Embed presentation
Download to read offline



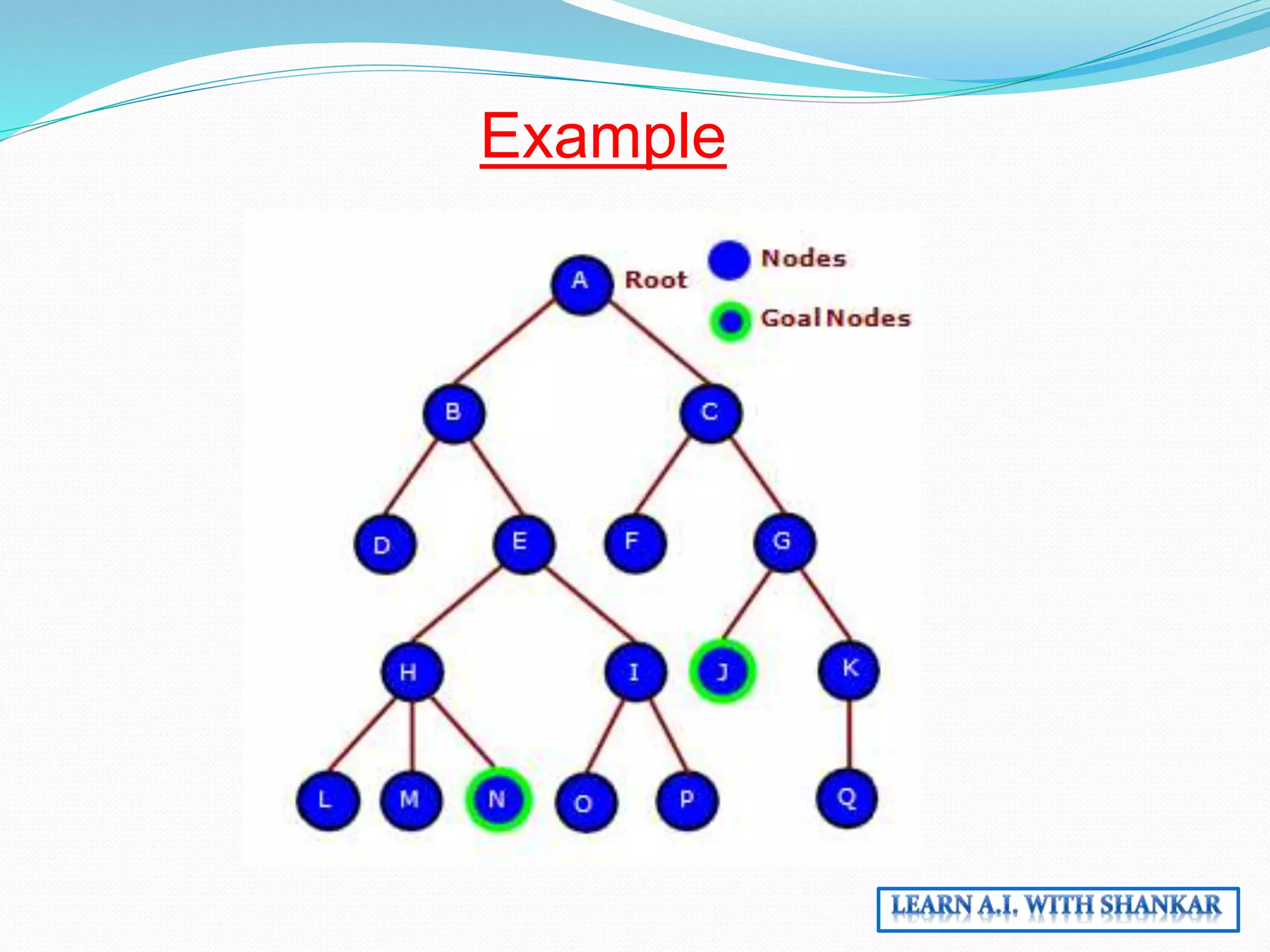

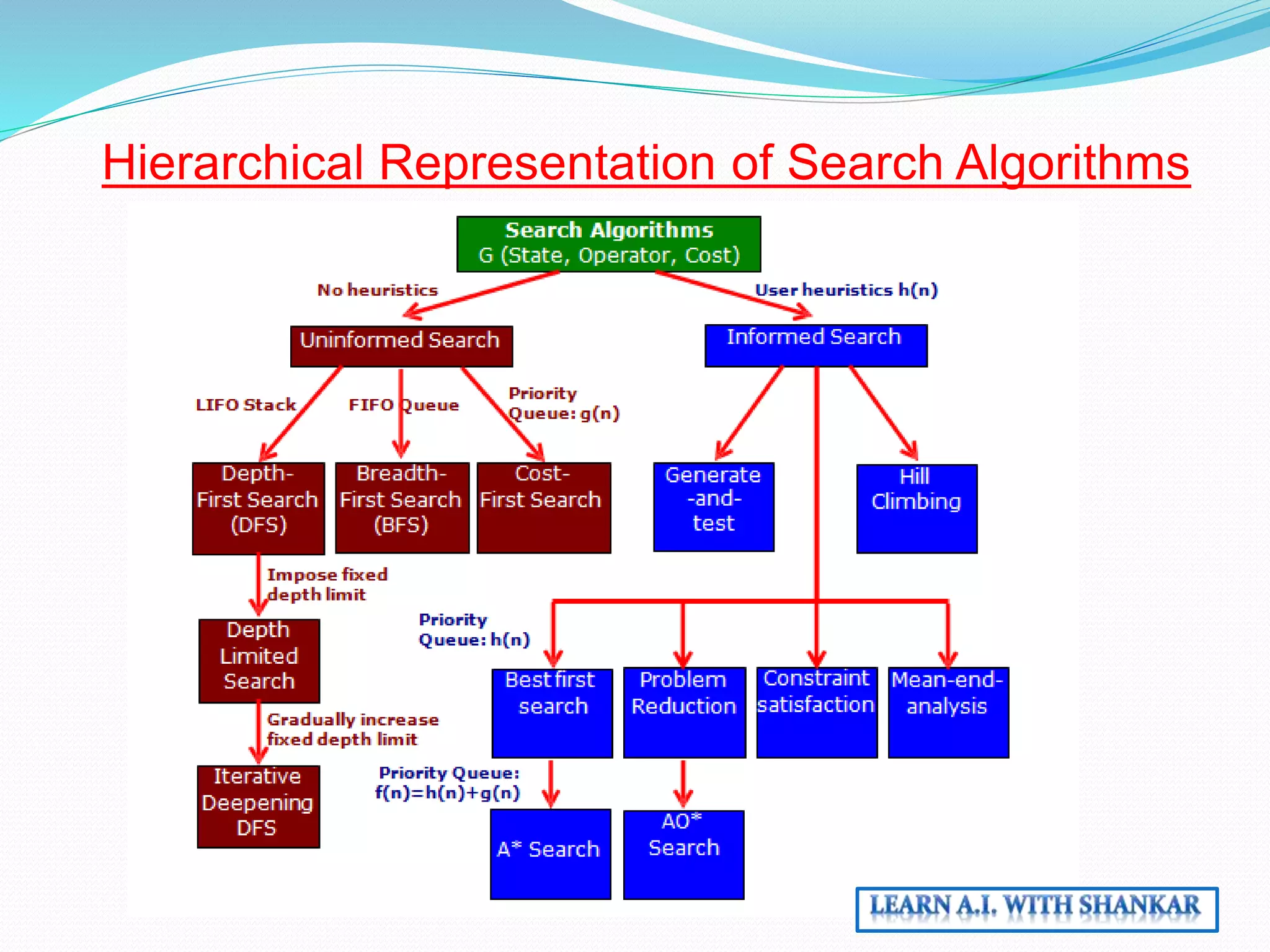
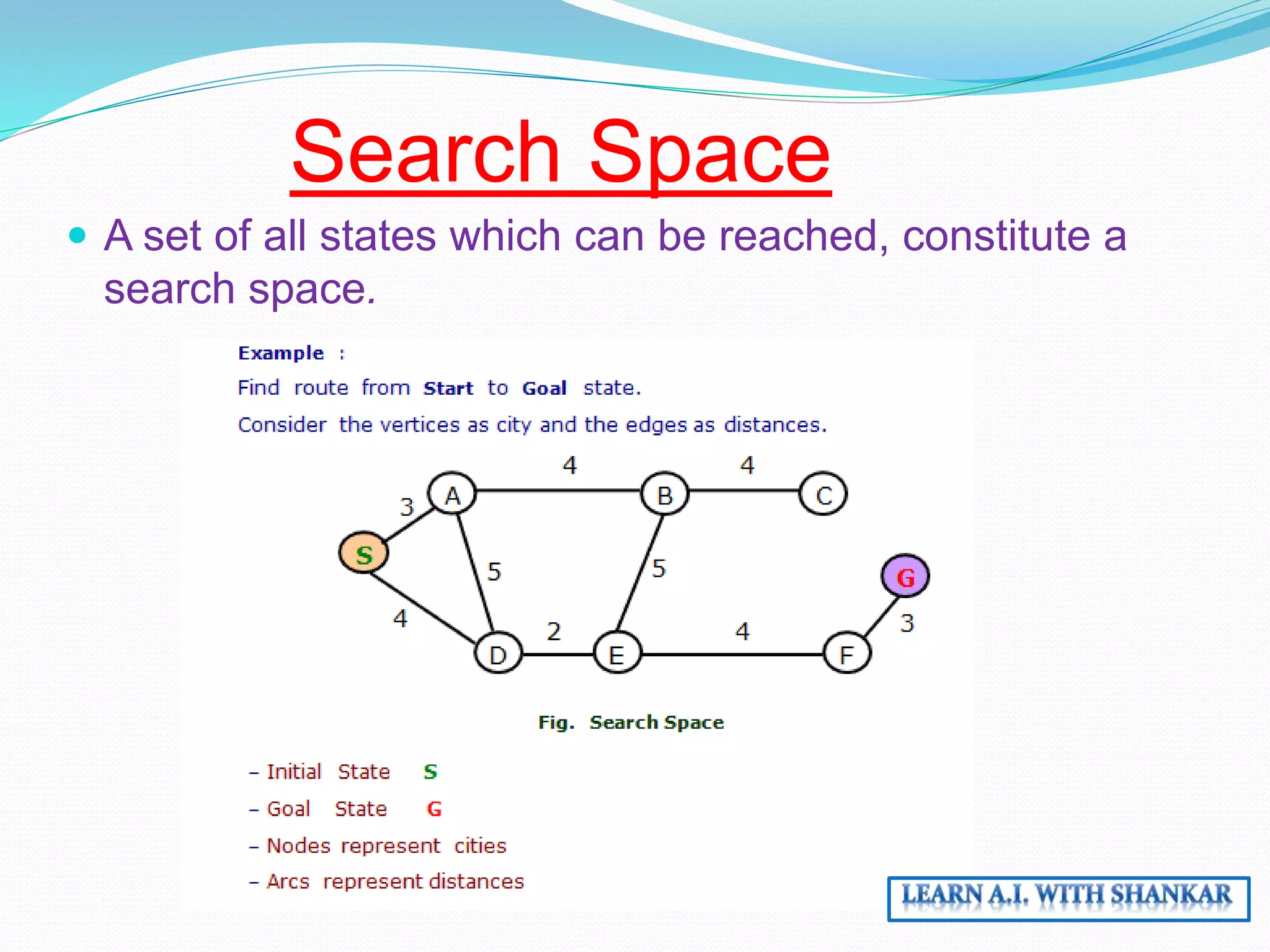

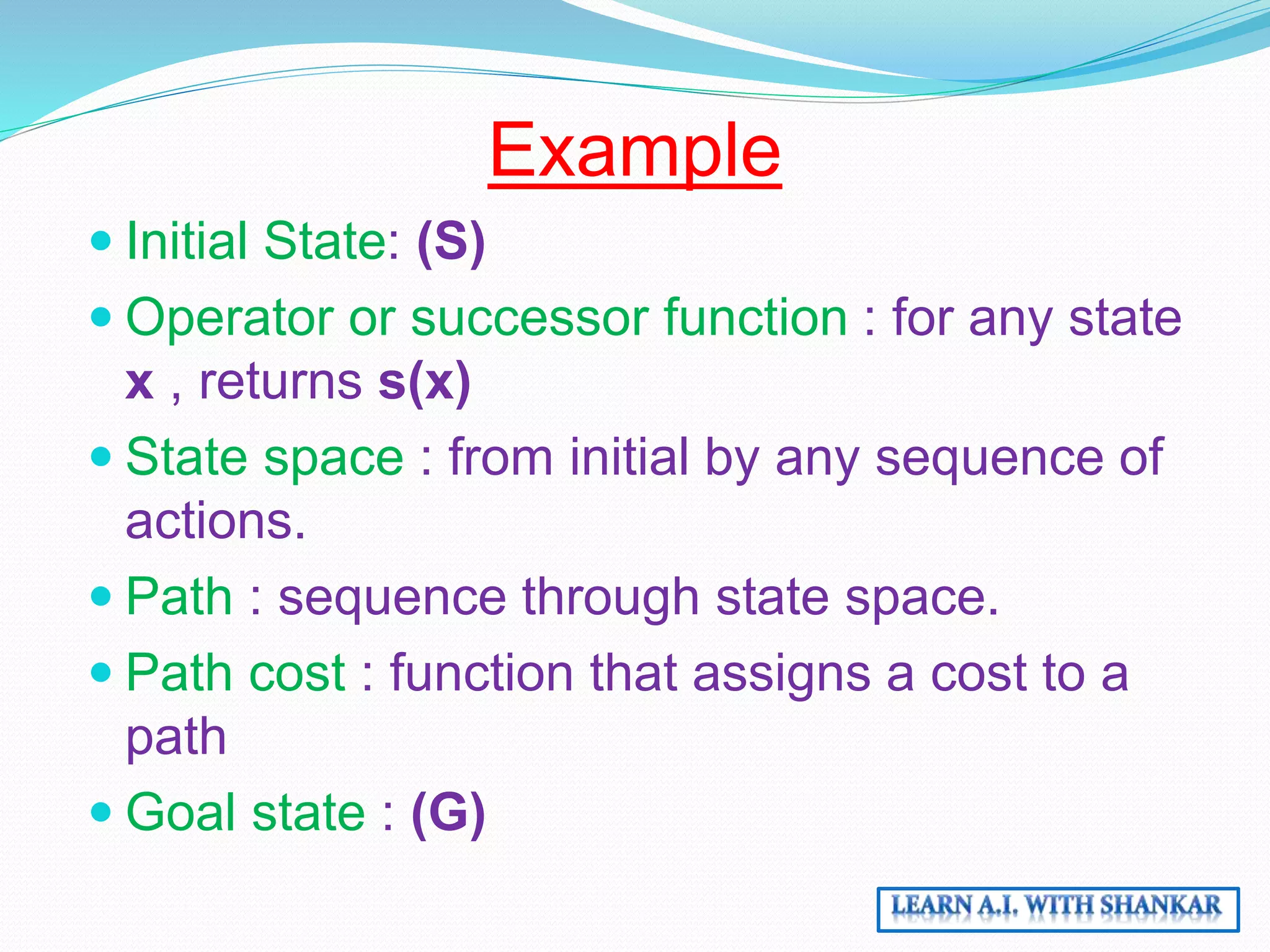
The document discusses problem-solving in artificial intelligence through state space search and control strategies, emphasizing the systematic examination of states to find a path from the initial to the goal state. It covers various search algorithms, including heuristic and uninformed search methods, along with the concepts of search space, initial and goal states, and path costs. Overall, it outlines how actions change states within a structured framework to achieve desired outcomes.








