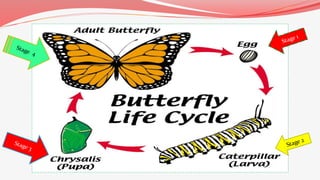
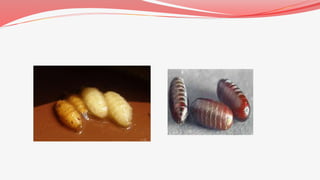
Pupa is the inactive life stage that occurs between larva and adult for insects that undergo complete metamorphosis. During the pupal stage, the larval structures break down and adult structures grow from imaginal discs. Pupation allows the insect to transition from its larval form to its adult wings and other structures. The pupa is non-feeding and usually motionless. When development is complete, the adult insect emerges from the pupal case by splitting it open. The duration of the pupal stage varies between species and depends on temperature.