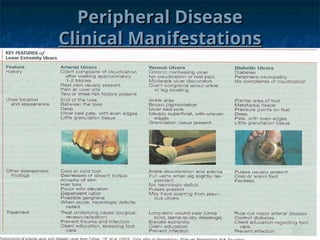
The document discusses peripheral arterial disease (PAD) affecting the lower extremities, including its symptoms such as intermittent claudication and rest pain, as well as diagnostic methods like Doppler studies and angiography. It outlines treatment options including risk factor modification, medication, interventional procedures, and surgical options for critical limb ischemia. Additionally, it covers related vascular disorders, including thromboangiitis obliterans and Raynaud's phenomenon, detailing their causes, manifestations, and treatment strategies.