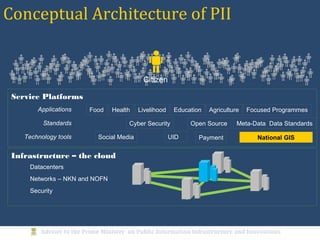
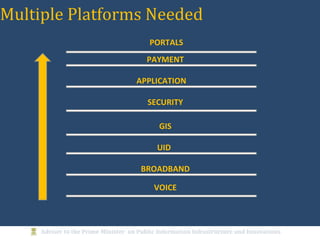
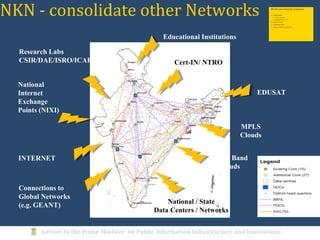
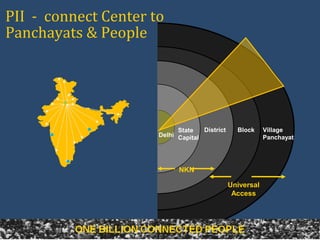
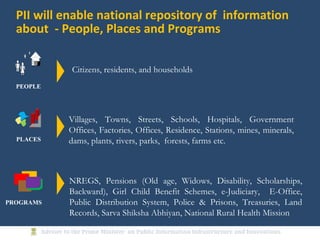
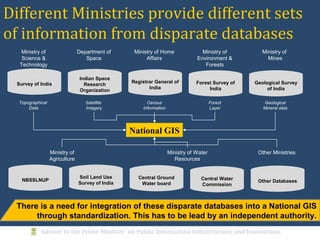
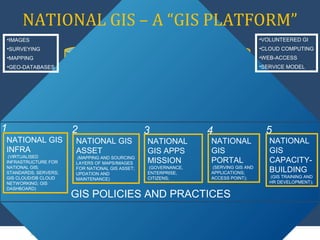
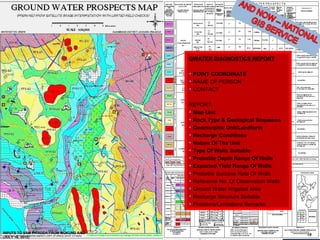
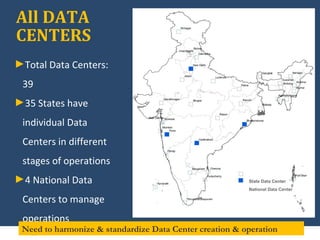
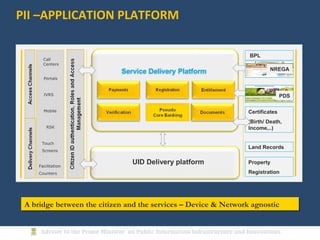
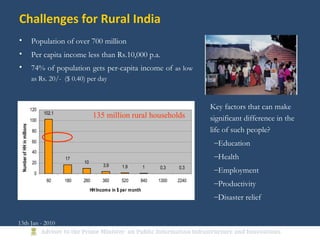
The document discusses the creation of a Public Information Infrastructure (PII) in India to strengthen democracy. Key elements of the PII include building a National Knowledge Network (NKN) to connect universities and research institutions, providing broadband connectivity to all 250,000 panchayats, establishing a unique identification (UID) system for citizens, creating a National GIS to integrate mapping data from different sources, setting up standardized national and state data centers, and ensuring cyber security. The PII aims to make information a public good that empowers citizens, improves governance and public service delivery, and drives social and economic development.