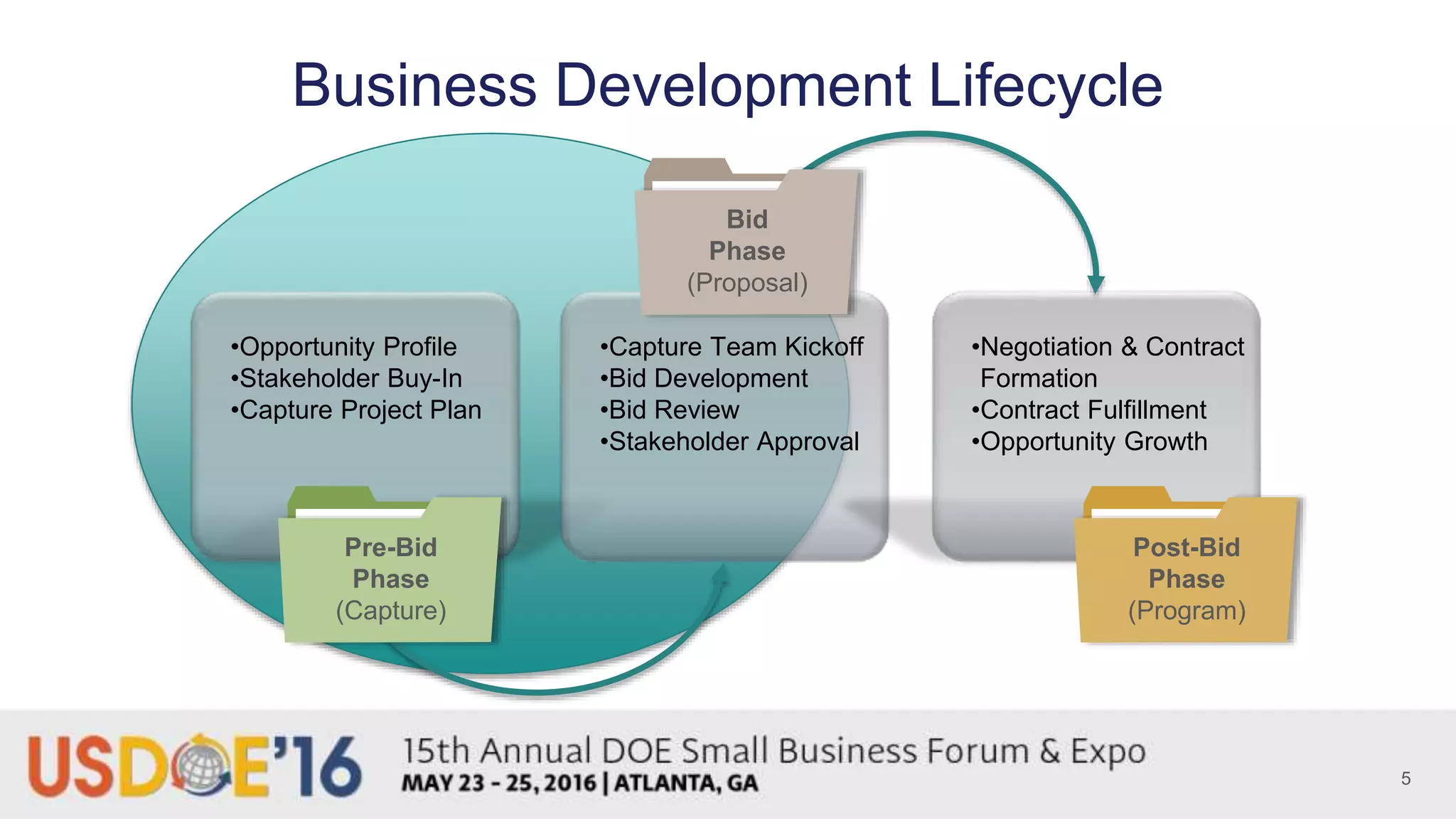
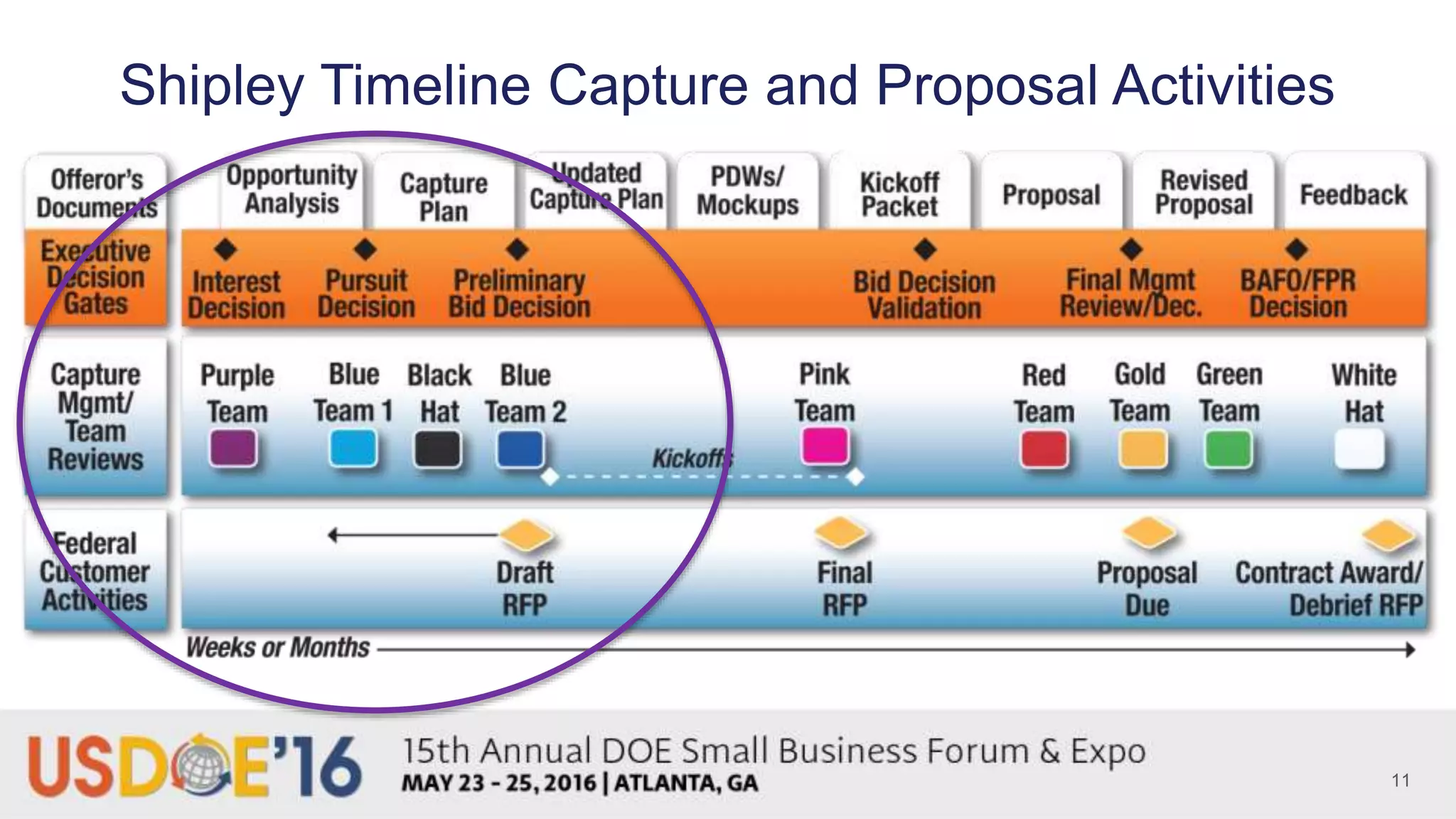
The document provides background on Tan V. Wilson and discusses key aspects of proposal preparedness. It outlines Tan's experience and credentials. It then covers topics like the business development lifecycle, pre-solicitation activities, ensuring the right people, processes and tools are in place, timeline for capture and proposals, common preparedness challenges, and steps to get organized like understanding requirements and leveraging subject matter experts.