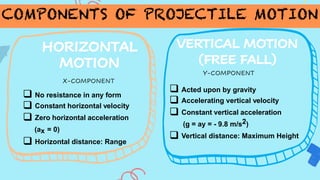
The document discusses projectile motion, explaining it as the path an object follows when thrown under the influence of gravity. It outlines the independence of horizontal and vertical motions, detailing the characteristics of both types of projectile launches and their effects on velocity and acceleration. Additionally, it references curriculum guides and educational resources relevant to the topic.









![REFERENCES
C.S. Lewis on Humility | Humility, Inspirational quotes, Quotable quotes. (n.d.). Pinterest.
https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/388646642816576065/
Department of Education (2016). K to 12 Curriculum Guide for Science: Kindergarten to Grade 10.
Retrieved from http://deped.gov.ph/sites/default/files/page/2016/Science%20CG.pdf
Garcia, R.J.G., Laurente, J.A.T., Montebon, D. R. T., & Auditor, E. (2015). Science for the 21st century
learner 9. [e-textbook]
Moros, E.M., Avilla, R.A., Greogorio, J.B., & Pineda, M.G.F. (2018). Practical science 9. Makati City:
University Press First Asia
Papa, E. C. R., Moros, E.M., Pineda, M. G. P., & Gregorio, J.B. (2018). Practical Science 7. Makati City:
University Press of First Asia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade9projectilemotionfinal-210602062645/85/Projectile-Motion-Grade-9-Physics-K-to-12-Science-11-320.jpg)