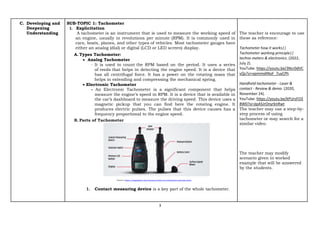
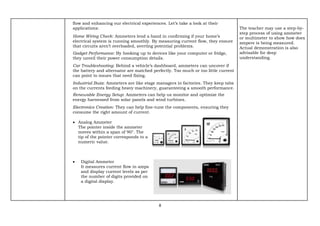
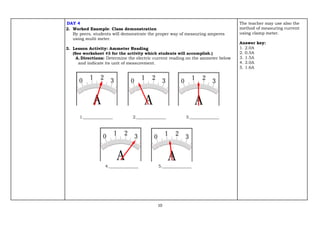
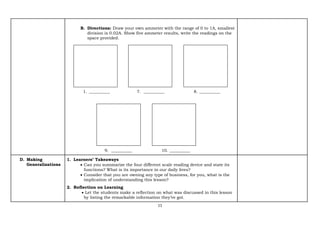
The document provides an exemplar lesson plan for TLE (Technology and Livelihood Education) for Grade 7, focusing on teaching measuring instruments such as tachometers, oscilloscopes, and ammeters during the 2024-2025 school year. It outlines objectives, standards, learning activities, and key concepts related to these instruments, along with instructions and resources for educators. The material emphasizes correct usage and understanding of each instrument while maintaining compliance with copyright regulations.