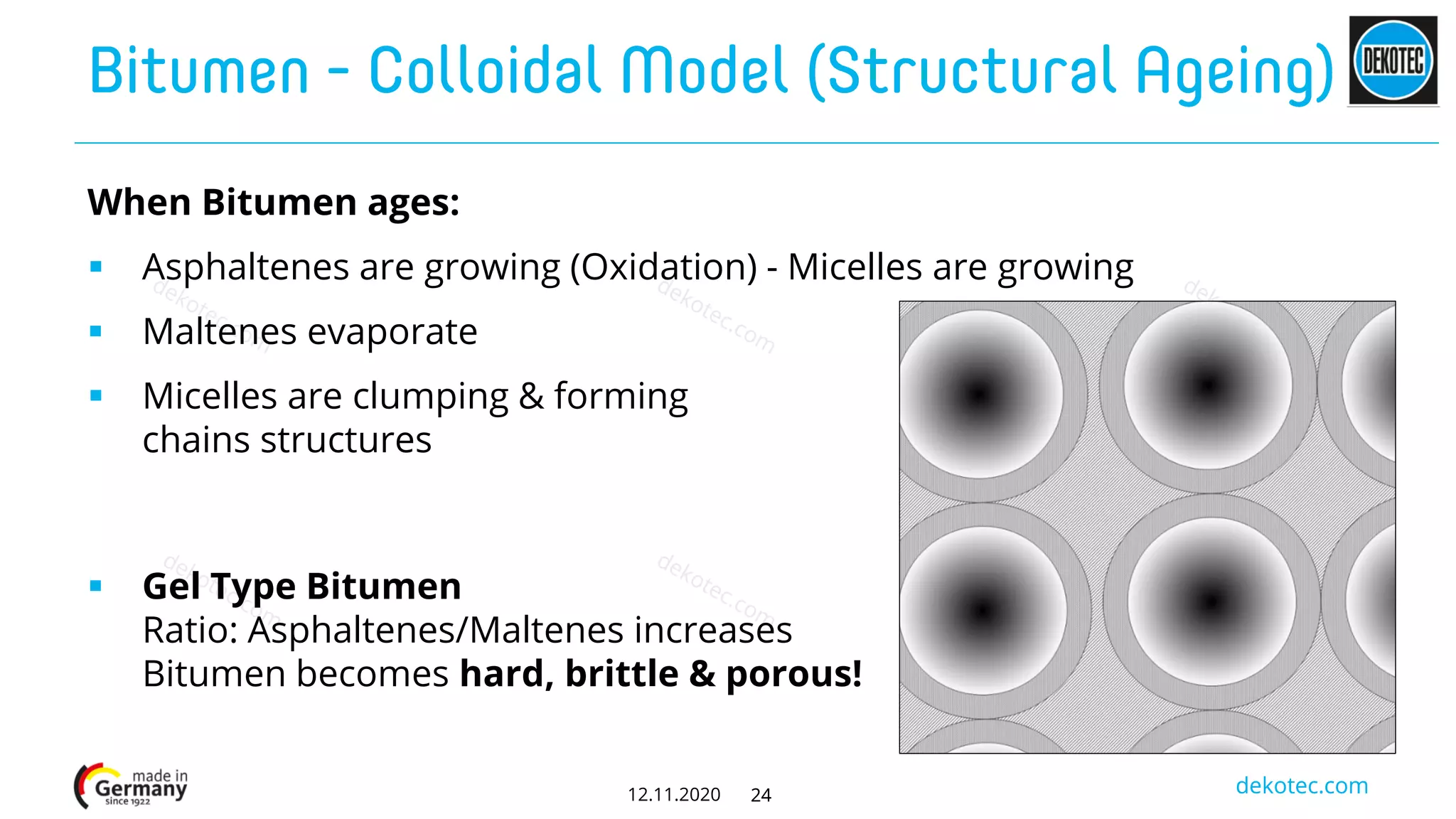
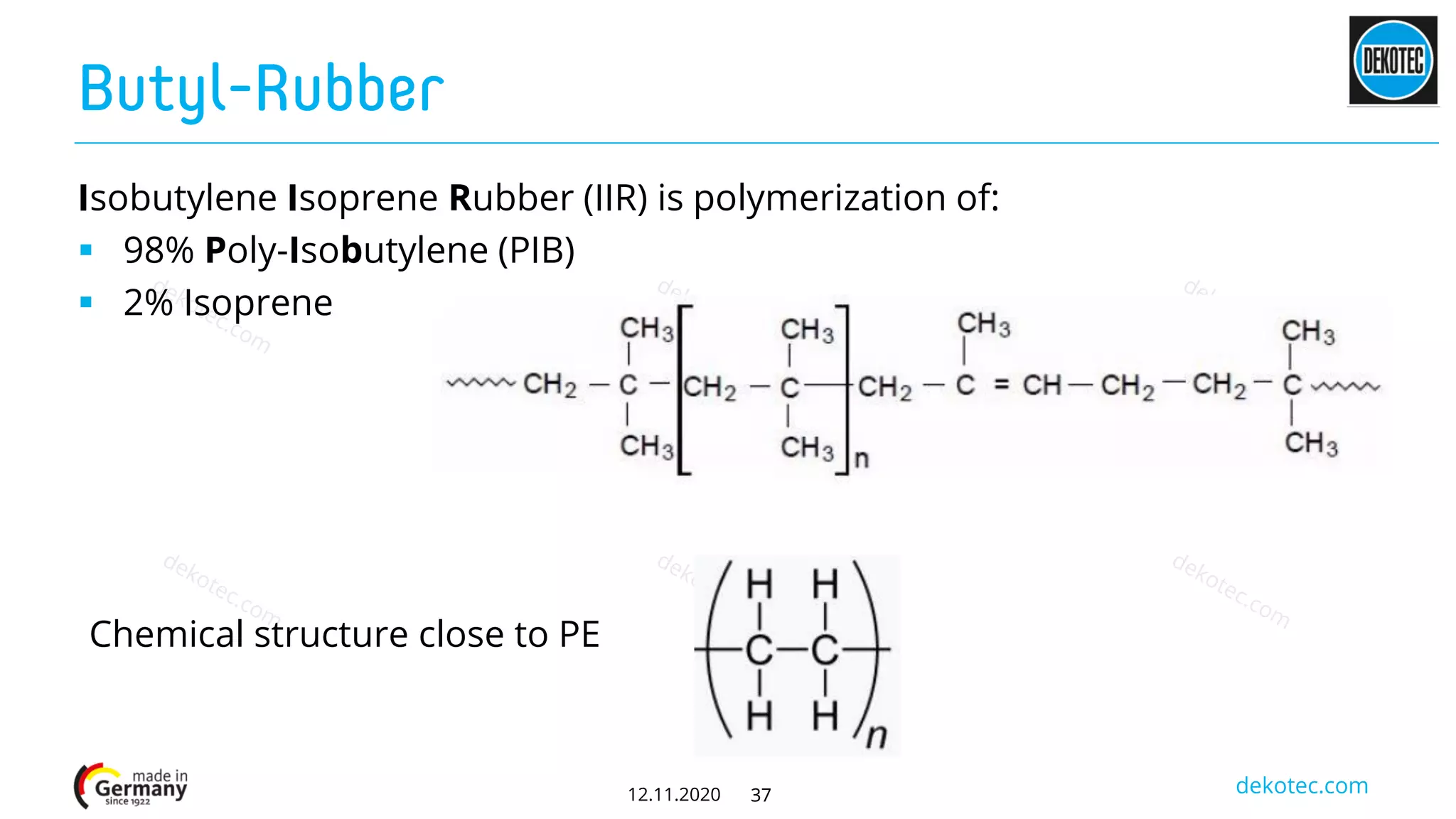
The document provides a comprehensive comparison of various materials used in corrosion prevention tapes, including PVC, polyethylene (PE), bitumen, and butyl rubber. It highlights the historical development, chemical properties, applications, and performance under different conditions, ultimately concluding that PE and butyl rubber are more suitable for long-term use than PVC and bitumen due to stability and aging factors. The performance evaluation of these materials underscores the superiority of modern 3-ply PE-butyl rubber technology over older PVC-bitumen alternatives.