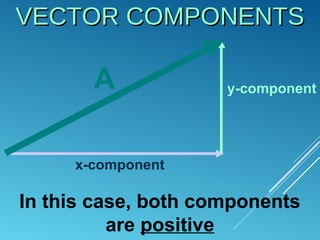
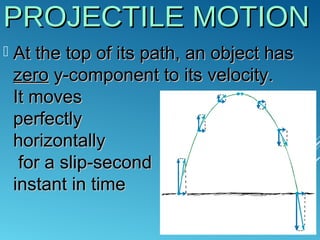
The document discusses vector components and projectile motion. It explains that a vector has an x-component determining horizontal tilt and a y-component determining vertical tilt. It then describes projectile motion, noting that it is influenced only by gravity and follows a curved 2D path. The horizontal velocity remains constant while the vertical velocity changes due to gravity, accelerating the object downward and combining to form a parabolic trajectory. The horizontal and vertical motions are independent and their equations should not be mixed.