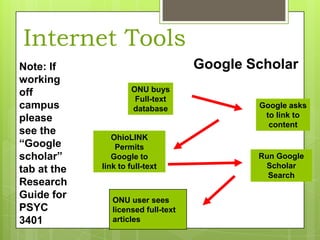
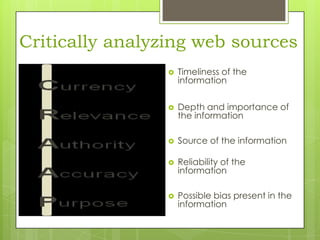
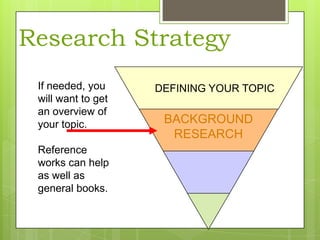
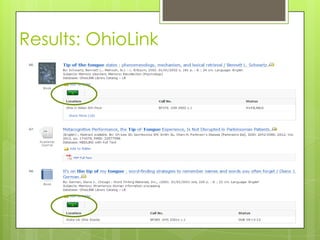
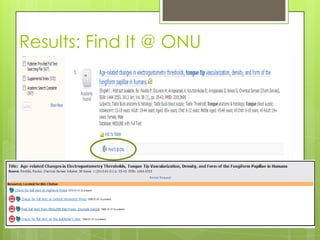
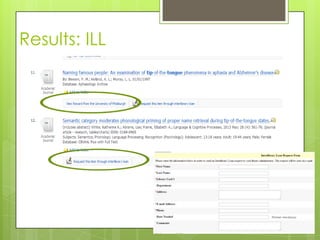
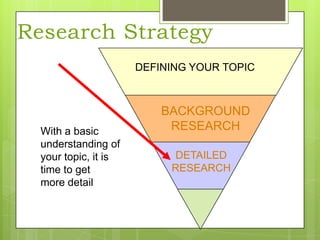
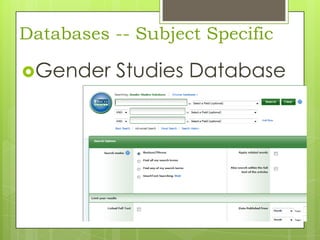
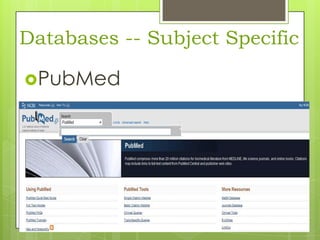
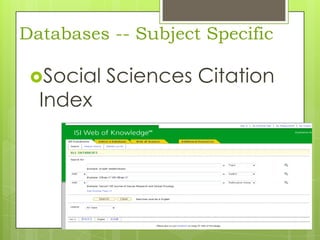
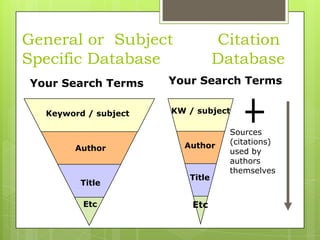
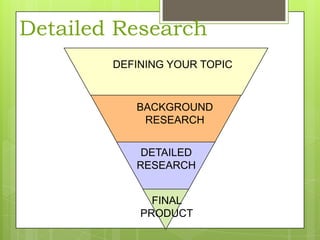
This document provides an overview of conducting research for a PSYC 3401 Experimental Psychology course. It discusses developing a research strategy, beginning with background research and selecting resources. The document outlines goals for a research session, including devising a strategy, selecting and accessing resources, and critically evaluating them. It also discusses primary, secondary, and tertiary sources; empirical research articles; searching databases; and citation software. Tips are provided for various stages of the research process from defining topics to detailed research.