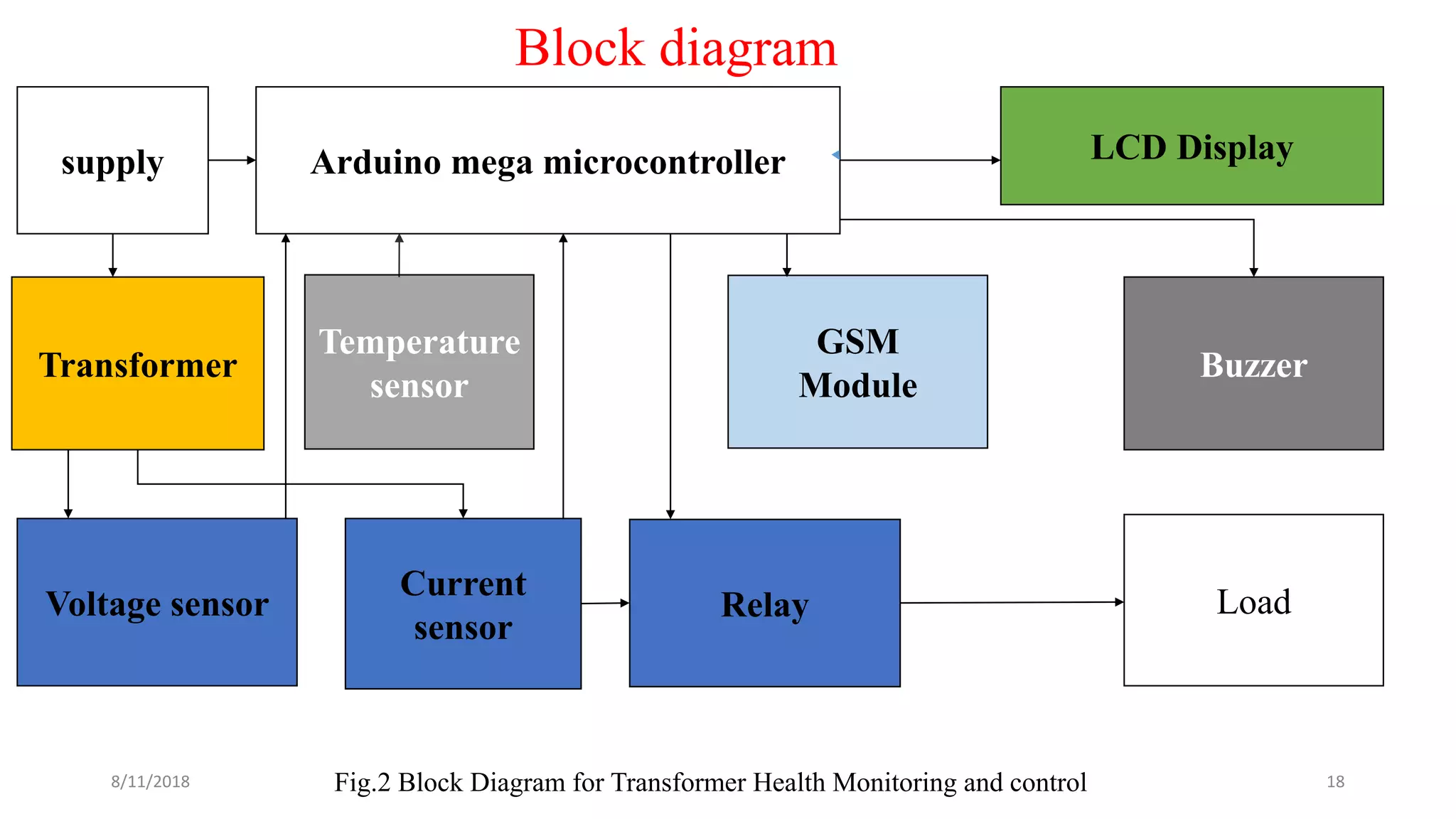
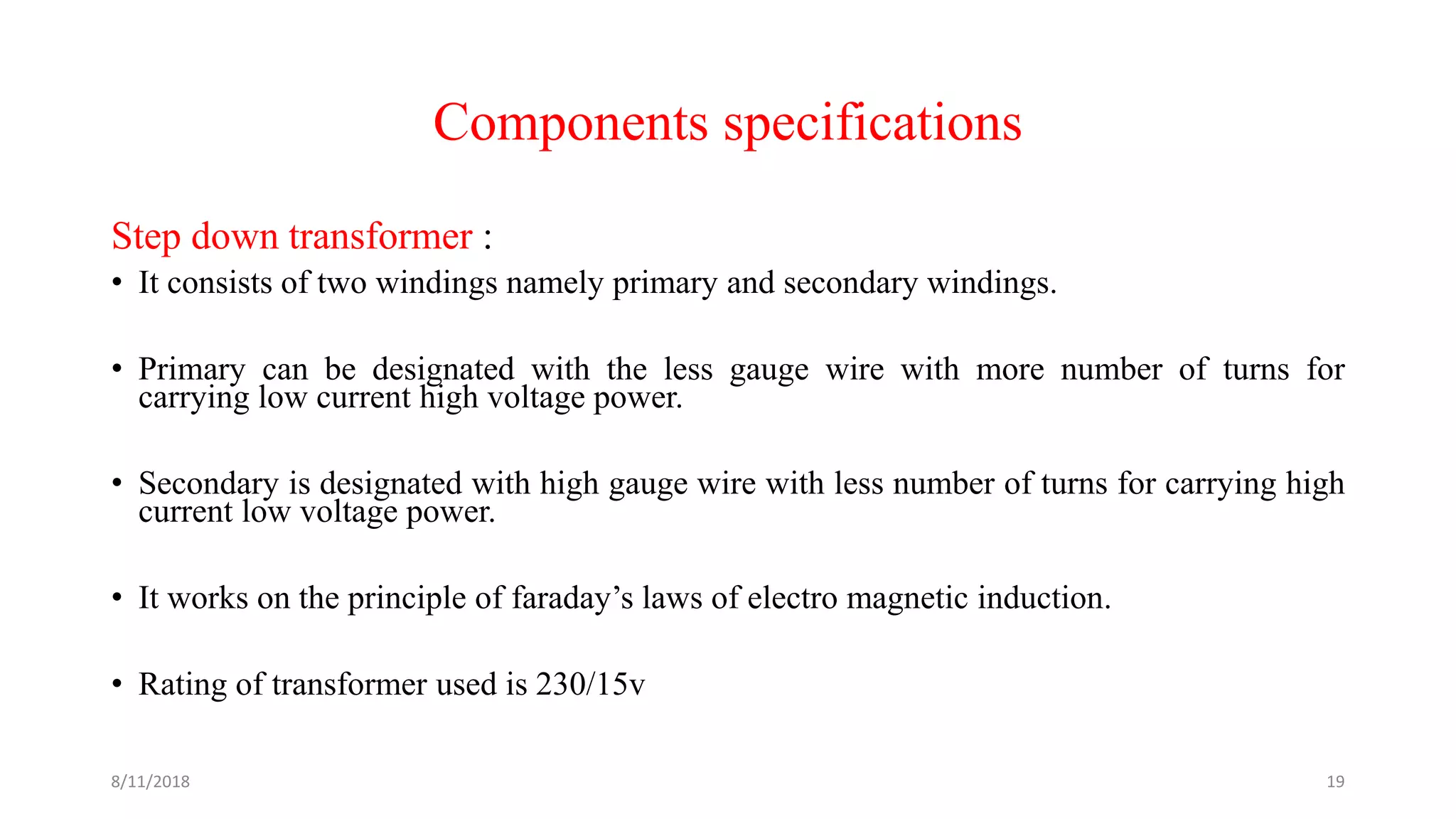
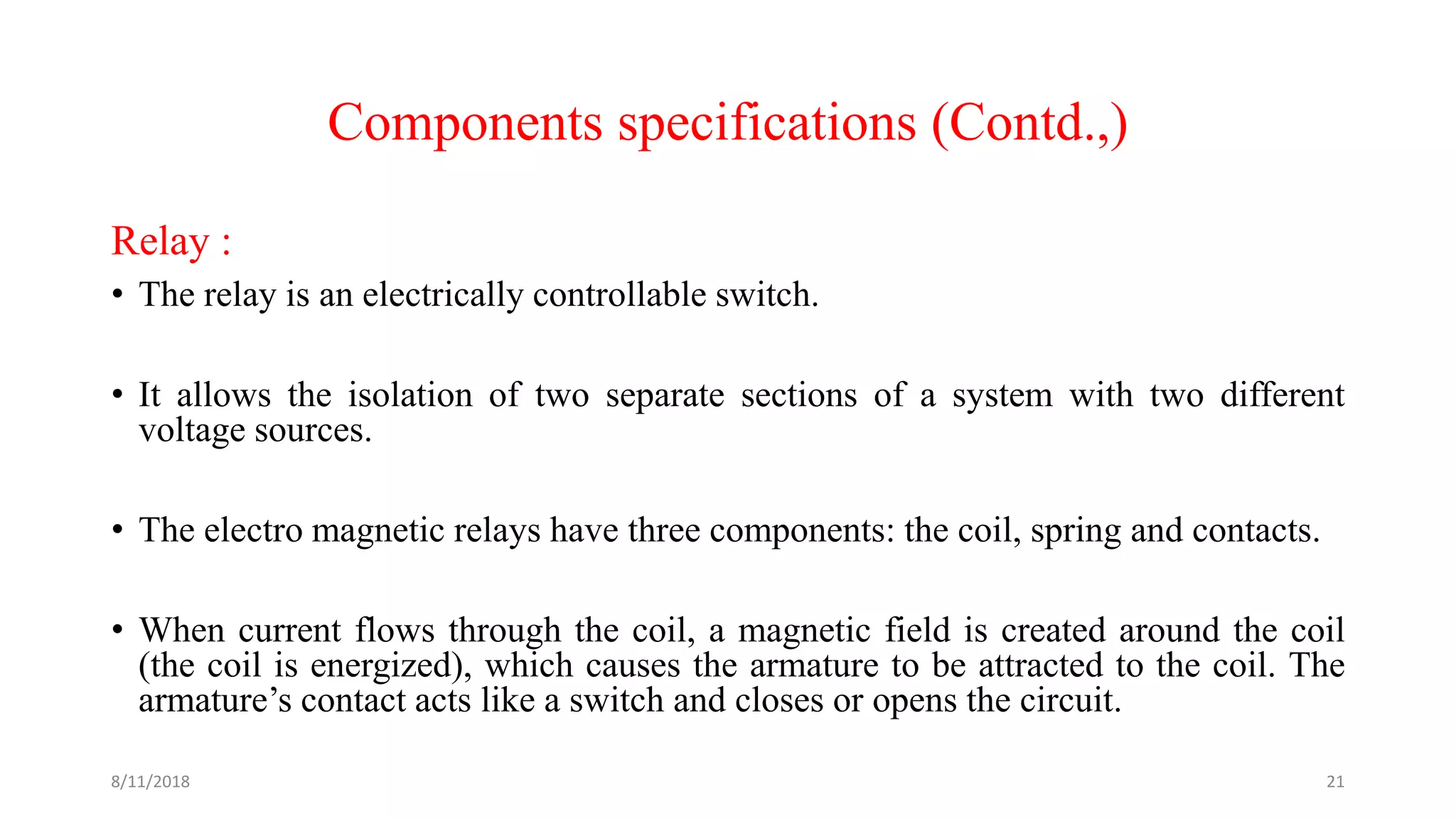
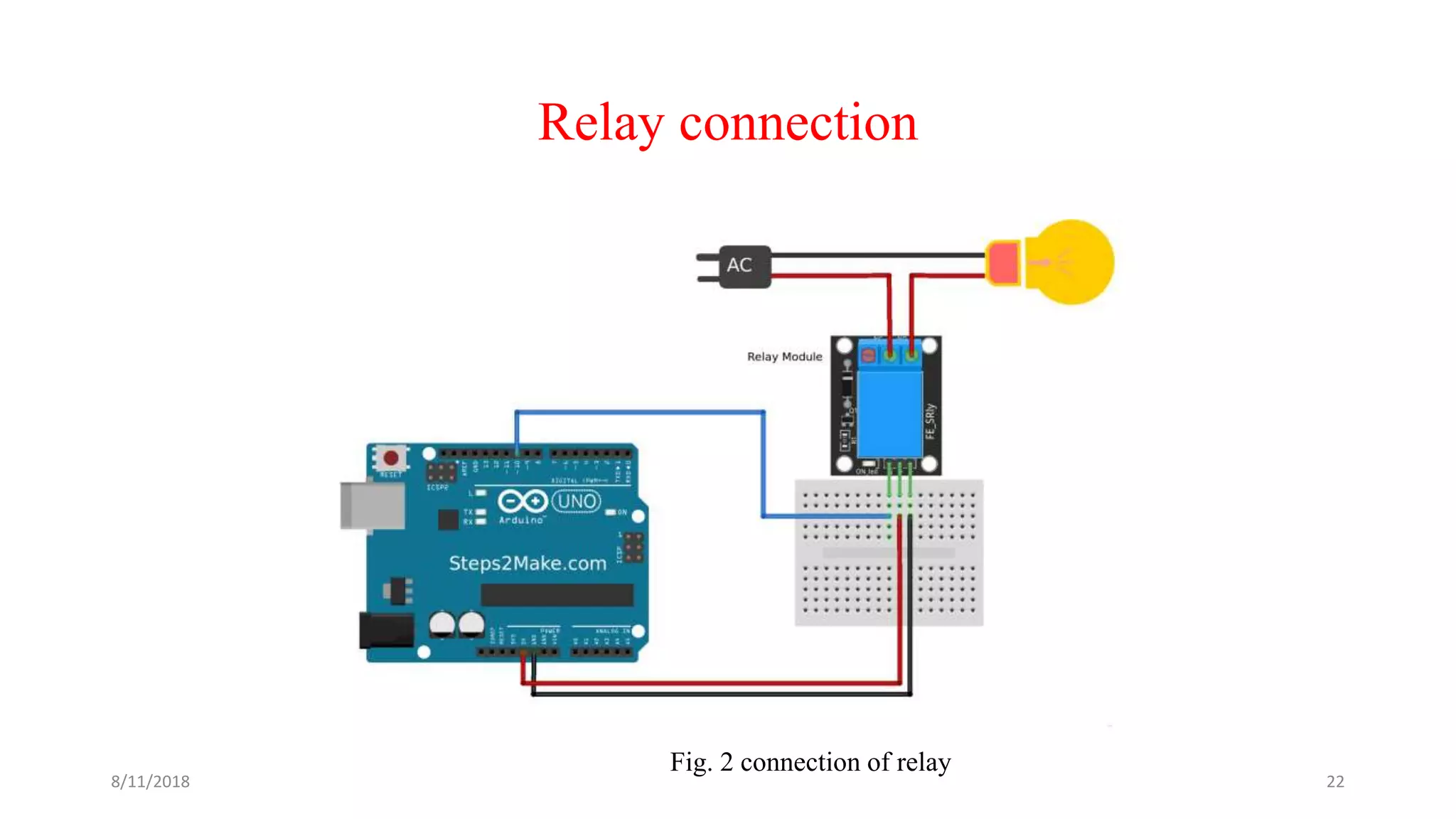
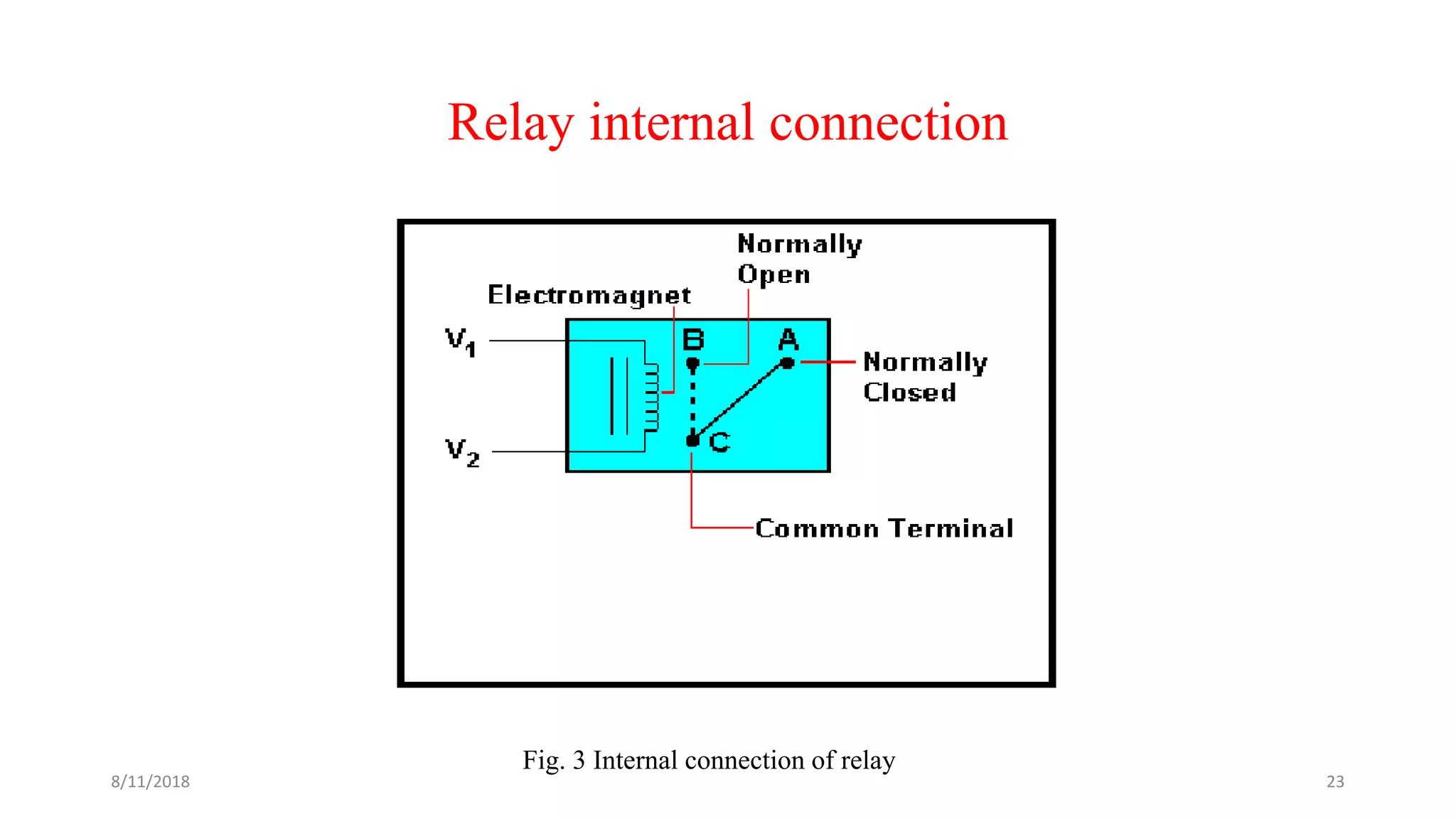
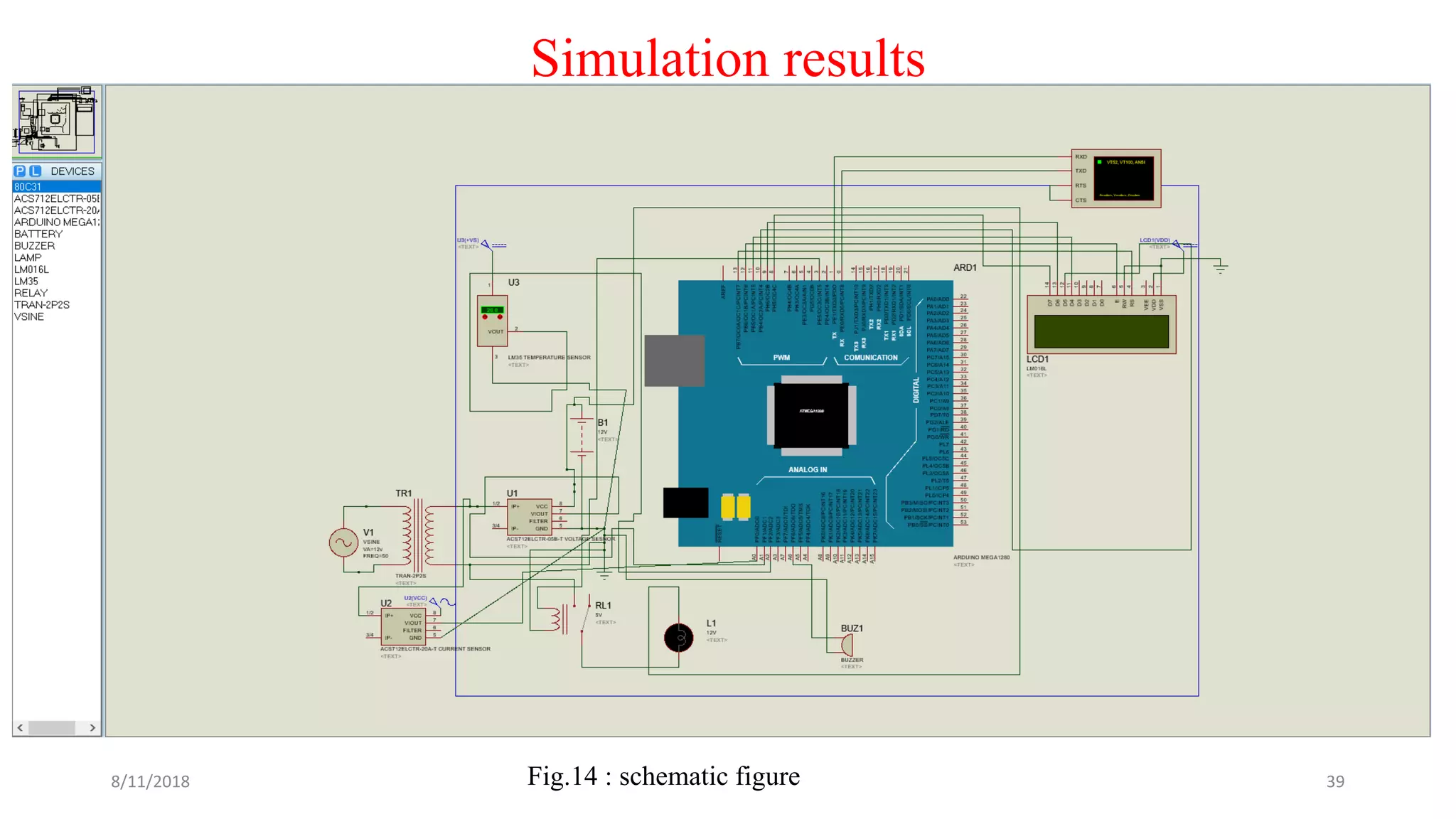
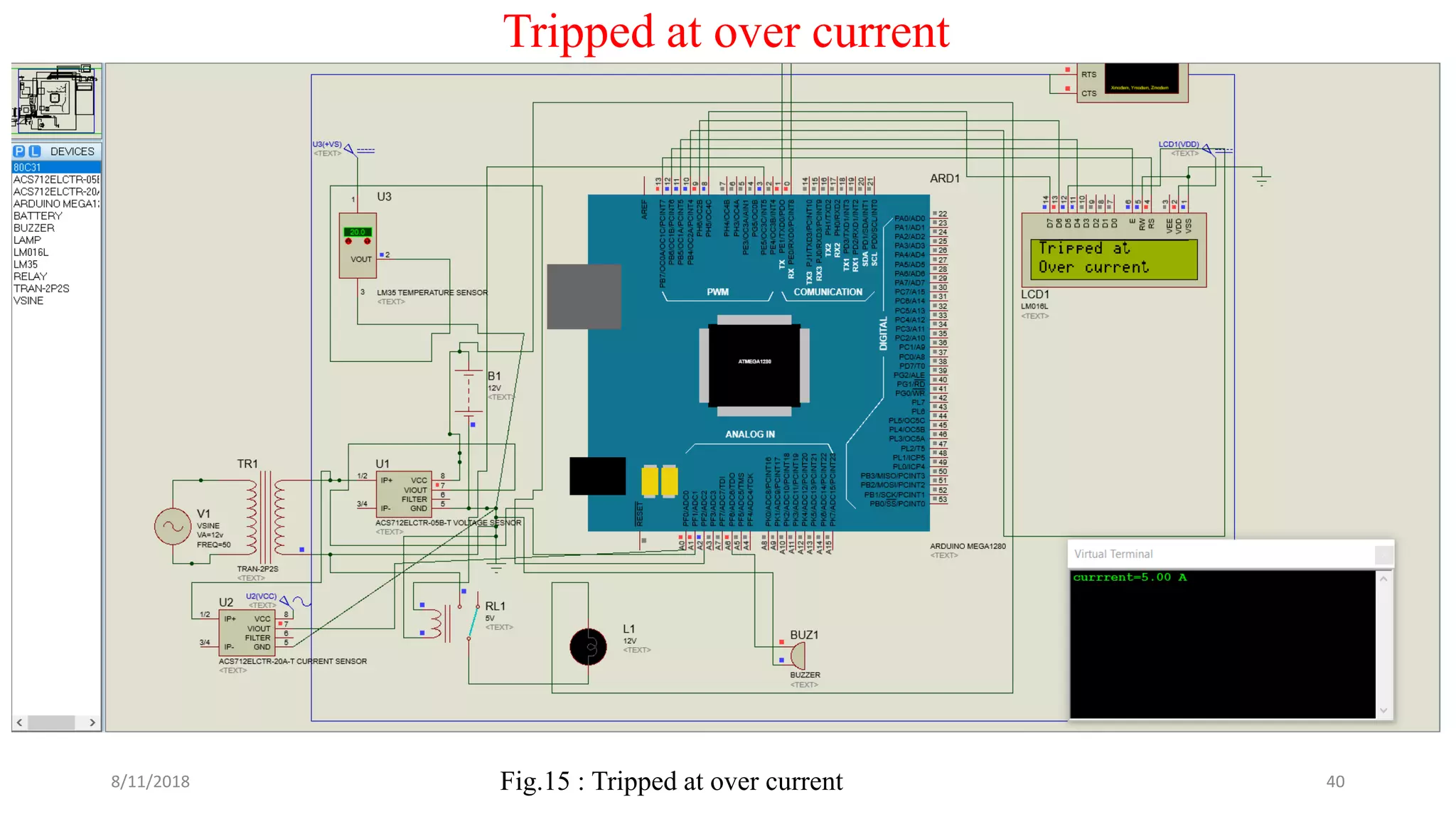
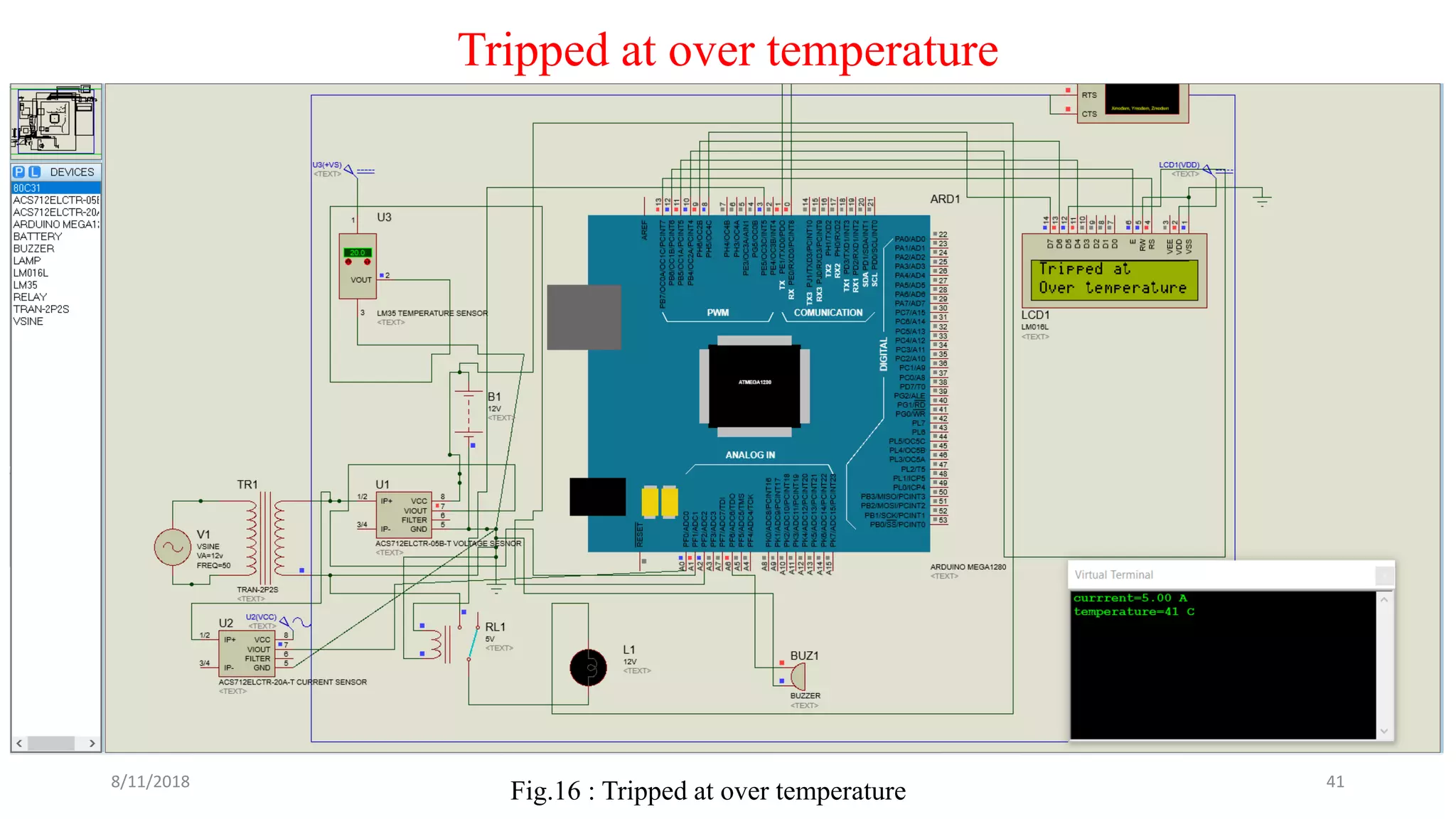
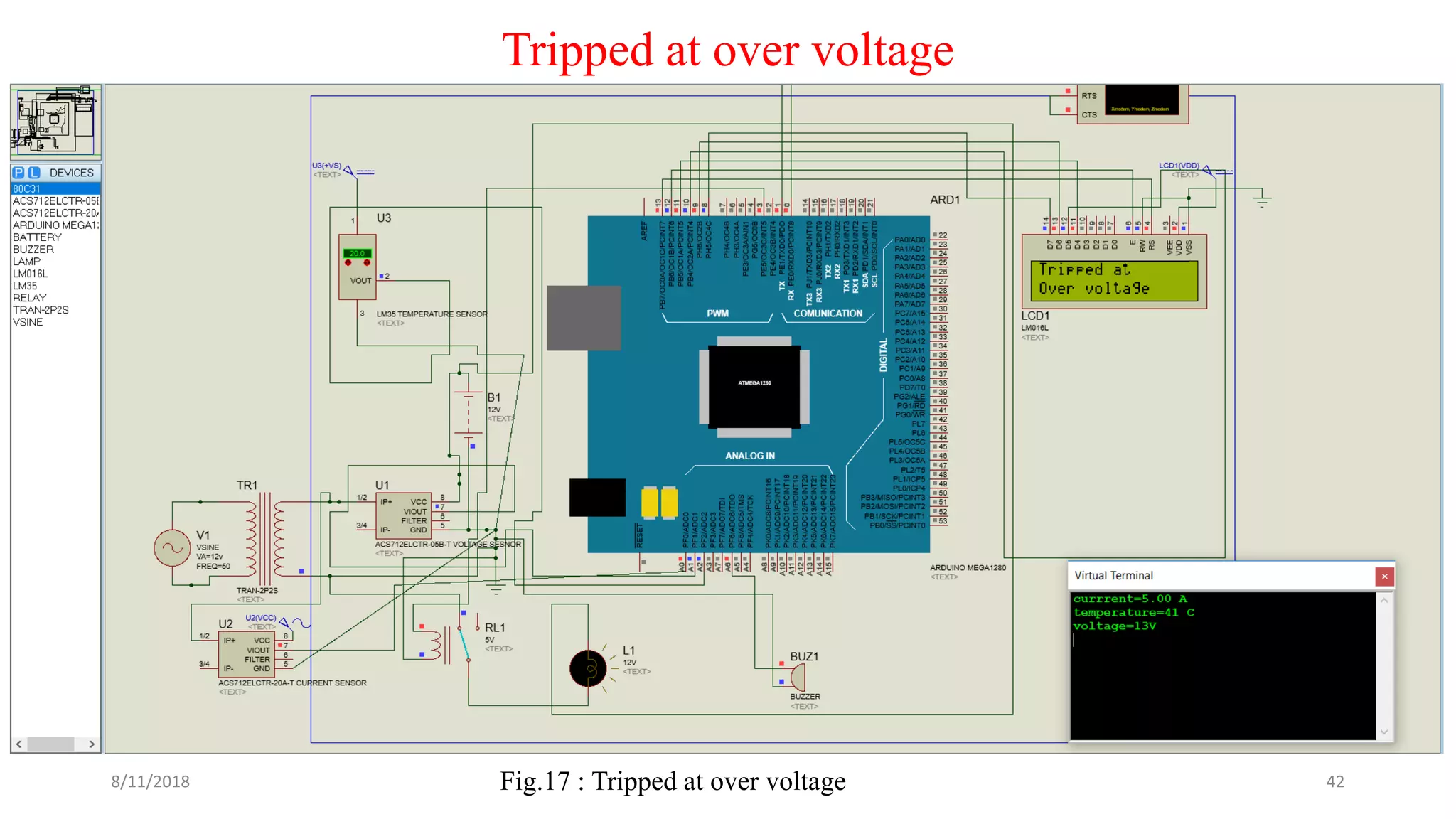
The document describes a project seminar focused on designing a protective circuit for transformers using Arduino, aiming to monitor key parameters such as temperature, voltage, and current via sensors. It highlights the project objective, methodology, and the benefits of using Arduino over existing transformer protection methods, emphasizing fast response and accurate fault detection. Additionally, the document includes detailed components specifications, a flowchart of the operational process, and results from the implementation.





![Literature Survey
• Online condition monitoring system for substation and service transformer
[1]
To get maximum profit with minimum maintenance cost by developing a
condition based monitoring. It is useful to replace reactive and preventive
maintenance.
Advantage: It is cost effective, online and accurate tool as it proposes corrective
actions and the results are evaluated by comparing with the results obtained from
utility model.
Disadvantage: It can be applied only to transformers without any abnormal faults
such as detected by dissolved gas analysis.
8/11/2018 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalreview-180811095123/75/project-presentation-on-THMC-6-2048.jpg)
![Literature Survey (Contd.,)
• Transformer health monitoring system [2]
As it is difficult to monitor the condition manually of every single transformer.
So, automatic data acquisition and transformer condition monitoring is issued.
It presents mobile embedded system to monitor load currents, over voltage,
transformer oil level and oil temperature by integrating GSM modem with single
chip micro controller and sensors installed at distribution transformer site.
This system is advanced step to the automation by diminishing human
dependency. As it is wireless, there is no need of large cables which is of high cost.
• A novel offline to online approach to detect transformer inter turn fault [3]
The time of acquisition and operation parameters is too long for ordinary
transformer but by using distribution transformer real time monitoring system to
detect all operation parameters in time.
8/11/2018 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalreview-180811095123/75/project-presentation-on-THMC-7-2048.jpg)

![Literature Survey (Contd.,)
• Health index calculation for power transformer using technical and
economical parameters [4]
The overall health condition of working transformers are evaluated by technical
diagnostic tests and economical lifetime assessment of transformers investigation.
Two artificial intelligence models including artificial neural network and adaptive
neuro-fuzzy inference system models are presented to determine the health index for
transformers.
The technical and economical parameters are used as input parameters to develop
the models. Technical parameters are extracted from oil characteristics and dissolved
gas analysis of different transformers. Economical parameters are constructed with
transformer capital investments, maintenance and operating costs. The models can
be used to determine the health condition of transformers with high accuracy.
8/11/2018 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalreview-180811095123/75/project-presentation-on-THMC-9-2048.jpg)

![Existing method (Contd.,)
Fig.1 Differential Protection [3]
8/11/2018 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalreview-180811095123/75/project-presentation-on-THMC-11-2048.jpg)




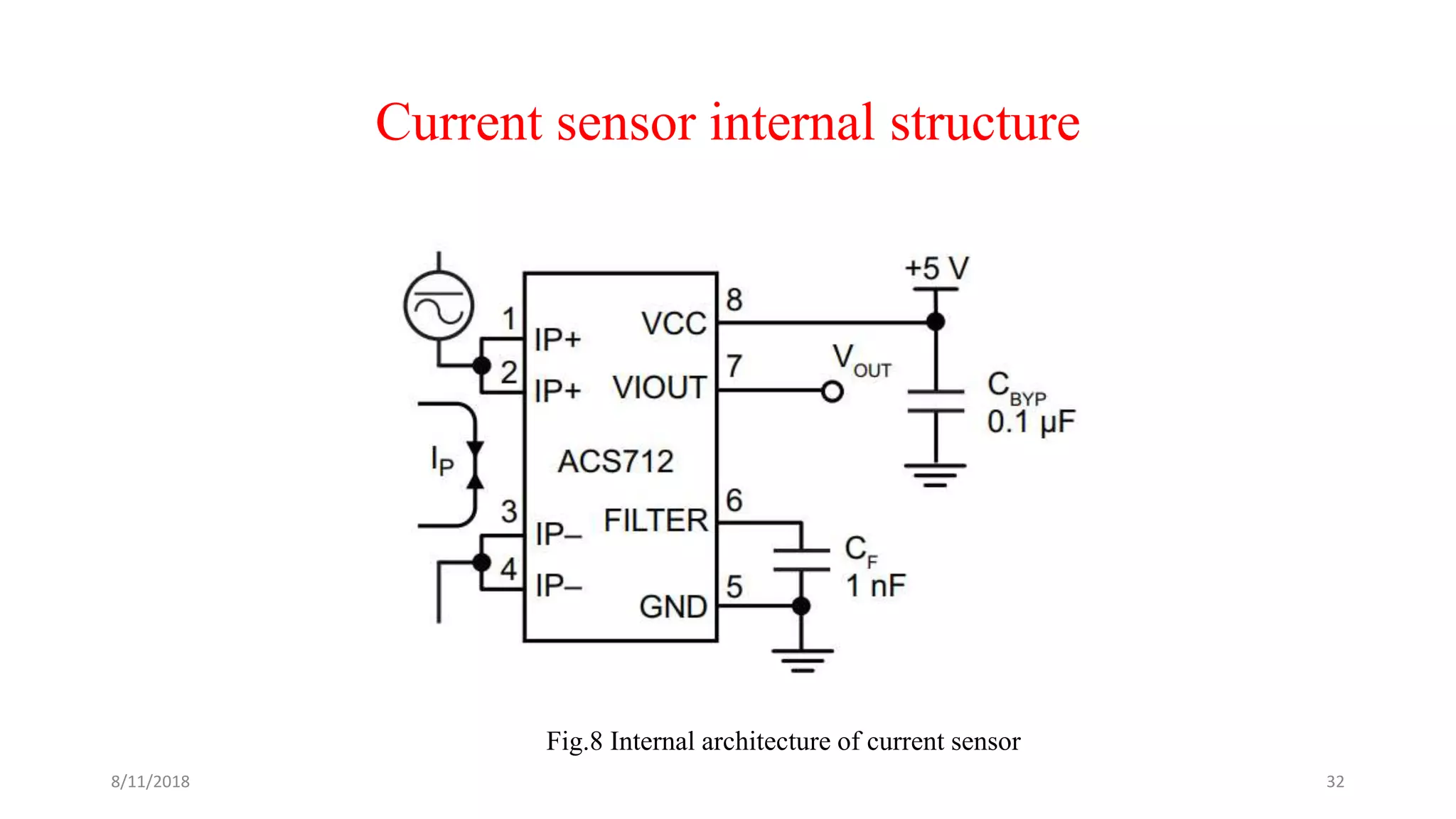

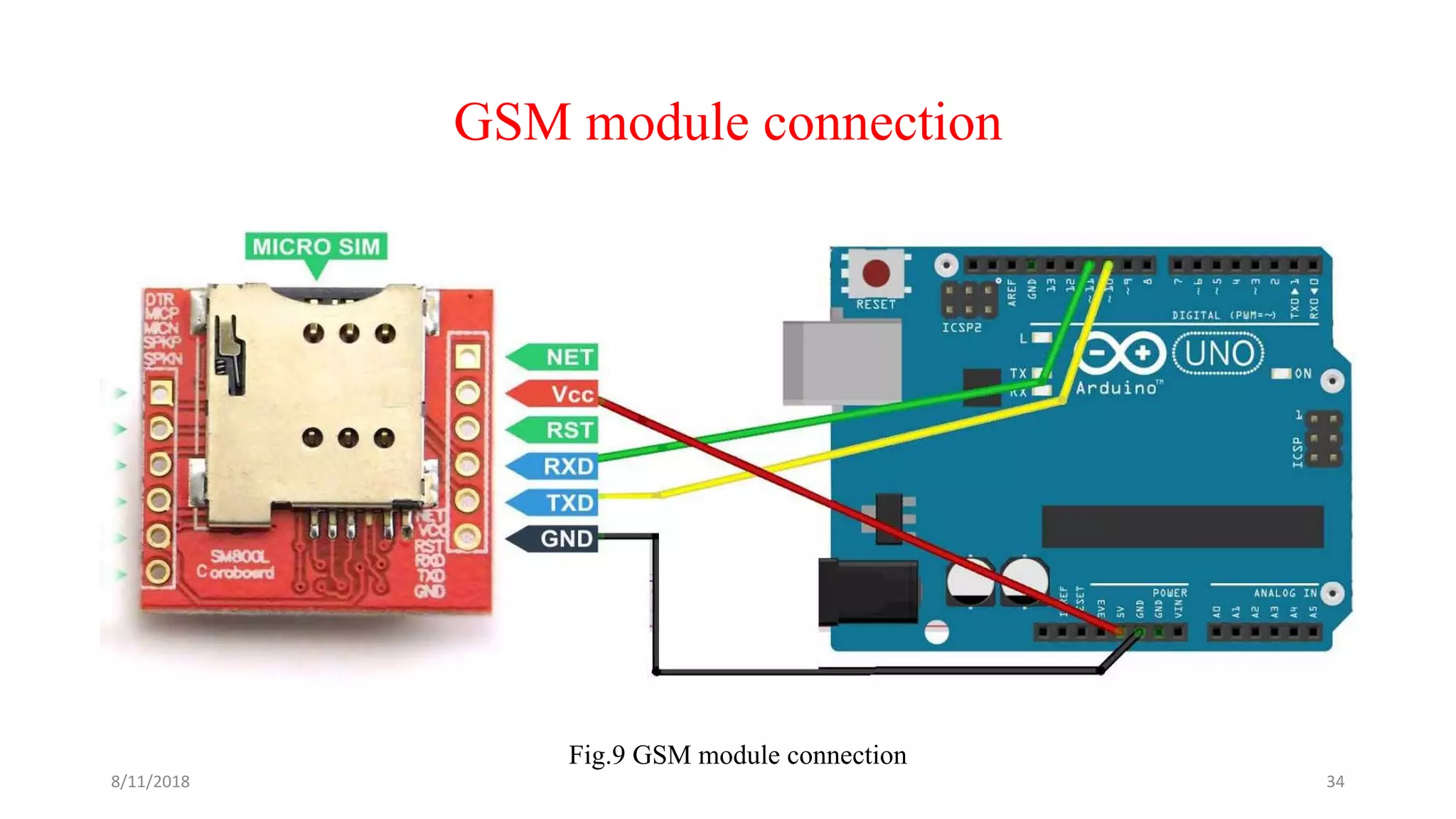
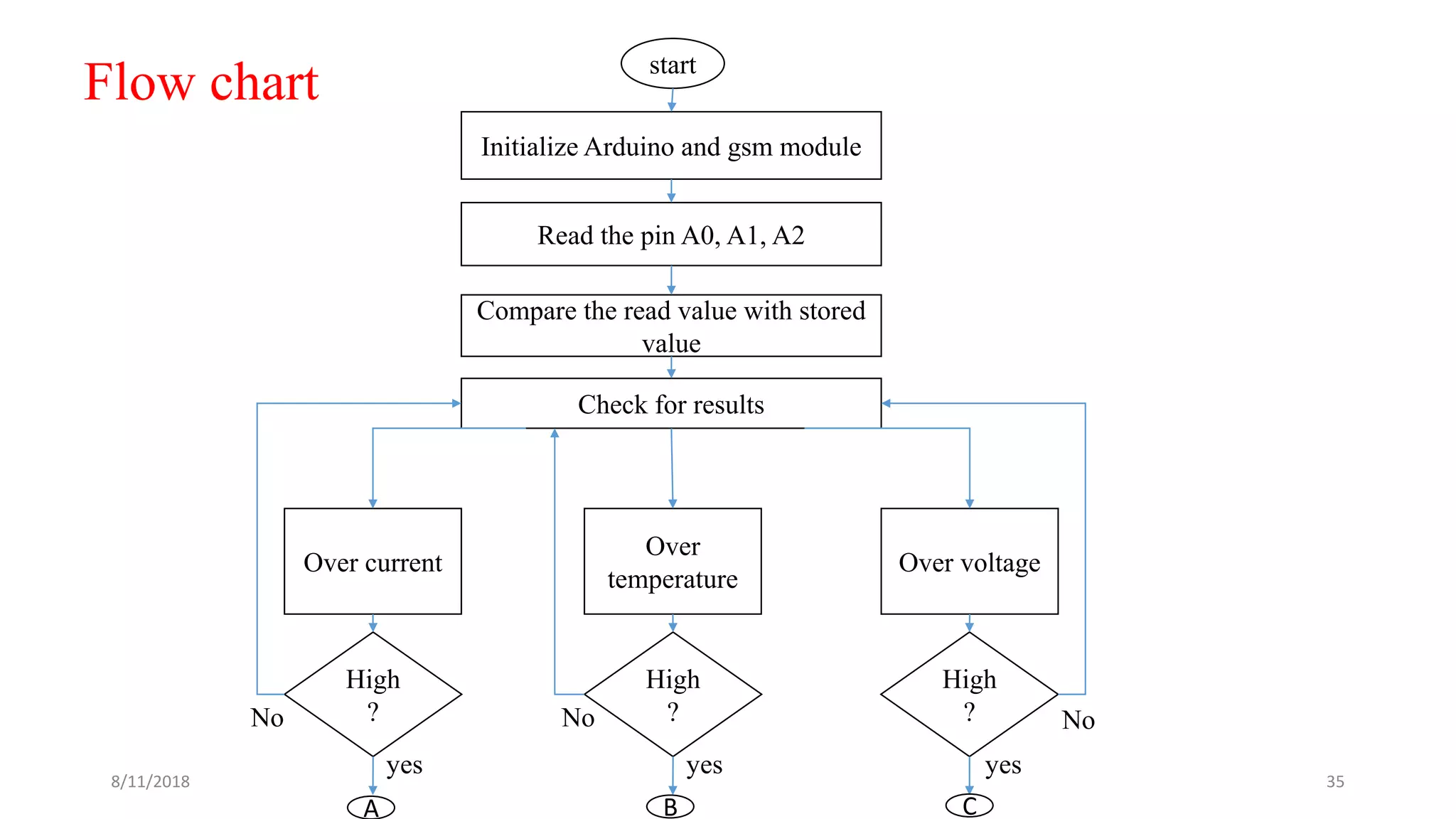
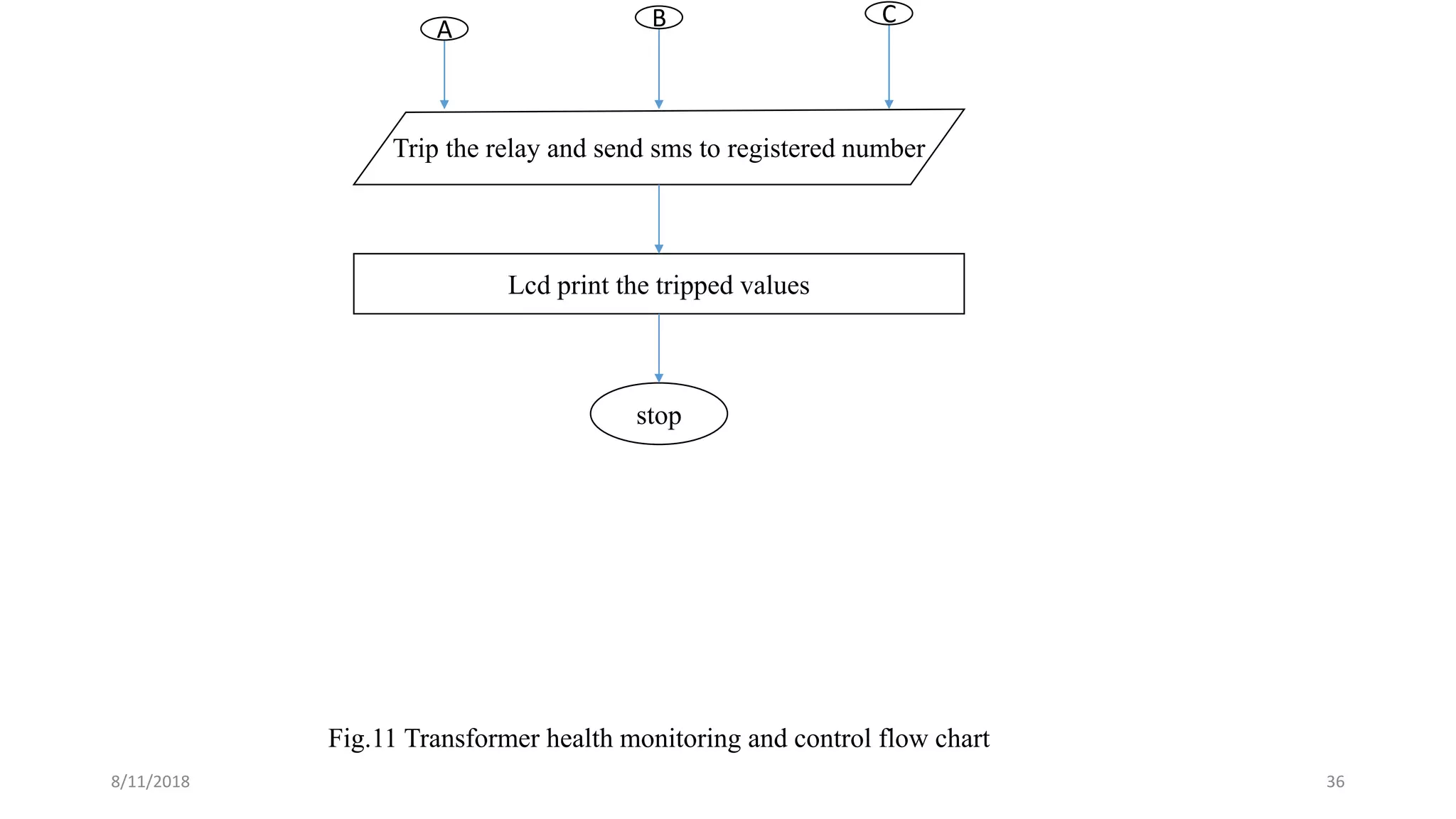

![Theoretical calculations
• 𝑡𝑒𝑚𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑡𝑢𝑟𝑒 =
𝑧×28
424
• 𝑐𝑢𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑡 =
𝑥×5
1024
• 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 =
5×𝑦×(𝑟1+𝑟2)
1023×𝑟
Z = resistance measured across thermistor [1]
x = output voltage of hall sensor [1]
y = output voltage of voltage sensor [1]
r1 = 2000ohms & r2 = 3000ohms [1]
8/11/2018 38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalreview-180811095123/75/project-presentation-on-THMC-38-2048.jpg)

![References
[1] Ballal, M. S., Jaiswal, G. C., Tutkane, D. R., Venikar, P. A., Mishra, M. K., & Suryawanshi, H. M. Online condition
monitoring system for substation and service transformers, IET Electric Power Applications, 2017, 11(7), 1187-1195.
[2] Patil R. V., Dhiraj Kalantre, Niranjan Hirugade, Arun More, Ashwinee Kakade, transformer health monitoring and
control through arduino, International Journal Of Electrical, Electronics And Data Communication, 2017, 5(1), 59-
62.
[3] Venikar, P. A., Ballal, M. S., Umre, B. S., & Suryawanshi, H. M. A novel offline to online approach to detect
transformer interturn fault. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2016, 31(2), 482-492.
[4] Zeinoddini-Meymand, H., & Vahidi, B. Health index calculation for power transformers using technical and
economical parameters. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 2016, 10(7), 823-830.
[5] Campelo, F., Batista, L. S., Takahashi, R. H., Diniz, H. E., & Carrano, E. G. Multicriteria transformer asset
management with maintenance and planning perspectives. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2016 10(9),
2087-2097.
[6] Patil1 U. V., Kathe Mohan, Harkal Saurabh, Warhade Nilesh Transformer Health Condition Monitoring Using GSM
Technology, International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering, 2(2), 2016.
[7] Ma, H., Saha, T. K., Ekanayake, C., & Martin, D. Smart transformer for smart grid—Intelligent framework and
techniques for power transformer asset management. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2015, 6(2), 1026-1034.
8/11/2018 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalreview-180811095123/75/project-presentation-on-THMC-47-2048.jpg)
