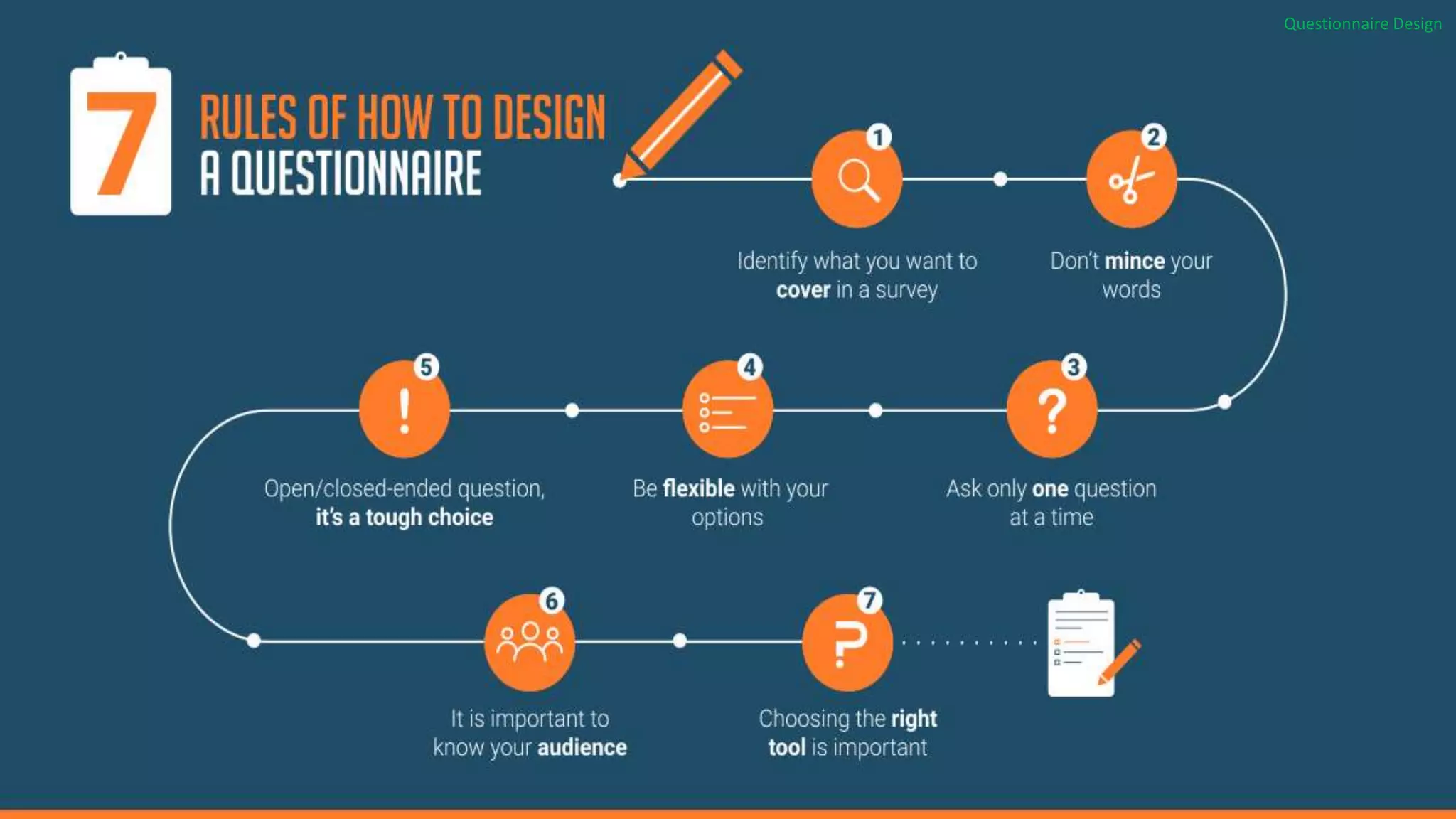
This document discusses the design of effective questionnaires. It outlines that initial considerations for questionnaire design include determining the type of information needed, nature of respondents, and method of administration. Key aspects of design covered include writing clear, unbiased questions; using appropriate response formats; ordering questions logically; and pretesting the questionnaire. The goal is to create a design that makes the questionnaire easy for respondents to understand and complete while obtaining the necessary information for analysis.