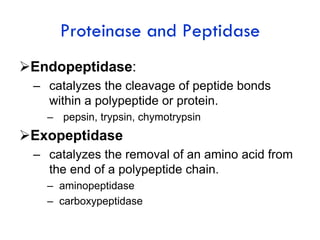
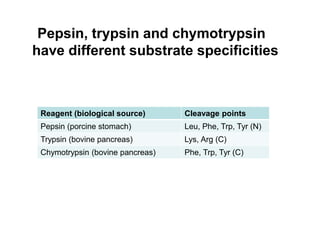
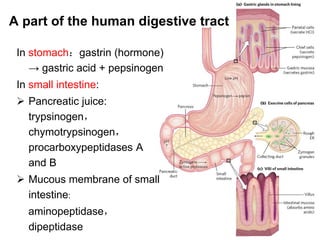
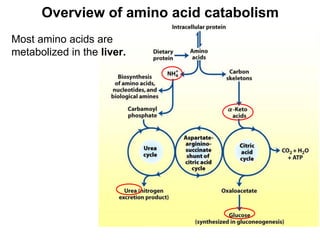
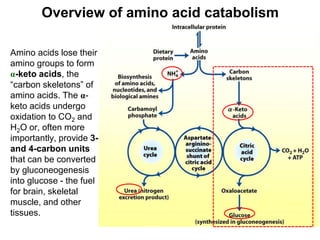
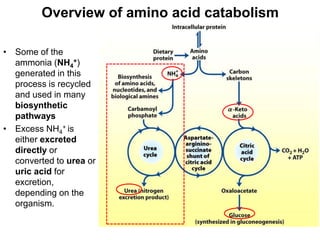
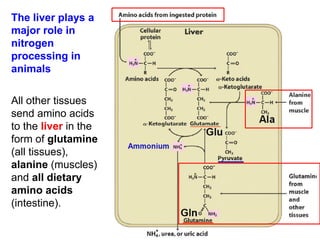
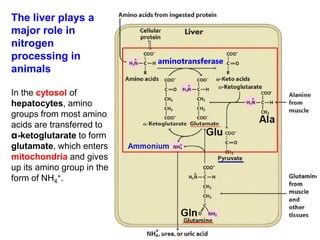
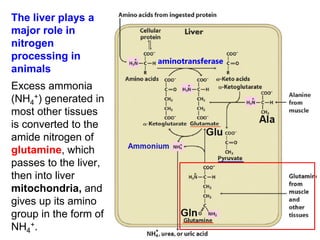
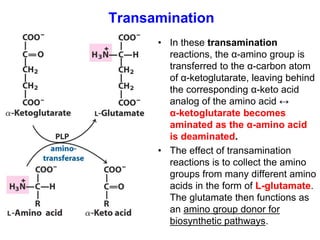
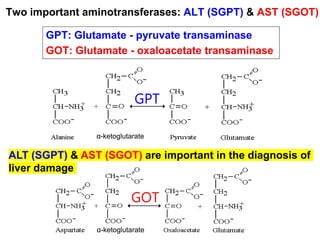
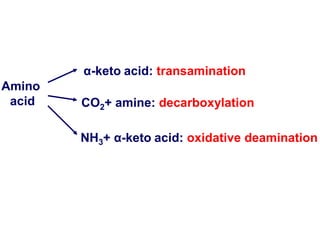
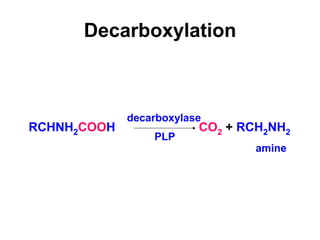
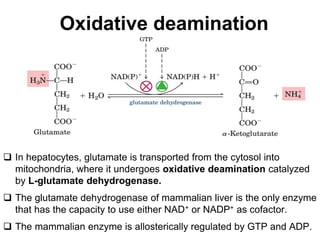
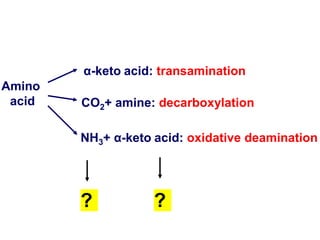
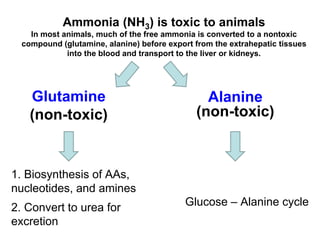
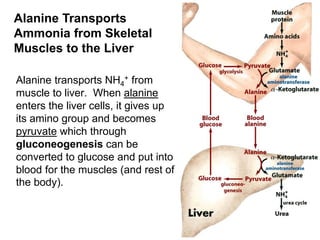
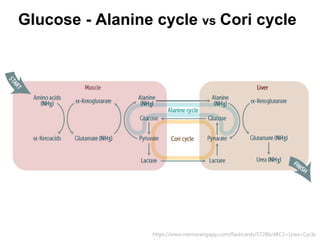
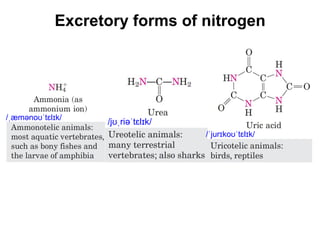
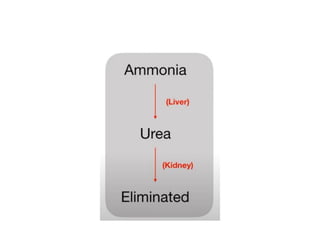
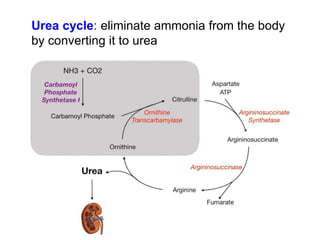
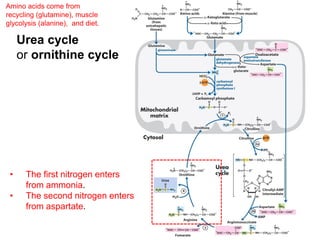
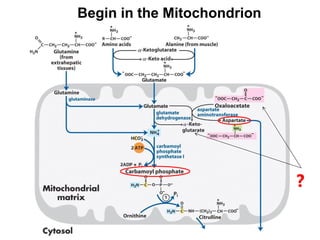
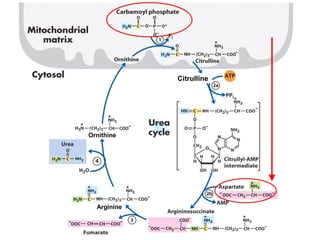
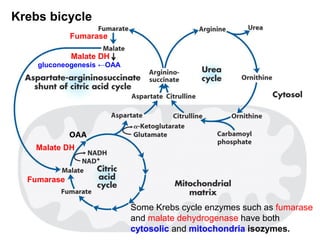
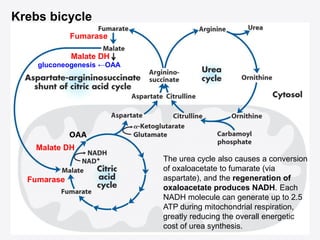
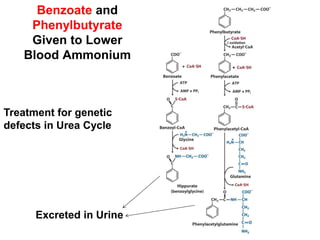
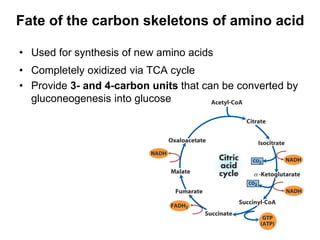
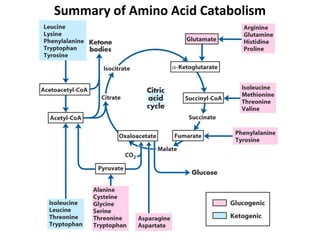
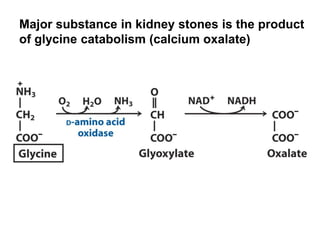
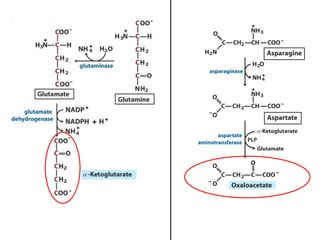
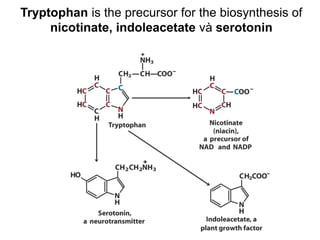
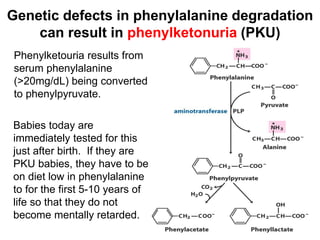
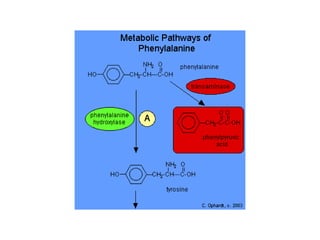
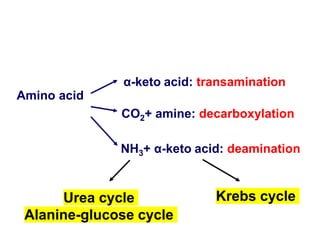
Protein degradation is accomplished by endopeptidases and exopeptidases that cleave peptide bonds within or at the ends of polypeptide chains. Pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin, secreted in the stomach and pancreas, have different amino acid specificities and work together efficiently to digest proteins. Amino acids are oxidized in the liver to produce energy, carbon skeletons for gluconeogenesis, and ammonia. Excess ammonia is processed through the urea cycle where it is combined with carbon dioxide to form the non-toxic urea for excretion.