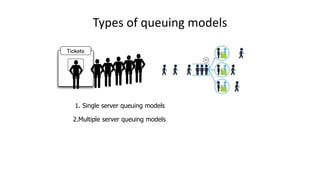
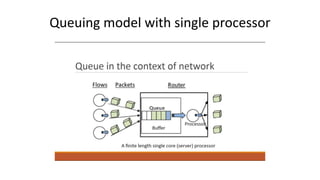
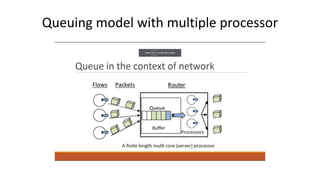
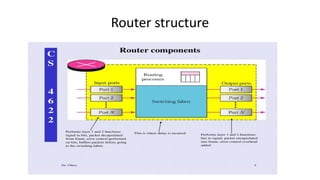
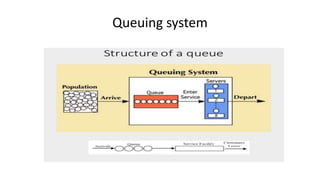
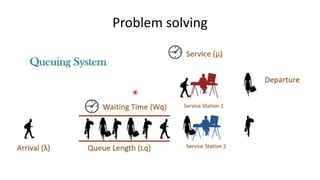
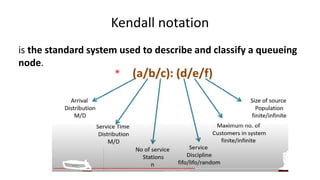
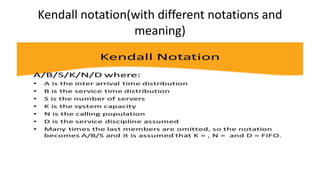
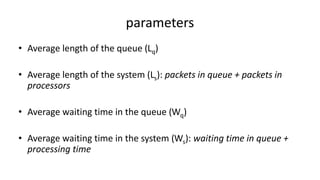
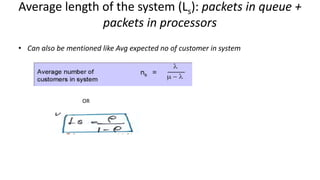
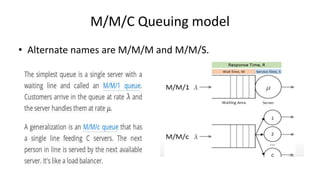
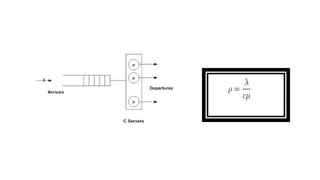
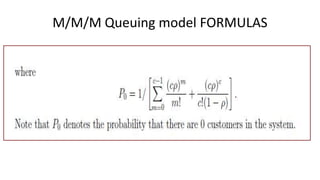
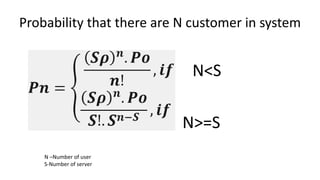
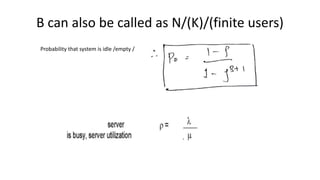
Queuing theory is a mathematical study of waiting lines, analyzing components like arrival and service processes, servers, and customer populations. It categorizes queuing models into types such as single and multiple server models, and finite as well as infinite queues, while addressing queuing discipline, utilization, and performance metrics. The document also presents various problems and simulations related to queuing scenarios across different service systems.