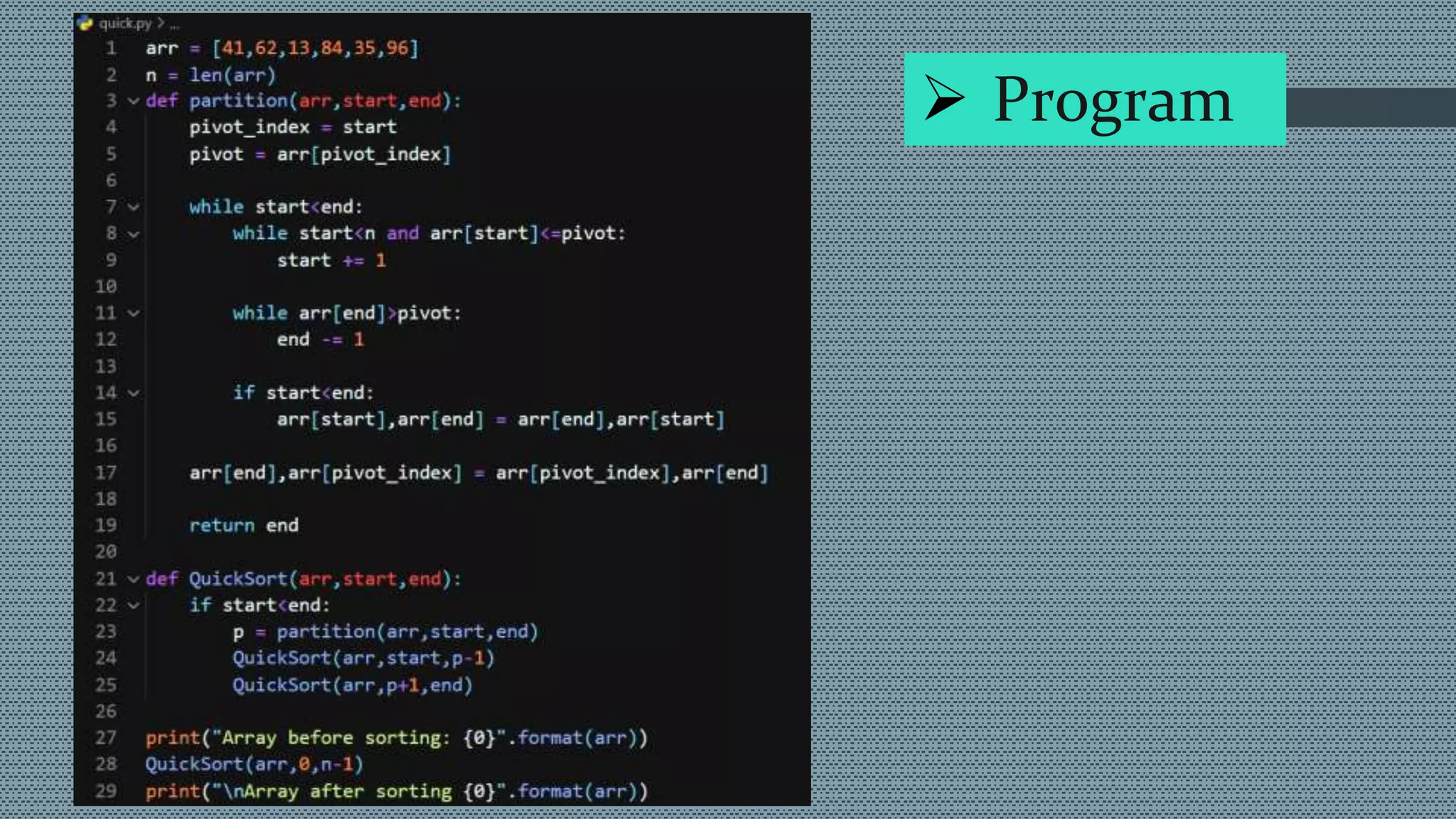
Quick sort is a widely used and efficient sorting algorithm that utilizes the divide and conquer strategy, partitioning an array into smaller arrays based on a specified pivot value. The algorithm sorts elements in place by recursively sorting sub-arrays and has a best and average time complexity of O(n log n), with a worst case of O(n^2). Space complexity can range from O(n) for the basic approach to O(log n) for the modified approach.

![How we use divide and conquer algorithm for
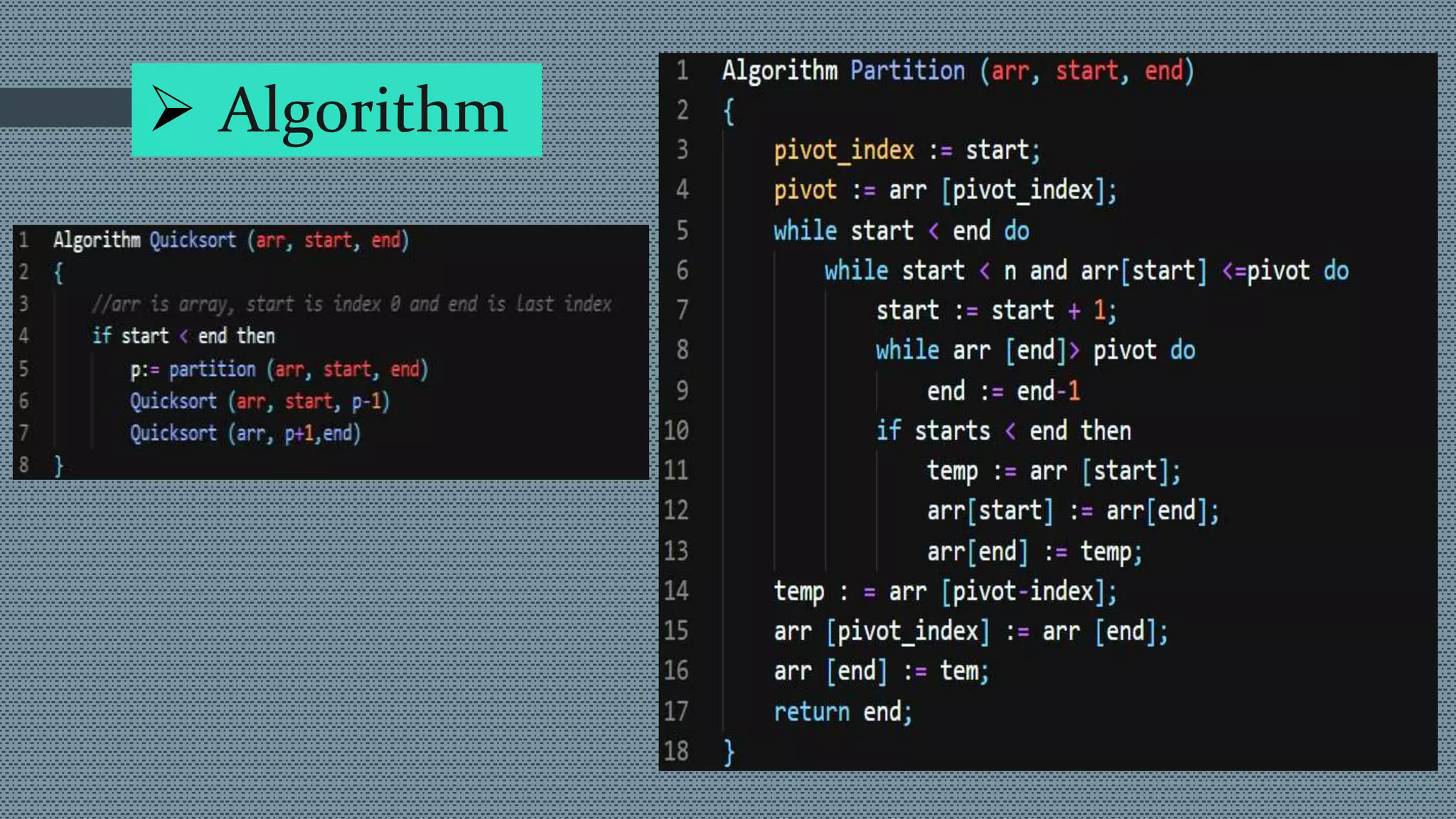
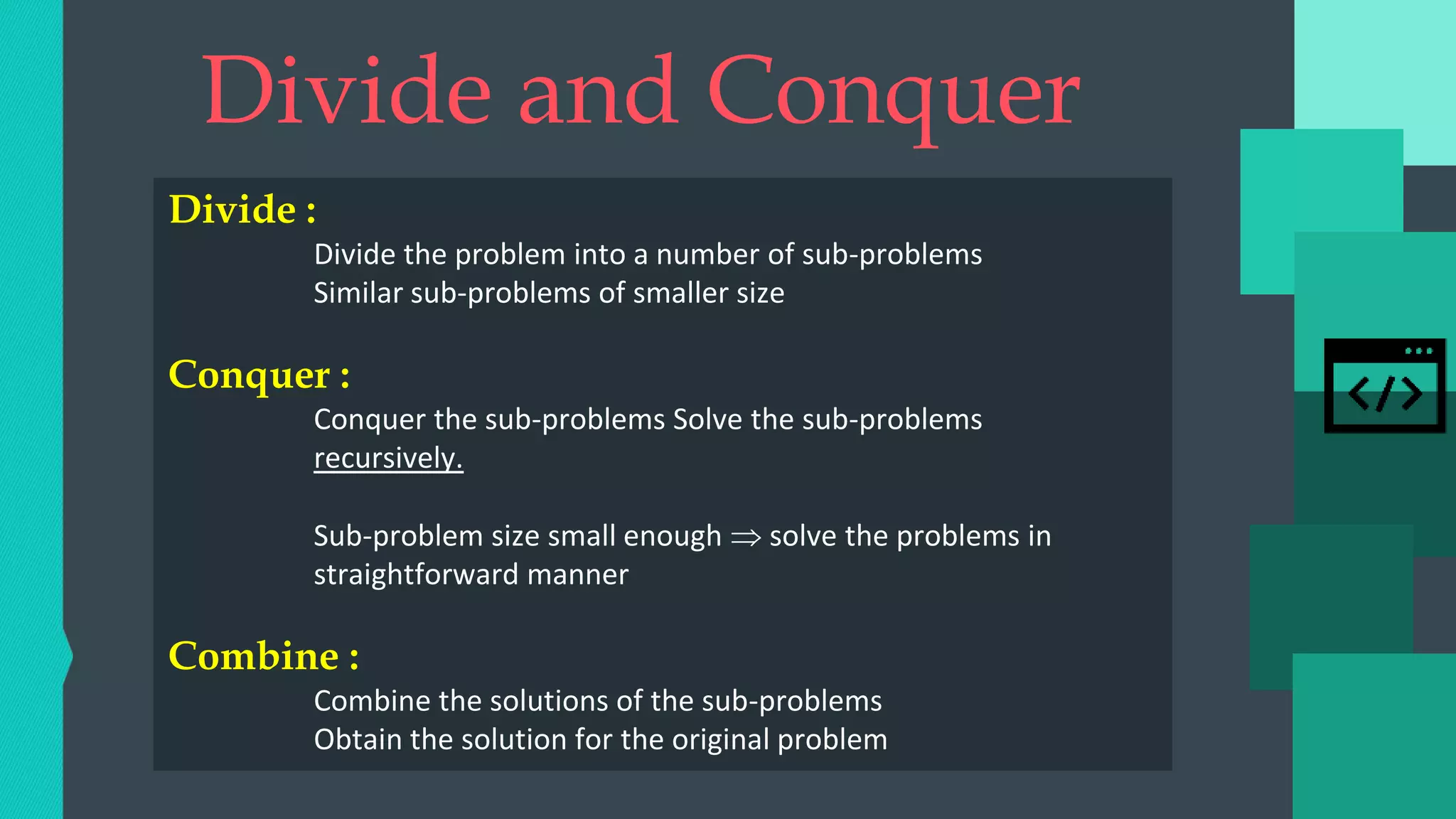
Quicksort
Sort an array A[p…r]
Divide
Partition the array A into 2 subarrays A[p..q] and A[q+1..r], such that each element of
A[p..q] is smaller than or equal to each element in A[q+1..r]
Need to find index q to partition the array
≤](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fymca2064daacarricularactivity-211201153311/75/Divide-and-conquer-4-2048.jpg)
![ Conquer
Recursively sort A[p..q] and A[q+1..r] using Quicksort.
First sort A[p..q] and then sort A[q+1..r] individually.
Combine
Trivial: the arrays are sorted in place
No additional work is required to combine them.
The entire array is now sorted.
≤](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fymca2064daacarricularactivity-211201153311/75/Divide-and-conquer-5-2048.jpg)

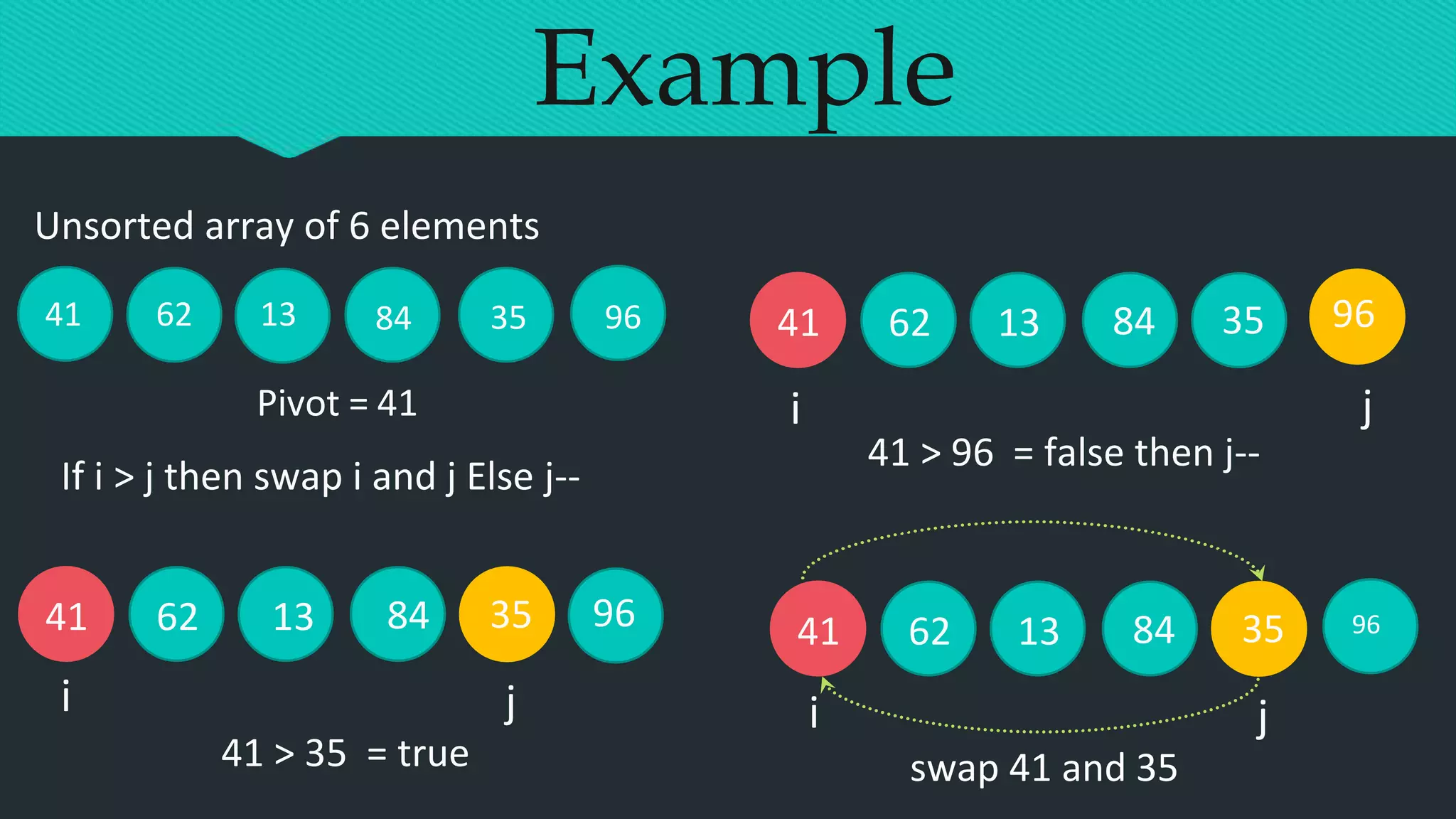
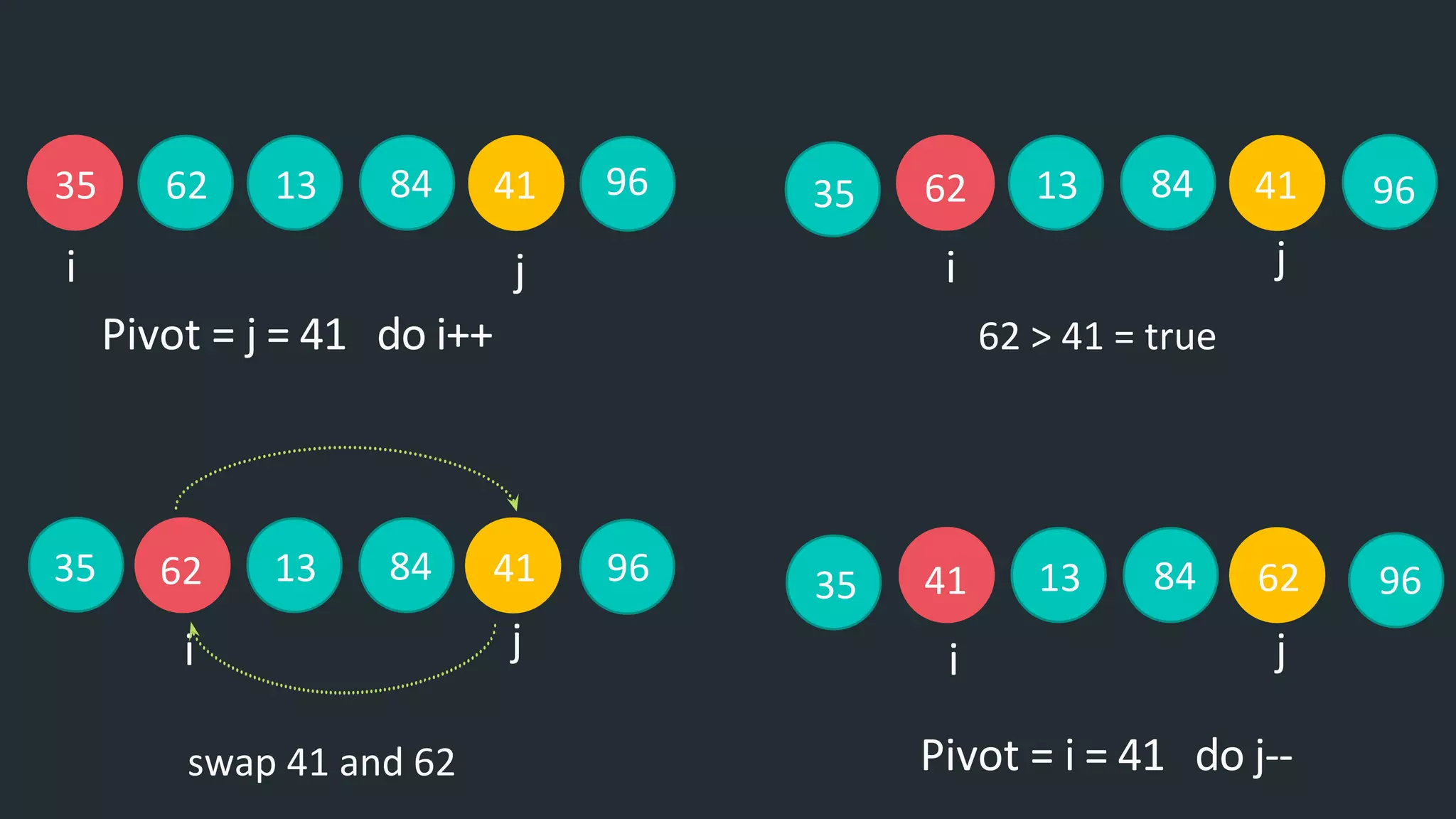
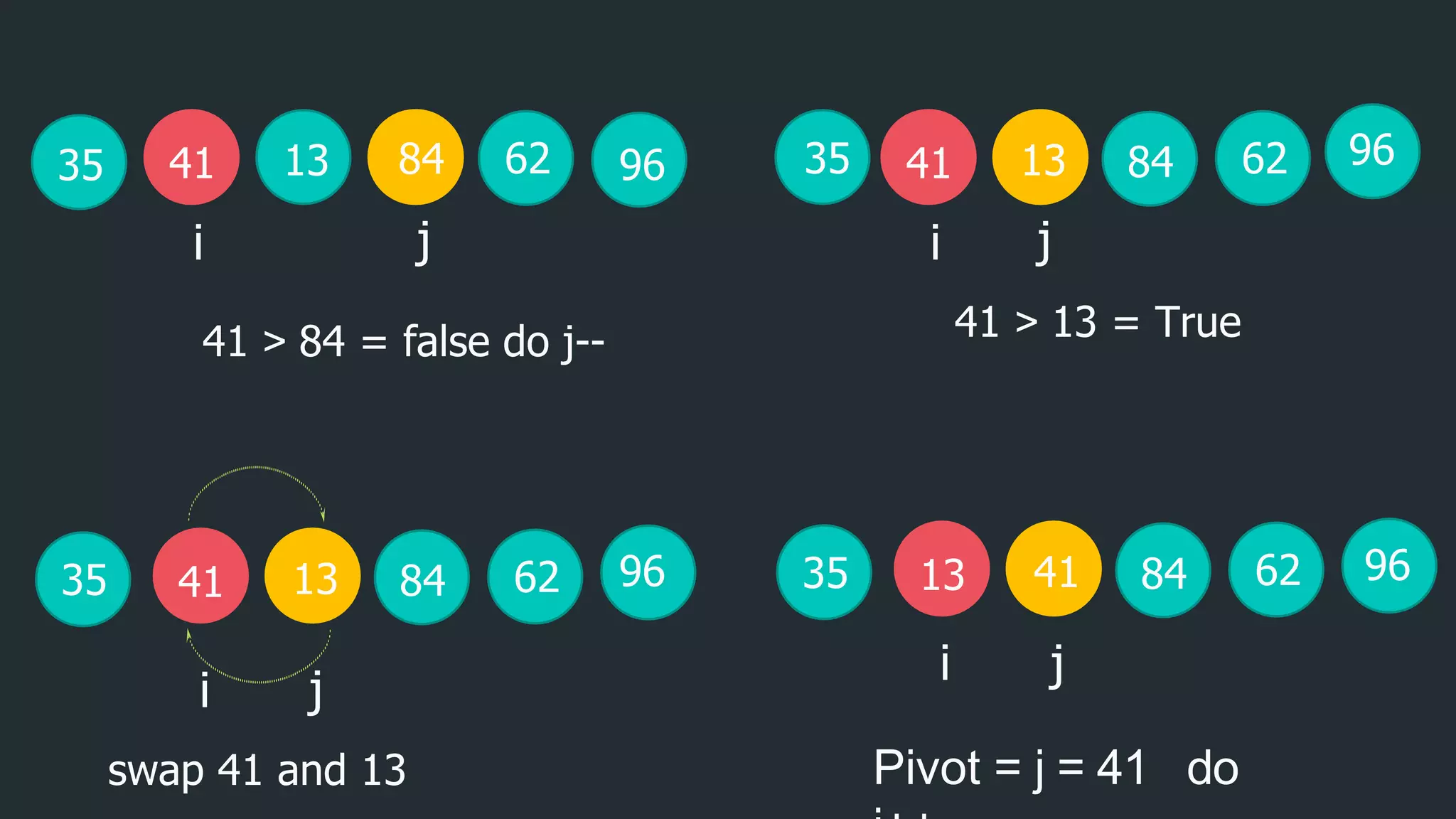
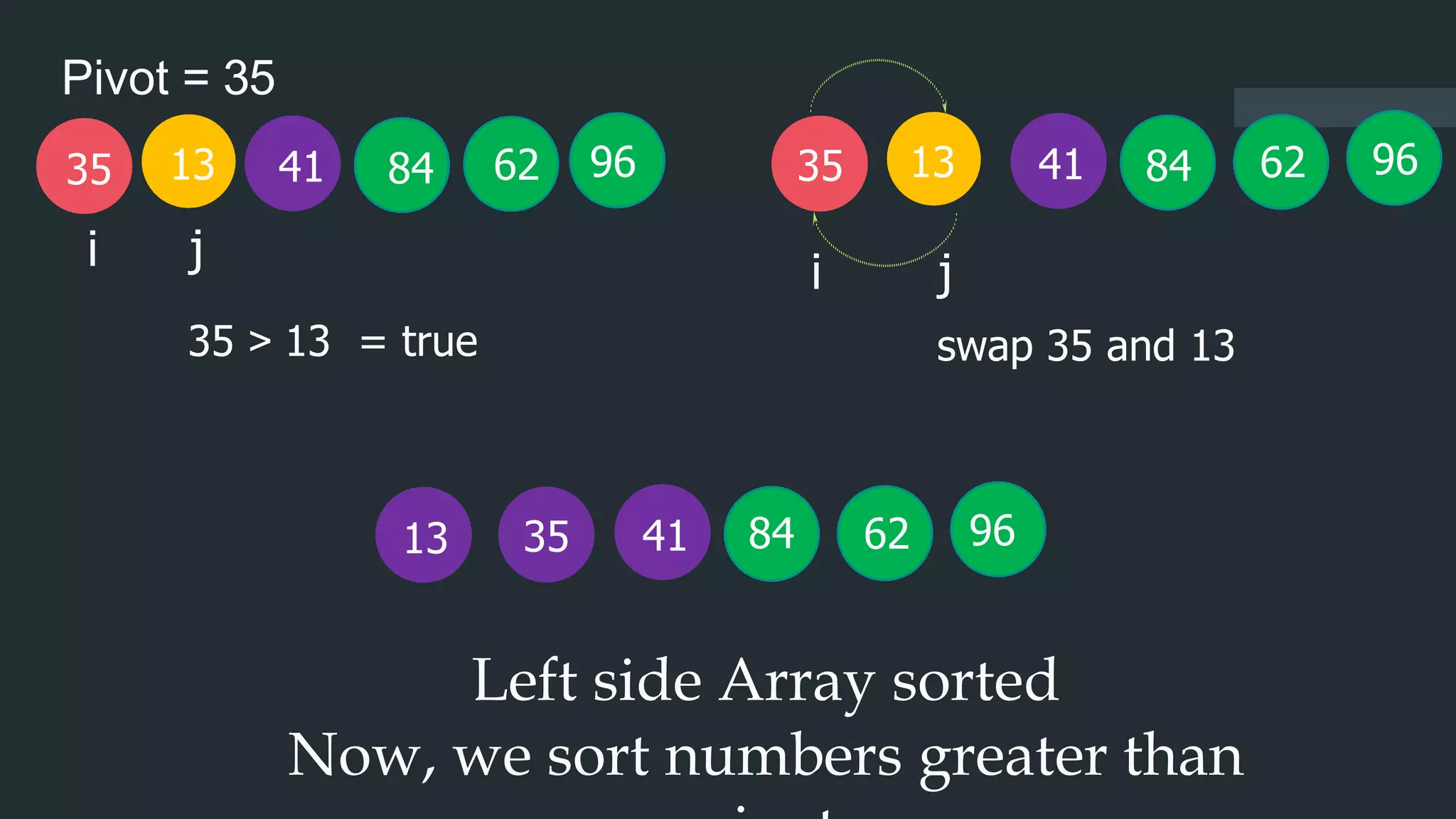
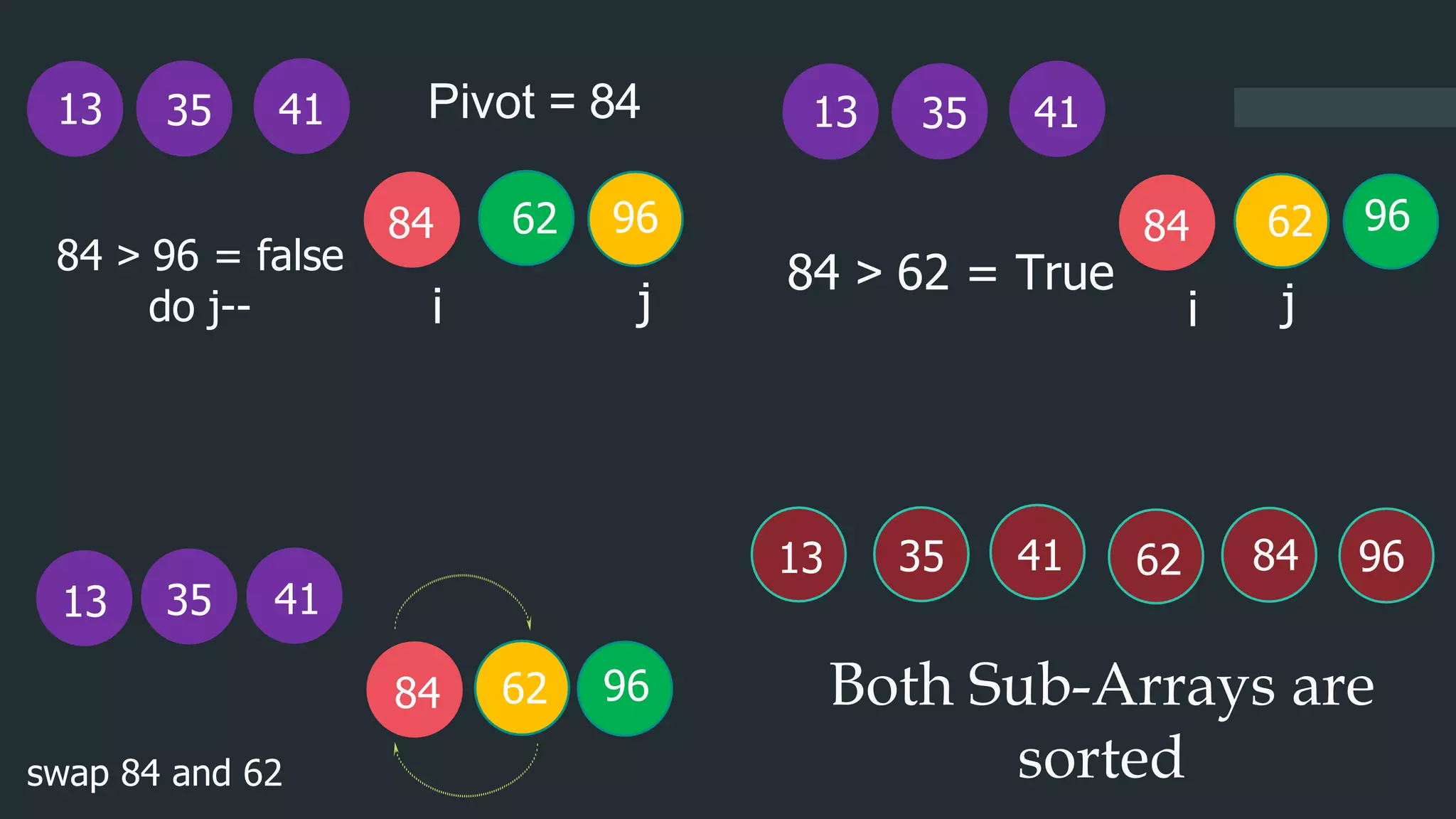
![i = j
41
13
35
a[0] a[1] a[2] a[3] a[4] a[5]
numbers less than
pivot
numbers greater than or
equal to pivot
Now we sort numbers less than pivot
13
35
41 62
84 96
62
84 96
j
41
i
13 62
84
35 96](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fymca2064daacarricularactivity-211201153311/75/Divide-and-conquer-10-2048.jpg)