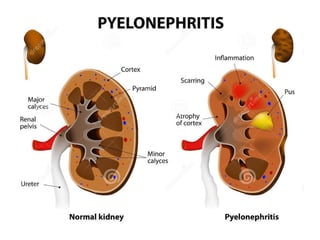
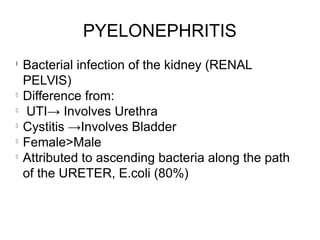
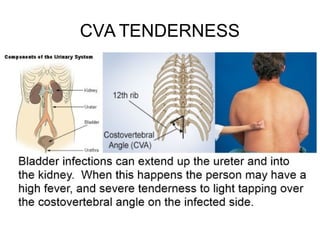
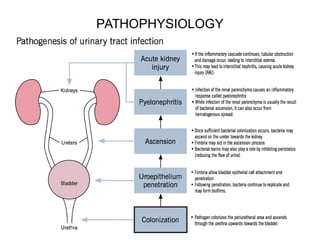
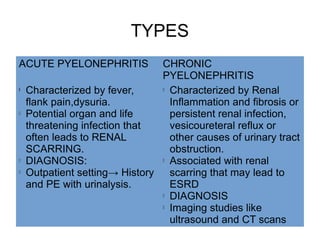
This document discusses pyelonephritis, which is a bacterial infection of the kidney. It notes that pyelonephritis differs from UTIs, which involve the urethra, and cystitis, which involves the bladder. The document outlines predisposing factors for pyelonephritis using the mnemonic "SCARRIN' UP" and lists common signs and symptoms such as fever, flank pain, and costovertebral angle tenderness. It also describes the types of pyelonephritis, including acute and chronic, and the diagnosis and treatment, which typically involves intravenous or oral antibiotics.