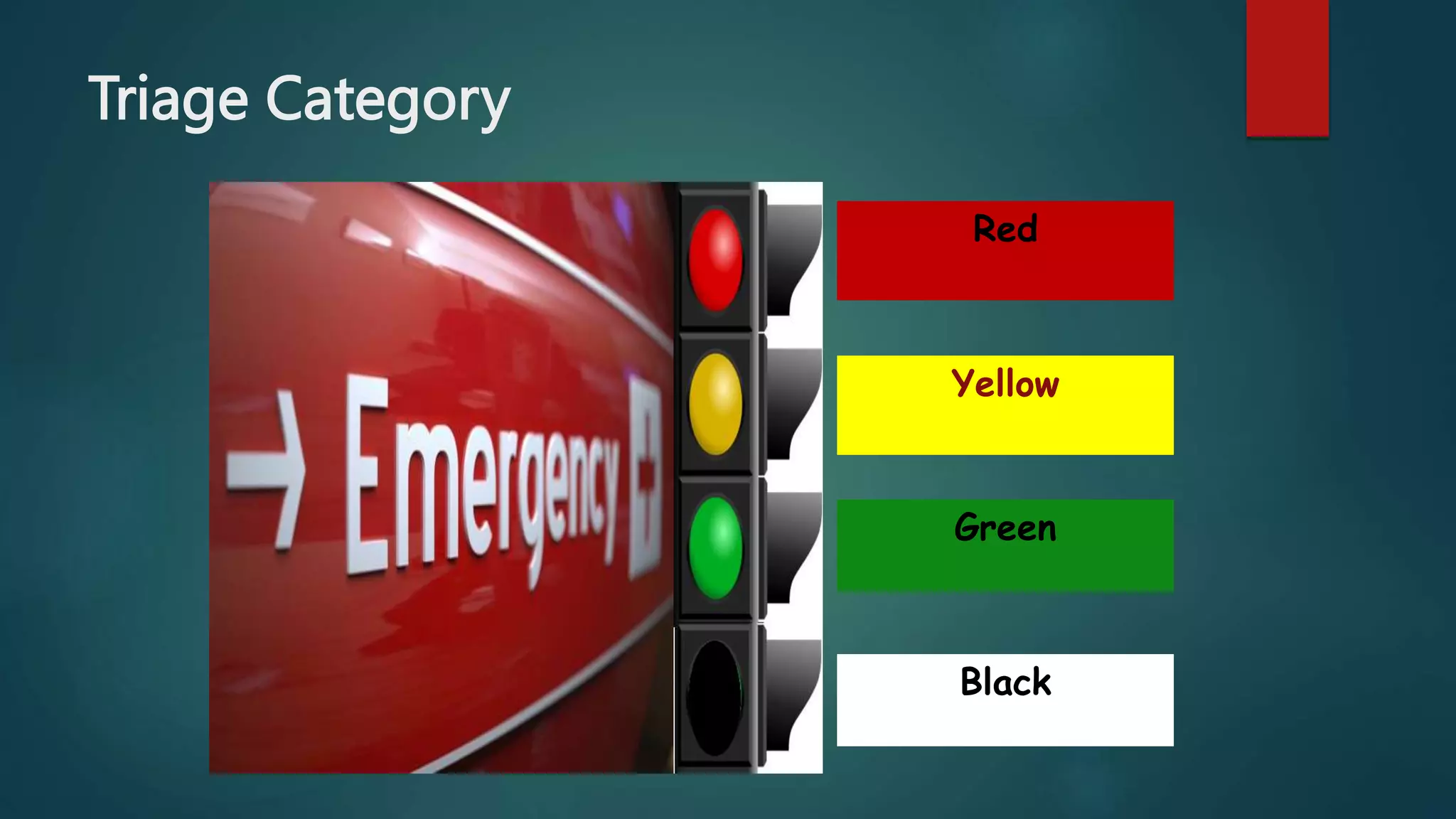
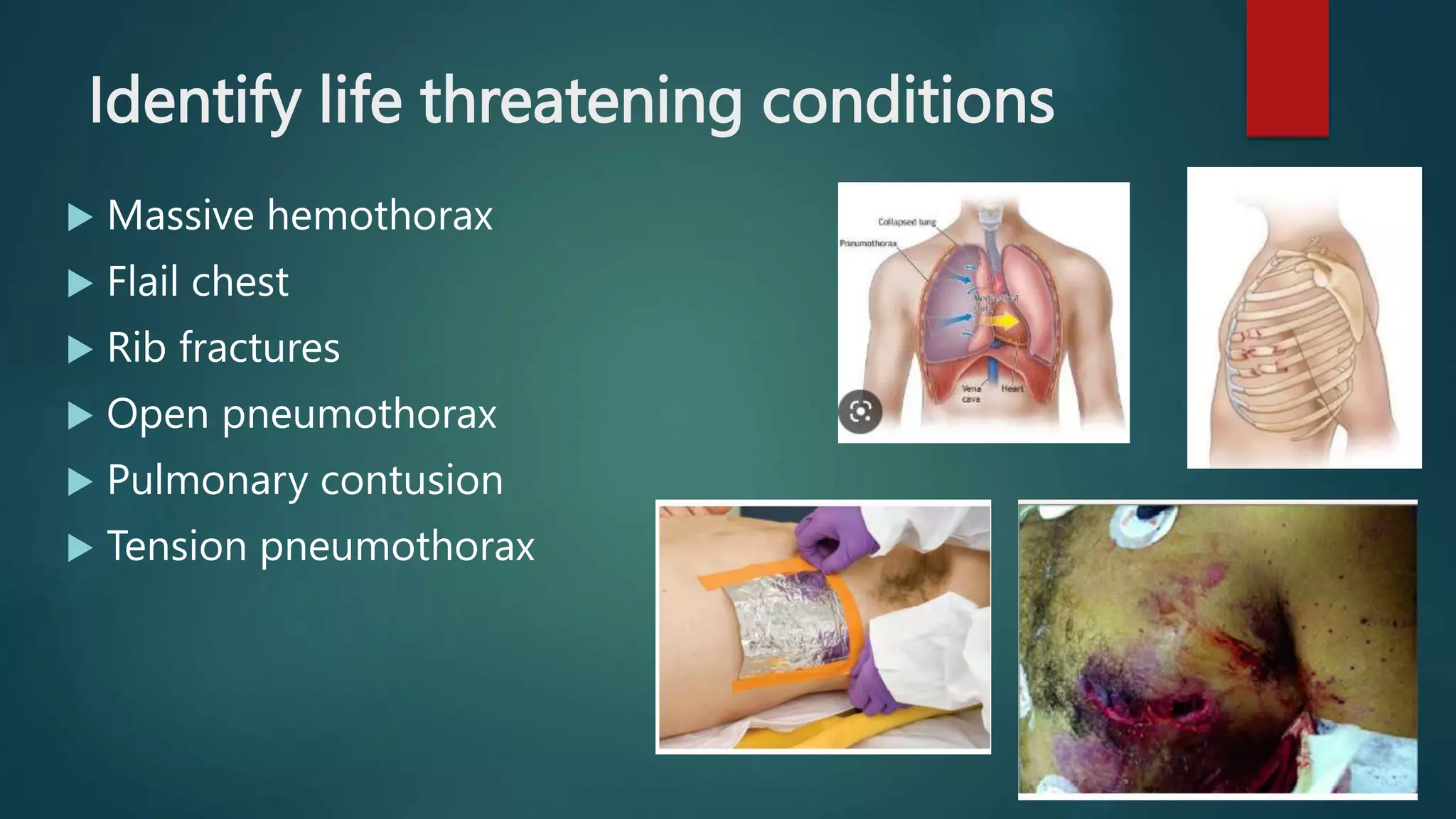
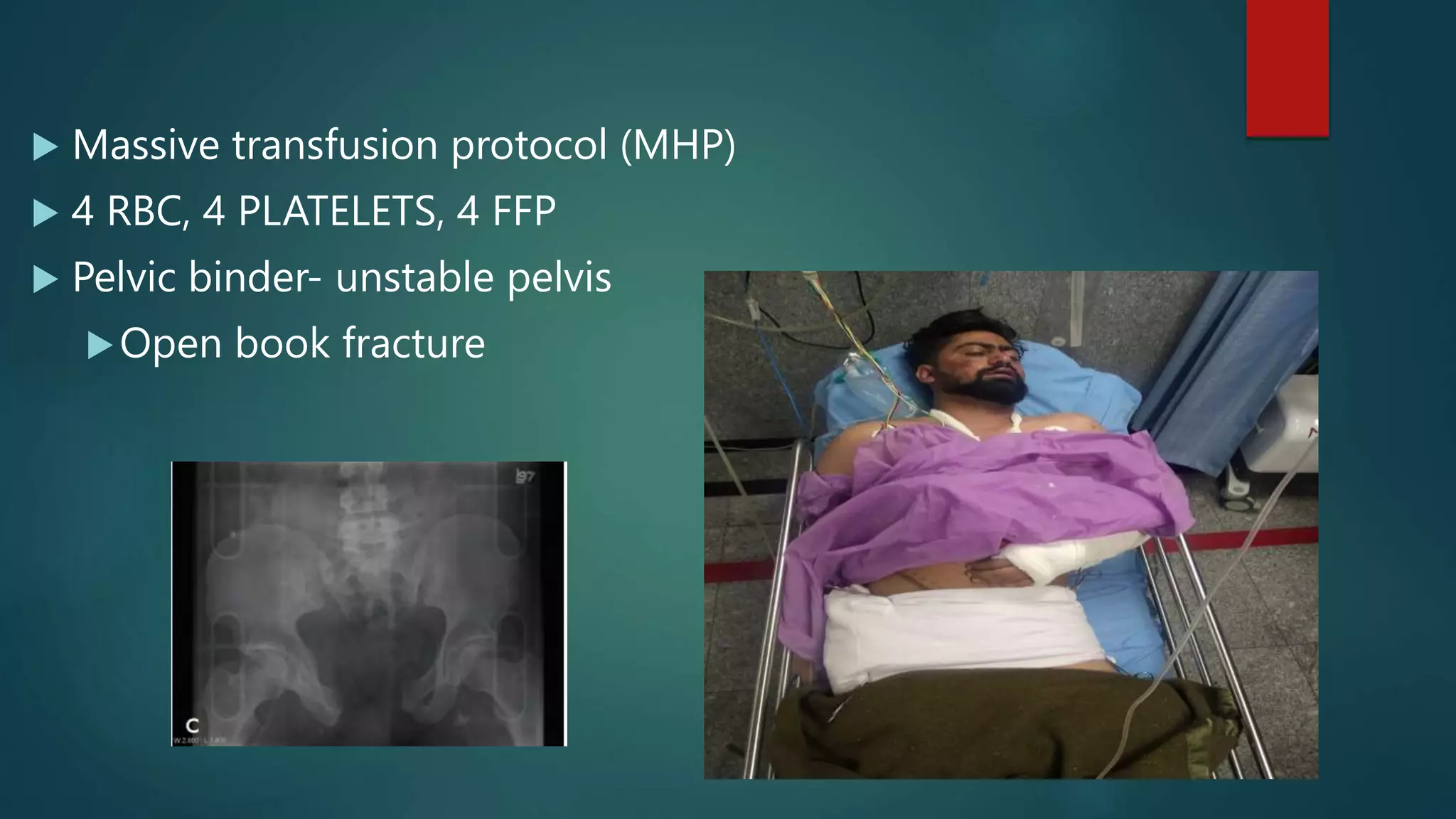
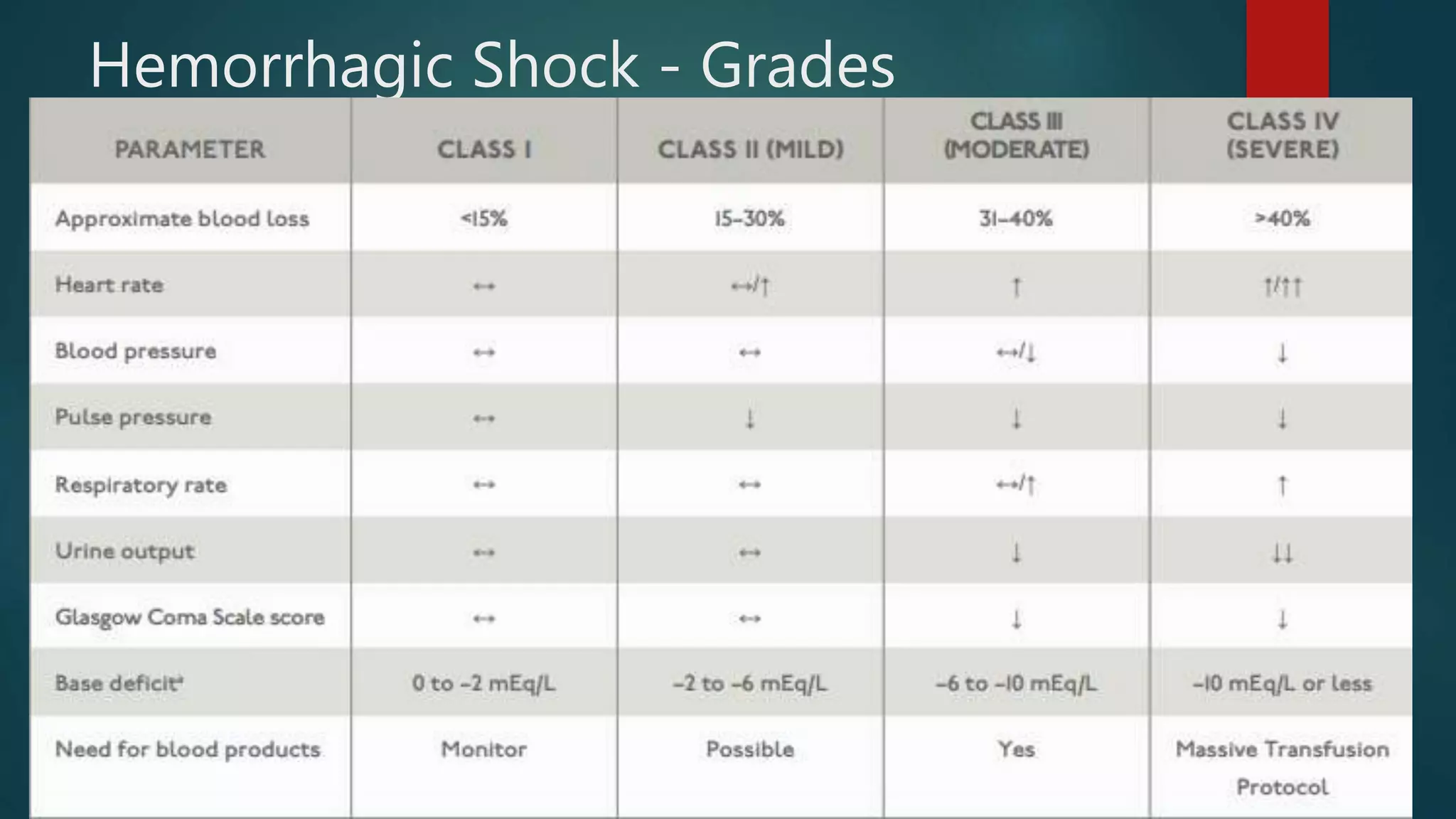
This document provides an overview of trauma nursing and management of trauma patients. It discusses the roles and skills of trauma nurses, including triage, primary and secondary surveys, airway management, hemorrhage control, and monitoring for shock. It also outlines the trauma patient workflow through red and yellow areas and use of investigations like x-rays, CT scans, and FAST ultrasound. Regular training through simulations and mock drills is emphasized to ensure trauma nurses have the expertise needed to effectively manage trauma.