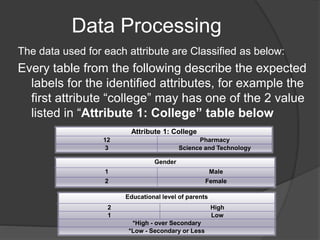
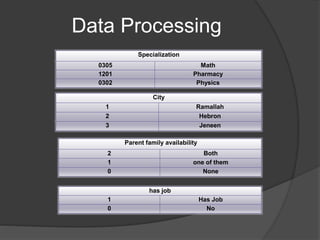
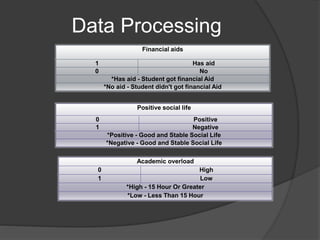
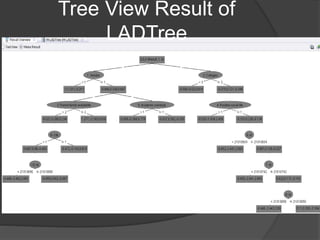
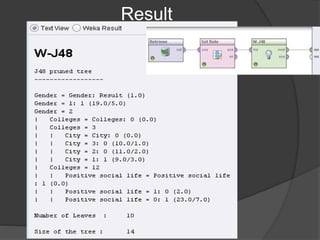
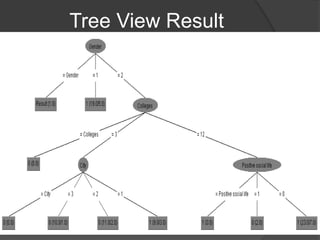
The document describes three experiments conducted on student data from AlQadi University to predict student performance. The first used a random tree algorithm and produced a decision tree with over 150 nodes. The second used a W-LADTree algorithm and produced a tree with 31 nodes, 21 predictor nodes, and 13 leaves. The third used a J48 algorithm, which is based on decision tree induction and employs two pruning methods.