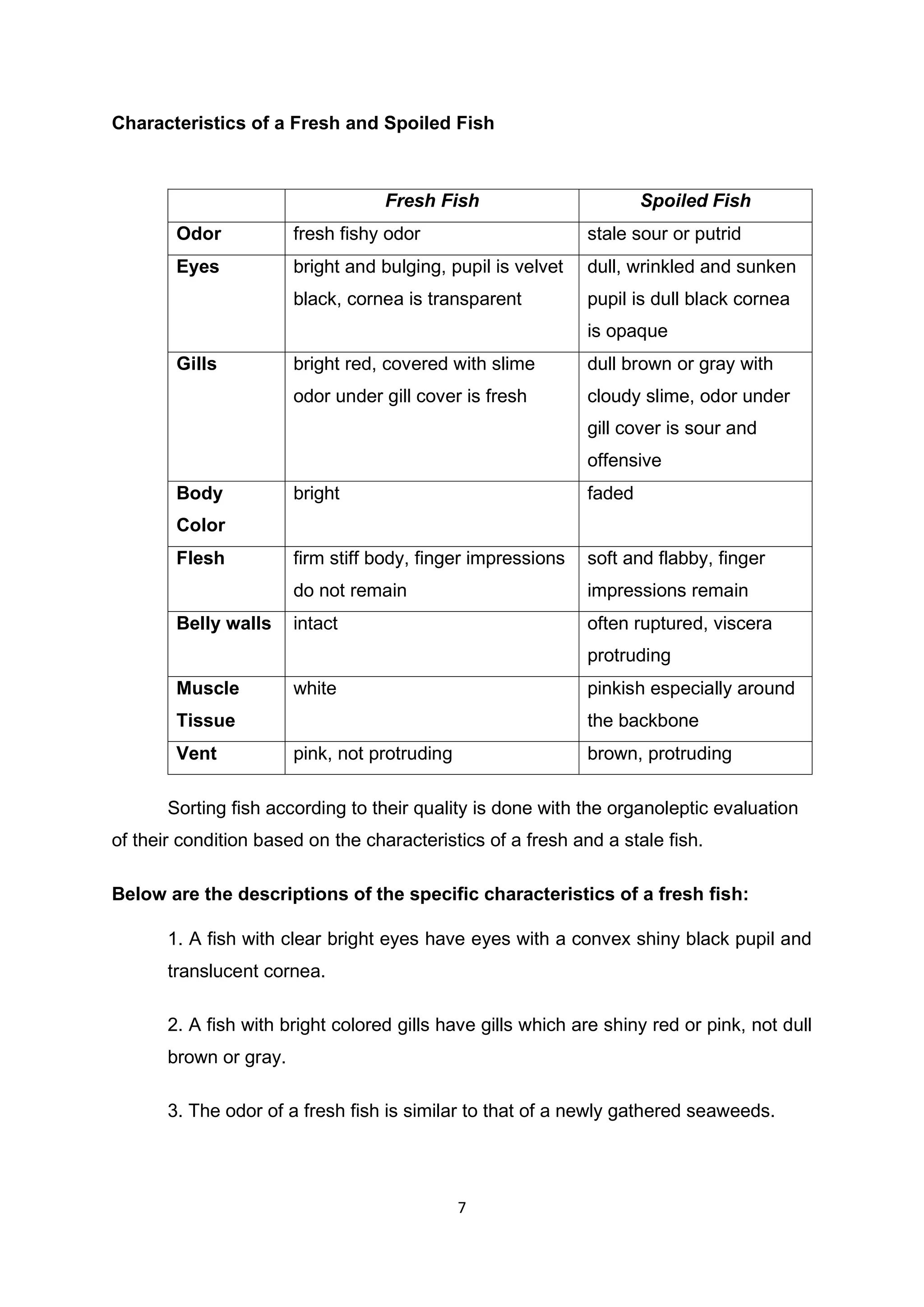
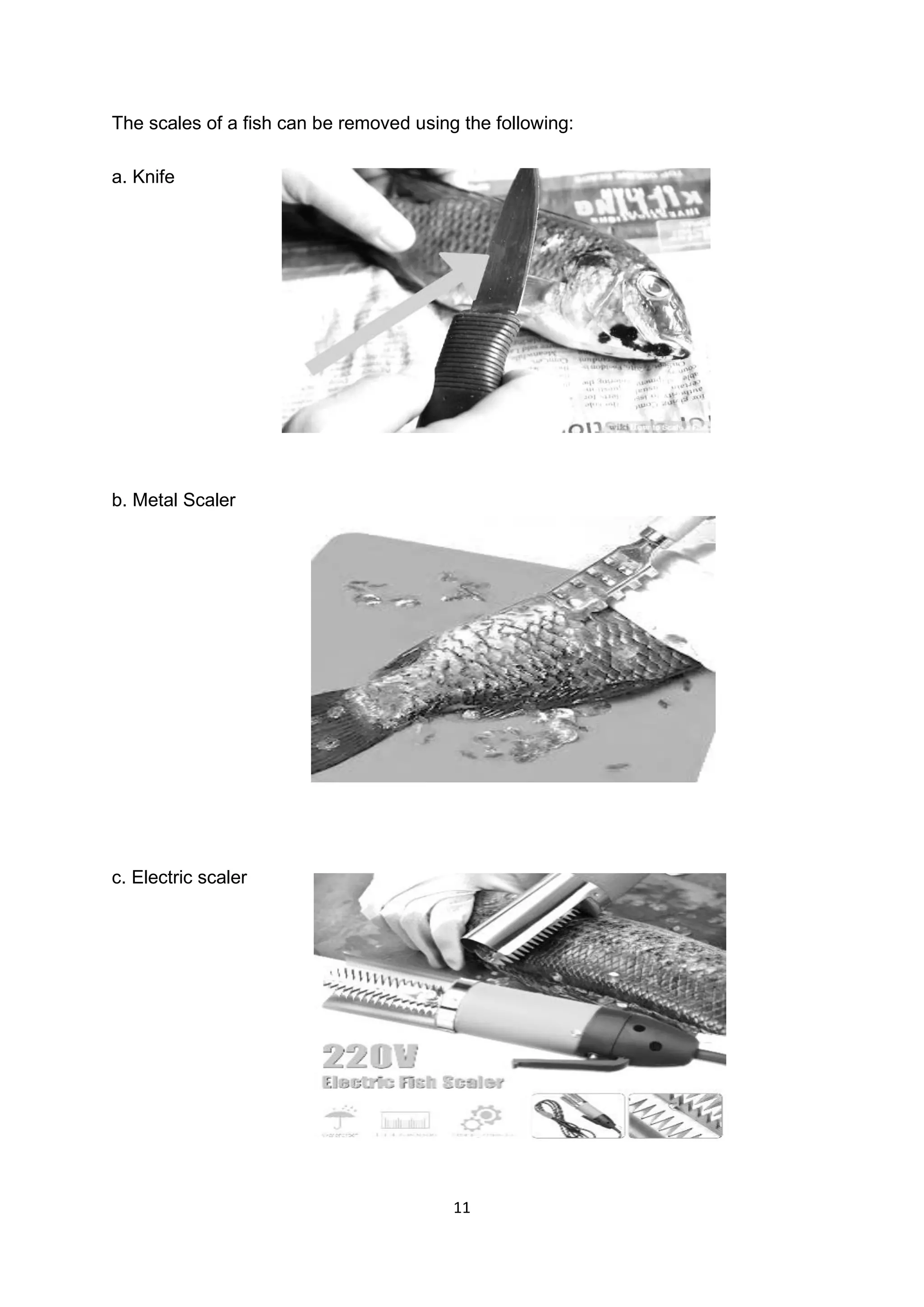
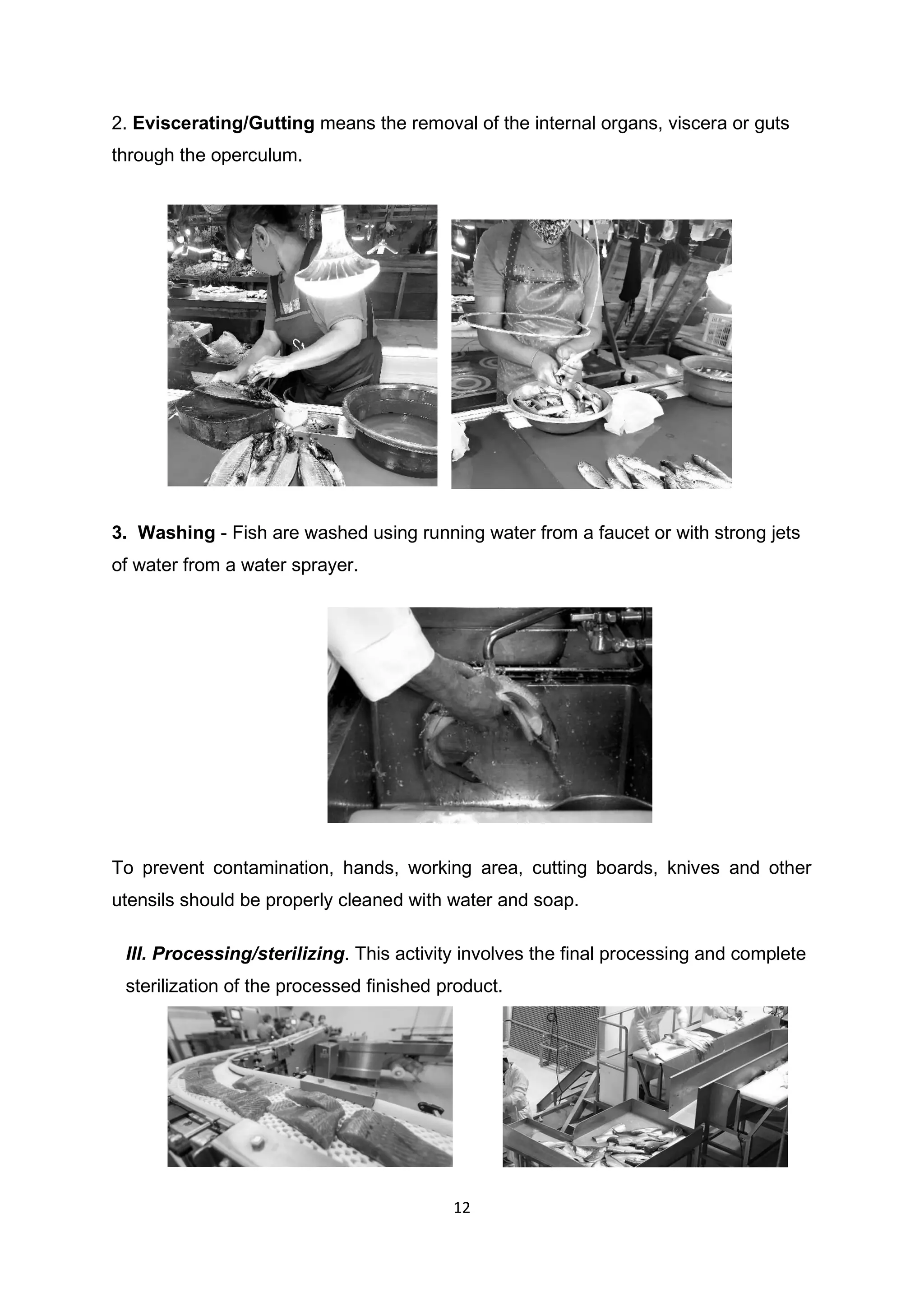
The main steps in cleaning fresh fish are: 1) scale the fish using a blunt knife to remove scales without damaging the flesh; 2) eviscerate or gut the fish by making a cut along the belly and removing the internal organs; 3) rinse the fish thoroughly under clean running water to remove blood and residue. Proper cleaning is important to prepare the fish for further processing and prolong its shelf life.