Embed presentation
Download to read offline


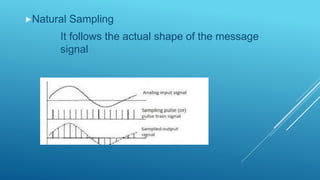
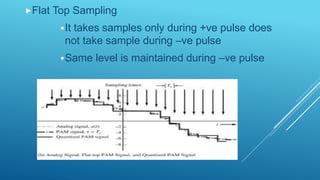
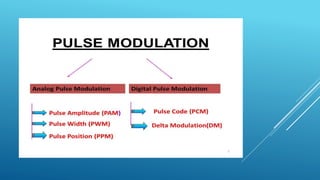
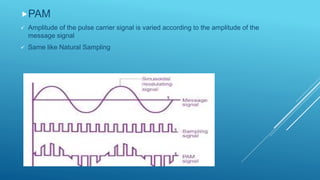
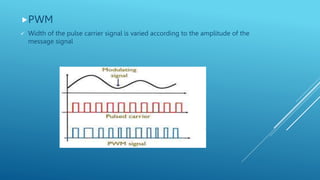

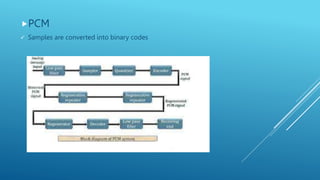
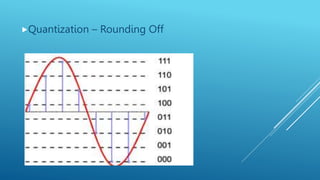
Pulse modulation is a process that takes periodic samples from an analog message signal and converts them into binary codes. There are two main types of sampling: natural sampling, which follows the actual shape of the message signal, and flat top sampling, which only takes samples during the positive pulse and maintains the same level during the negative pulse. Common pulse modulation techniques include PAM, which varies the amplitude of a pulse carrier signal; PWM, which varies the width of a pulse carrier signal; and PPM, which varies the position of a pulse carrier signal. Samples are then converted to binary codes through quantization and rounding off.










