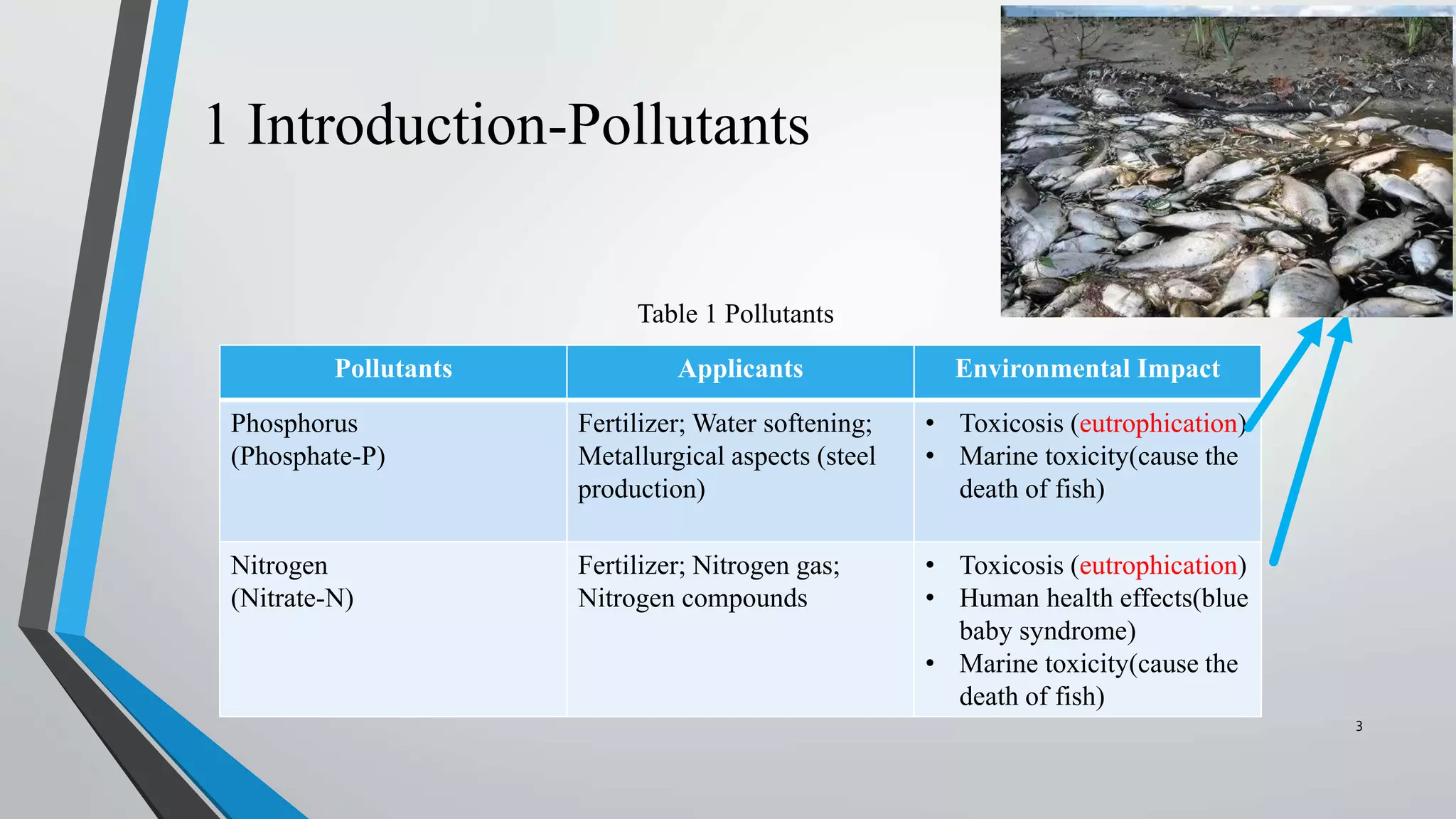
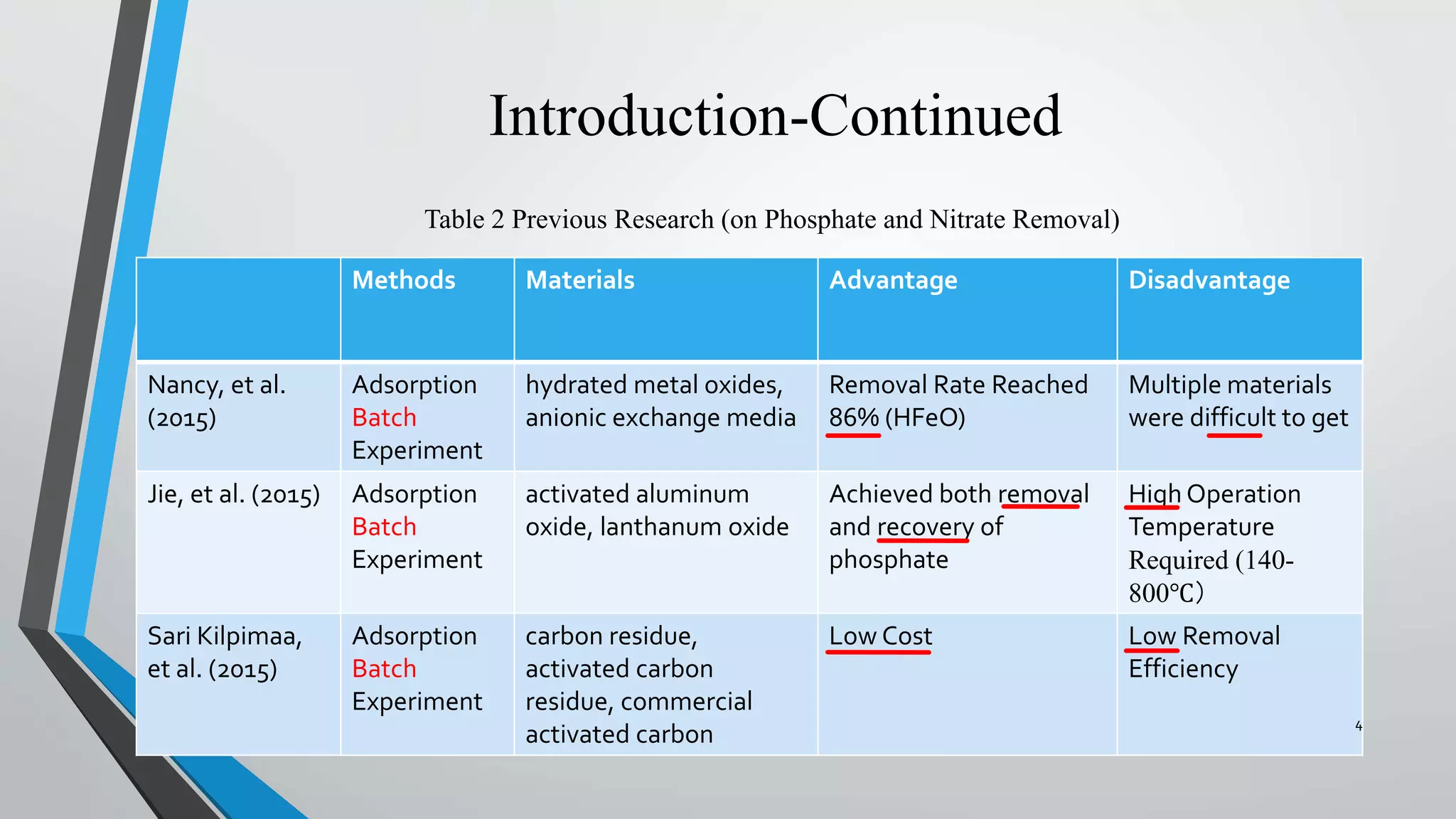
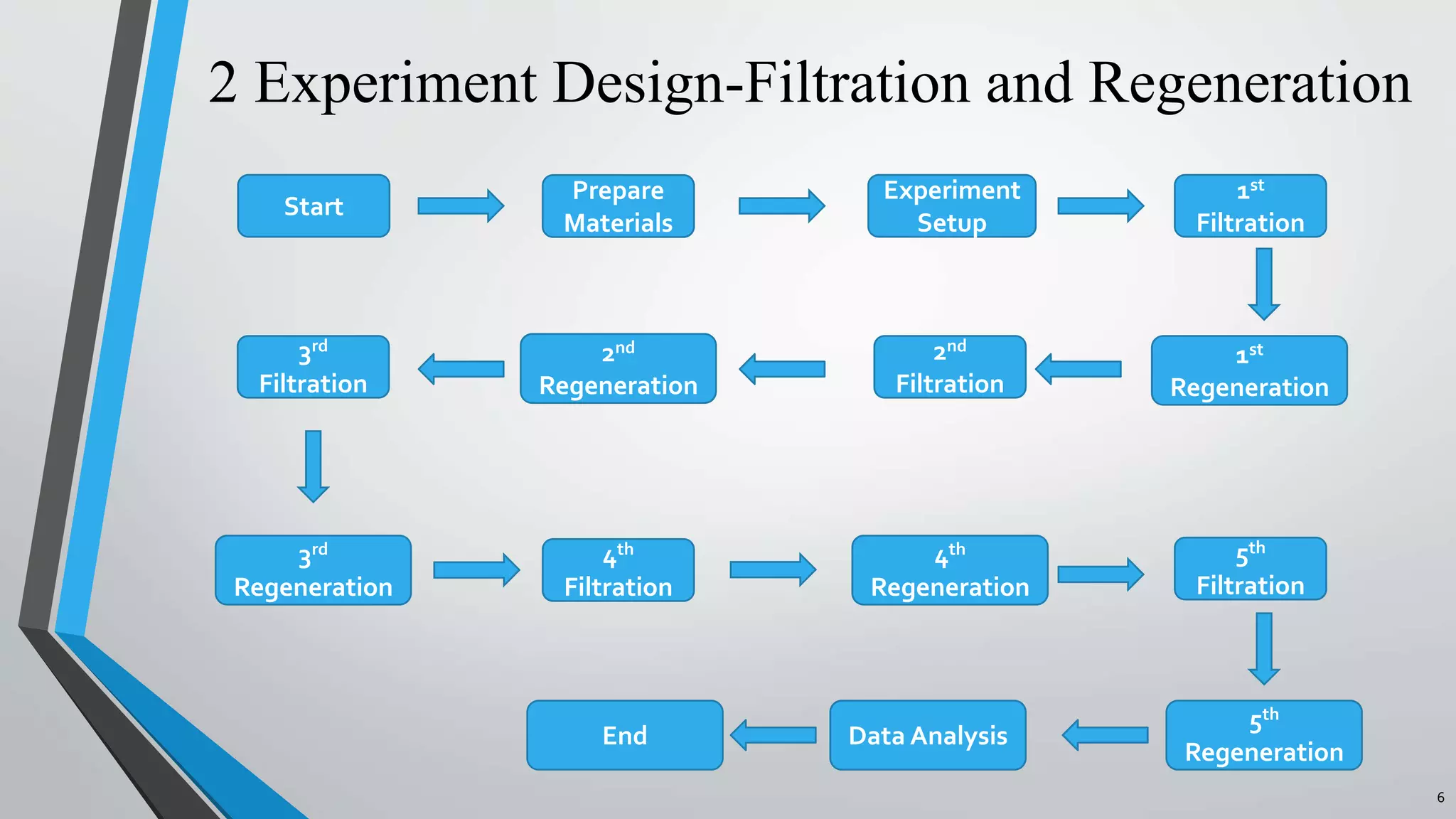
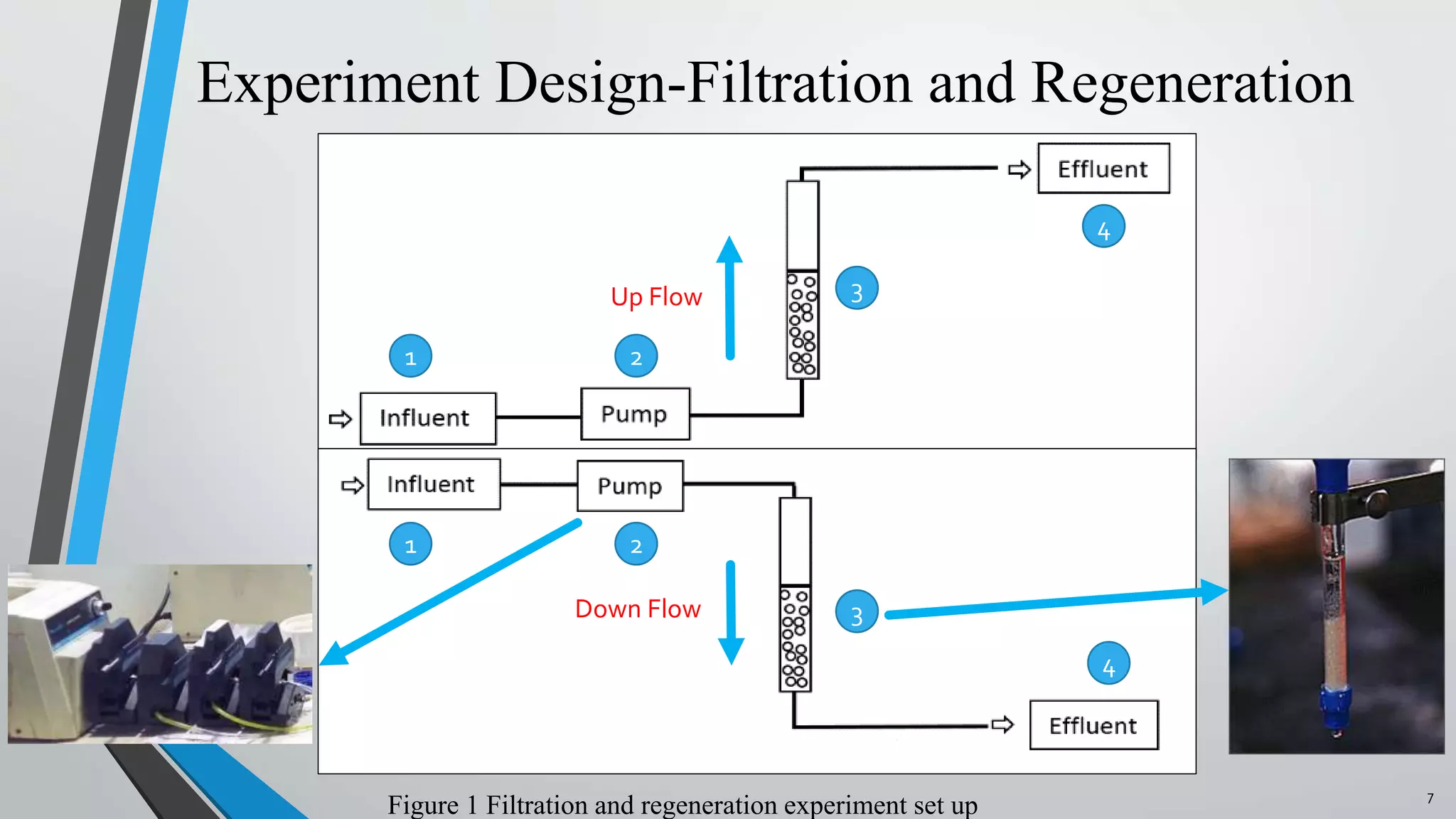
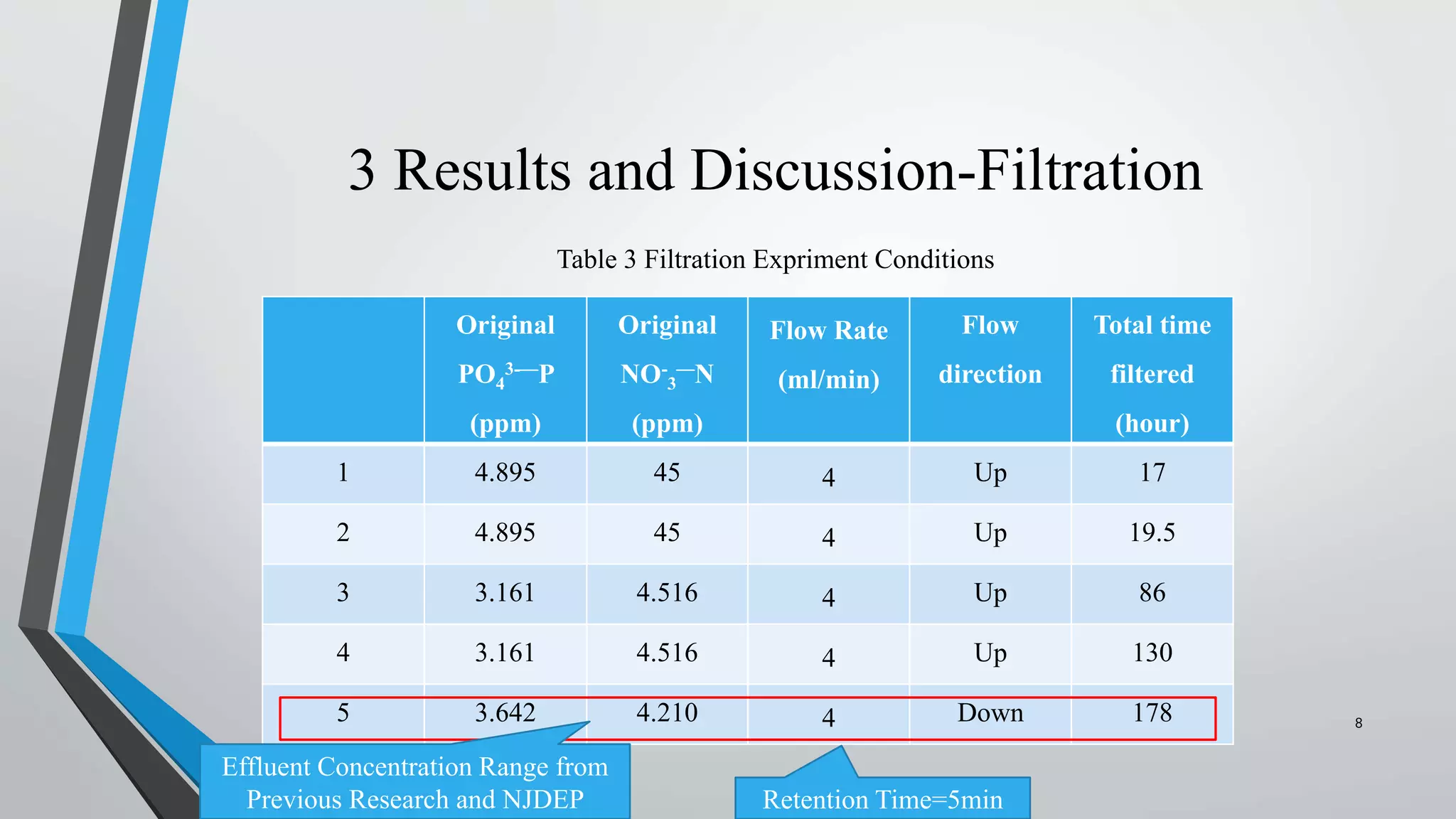
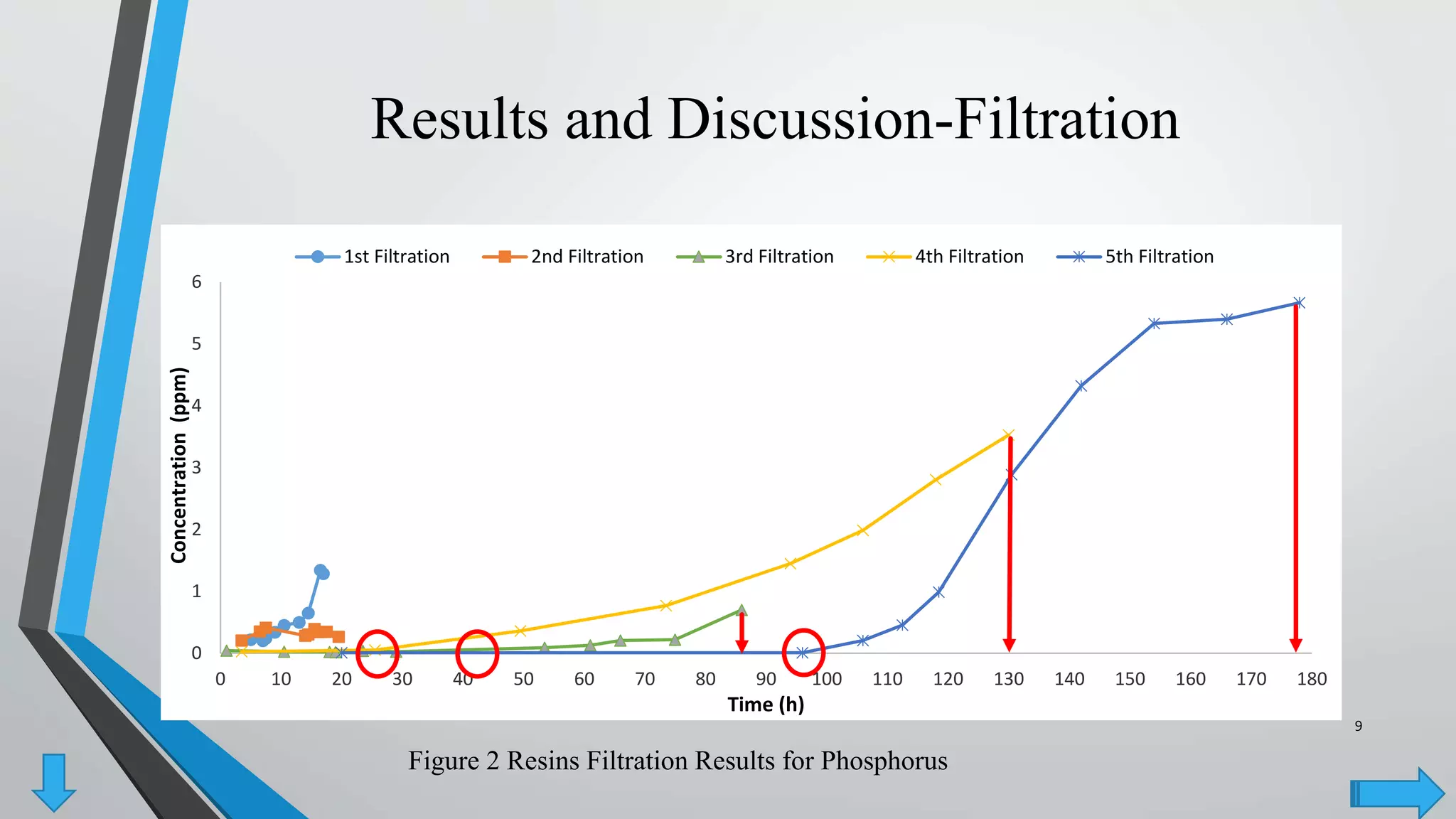
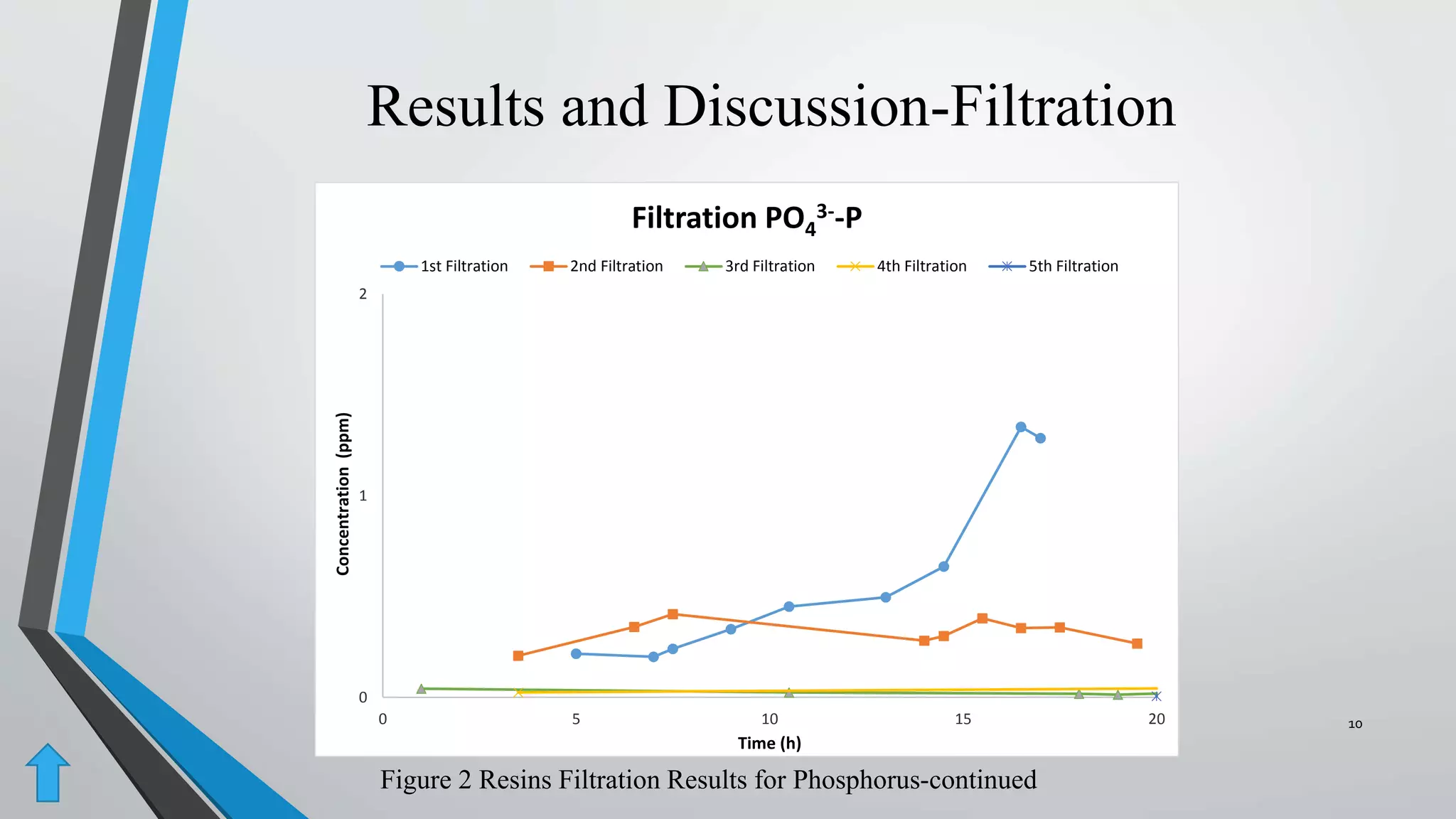
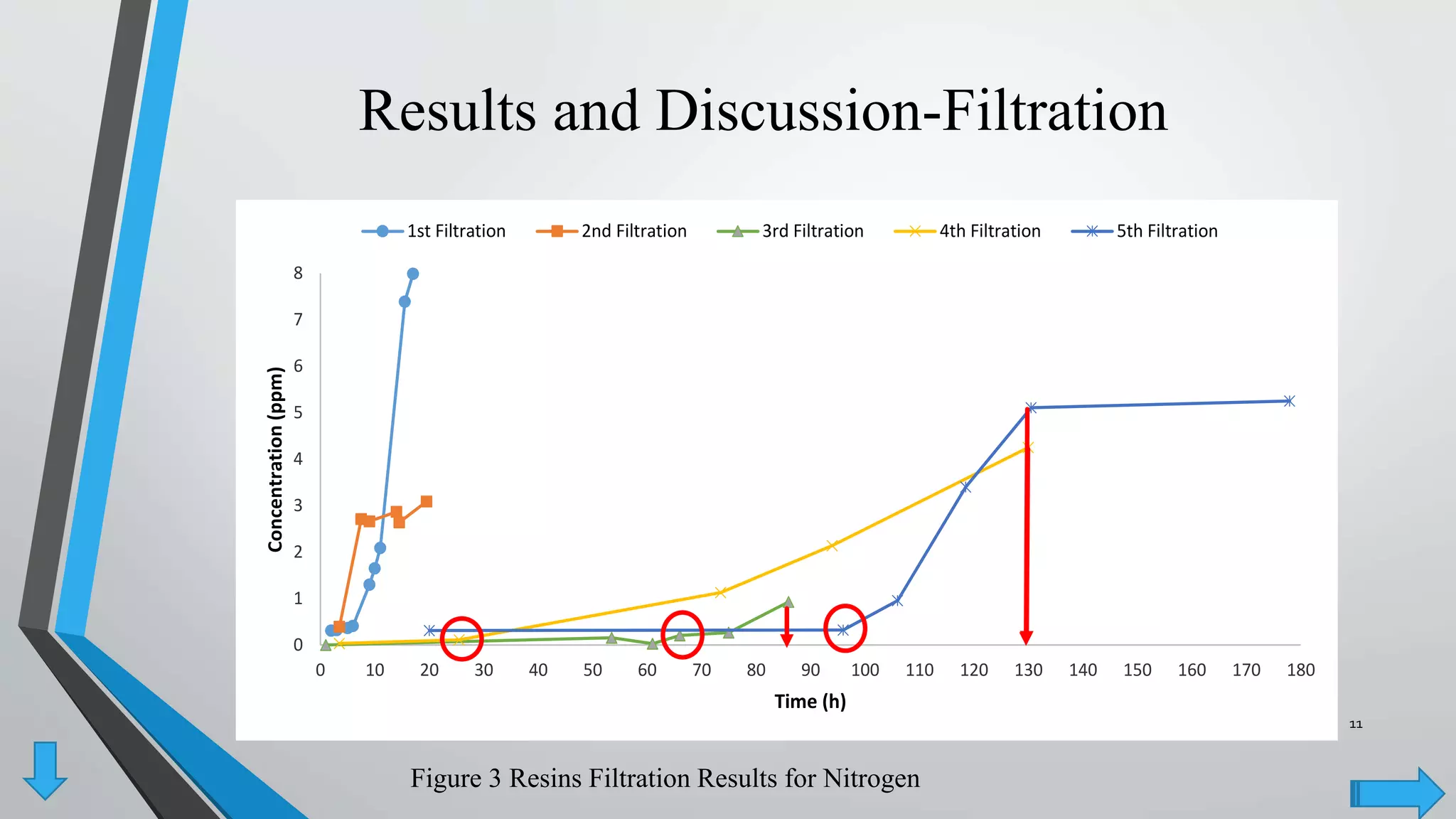
The document summarizes an experiment investigating the use of anion exchange resins (AER) to remove and regenerate phosphate and nitrate from wastewater. Key points:
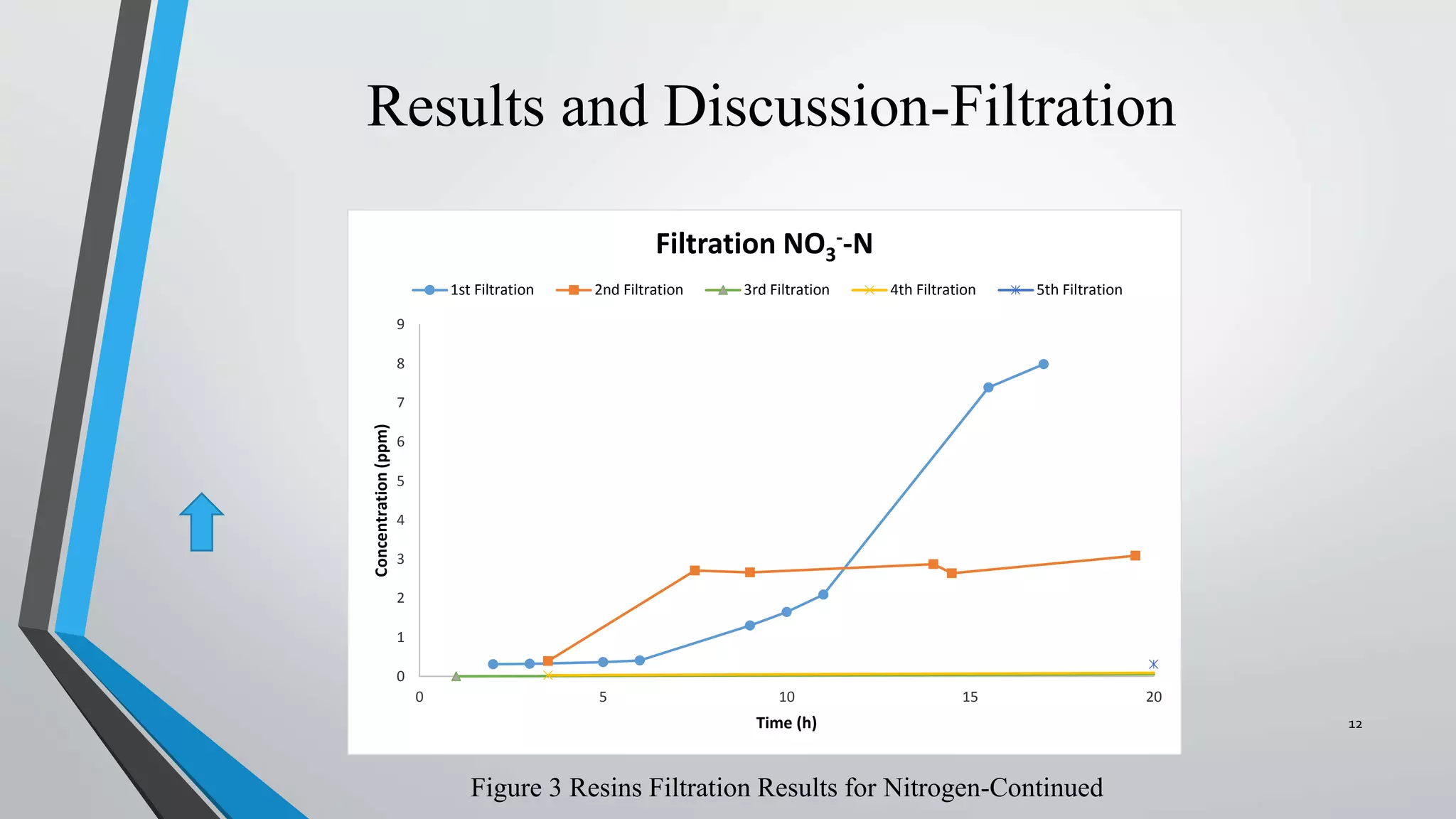
- AER were able to remove phosphate and nitrate from wastewater through a series of filtrations lasting up to 178 hours with effluent concentrations within regulatory limits.
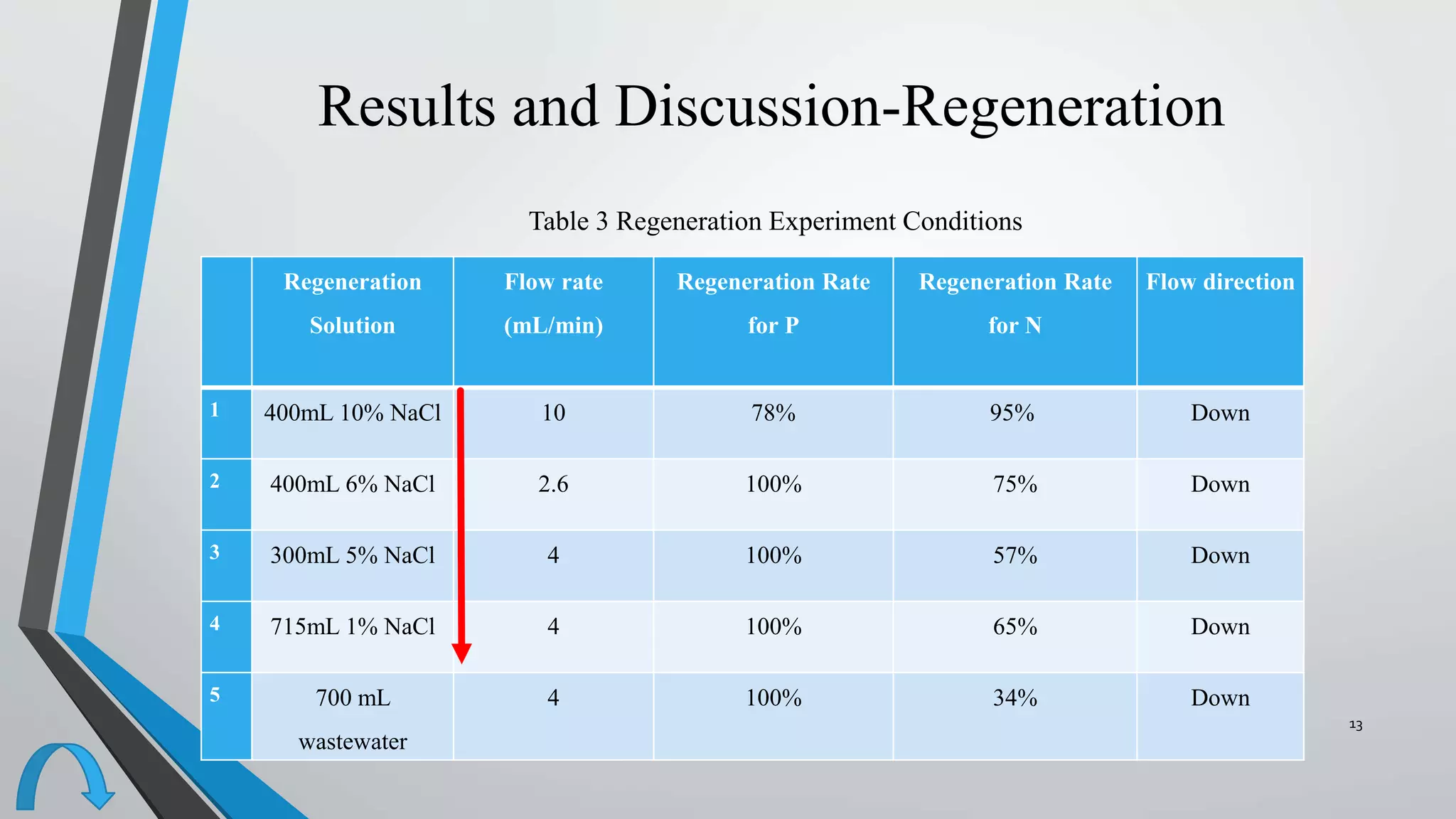
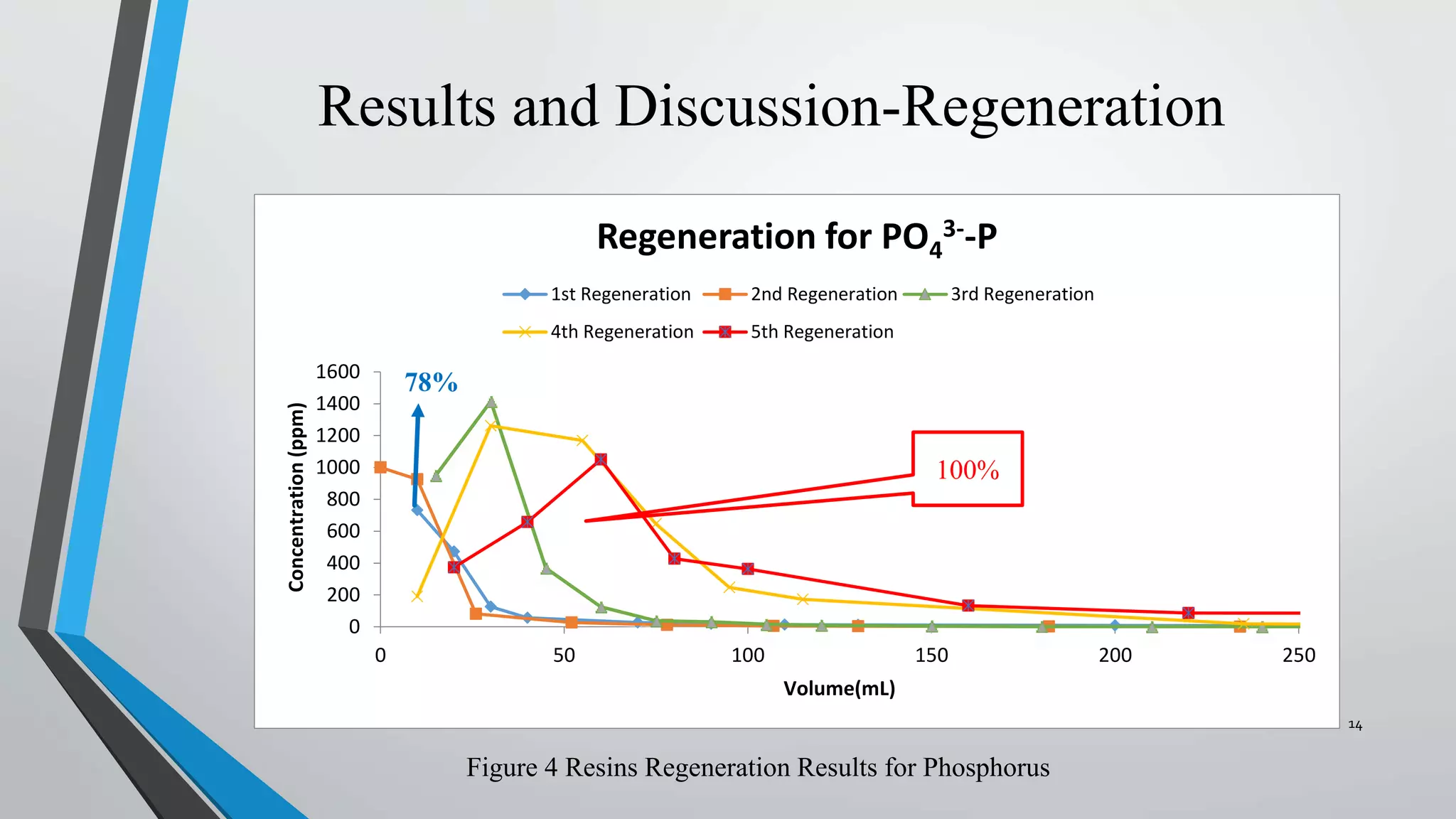
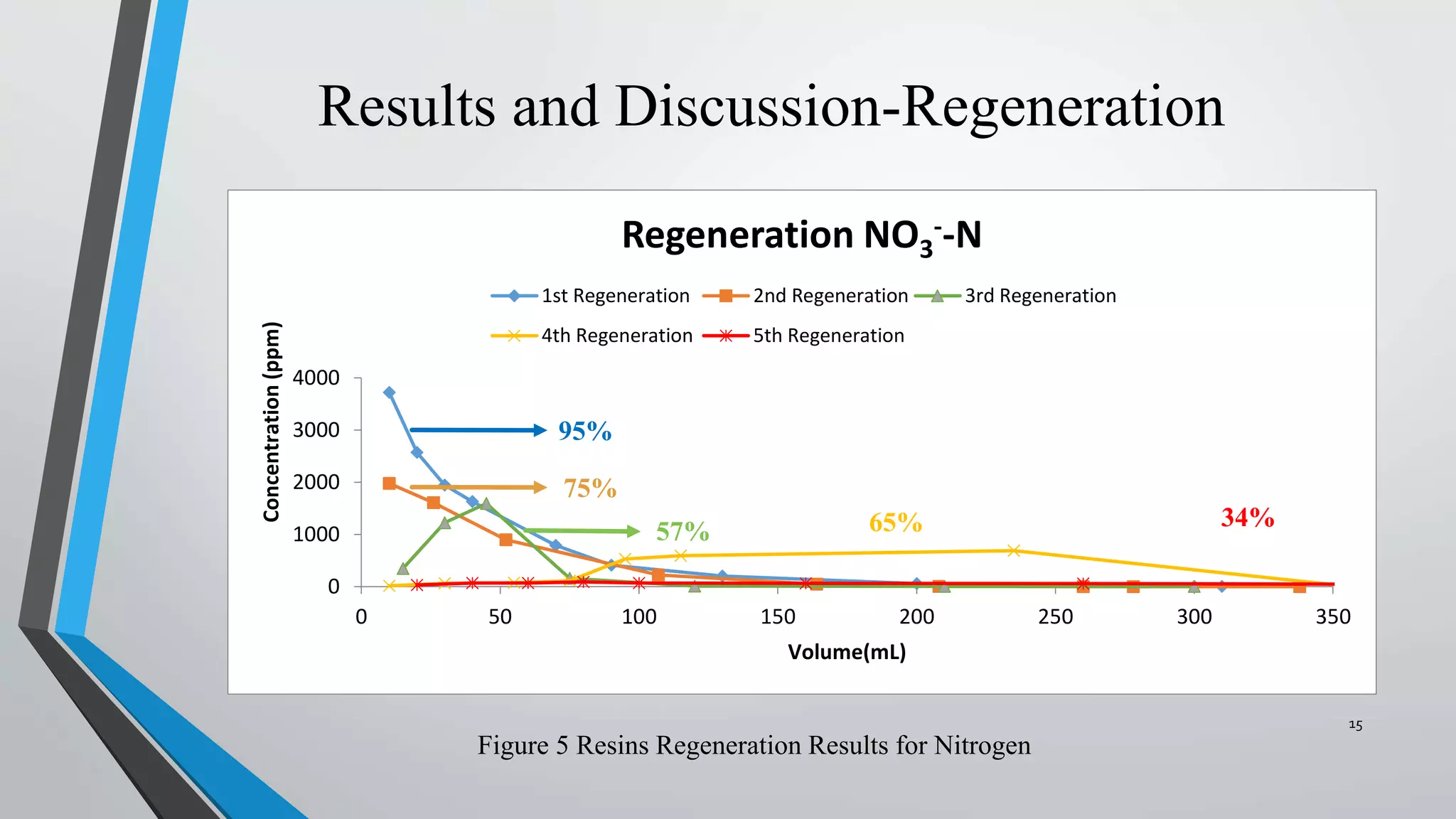
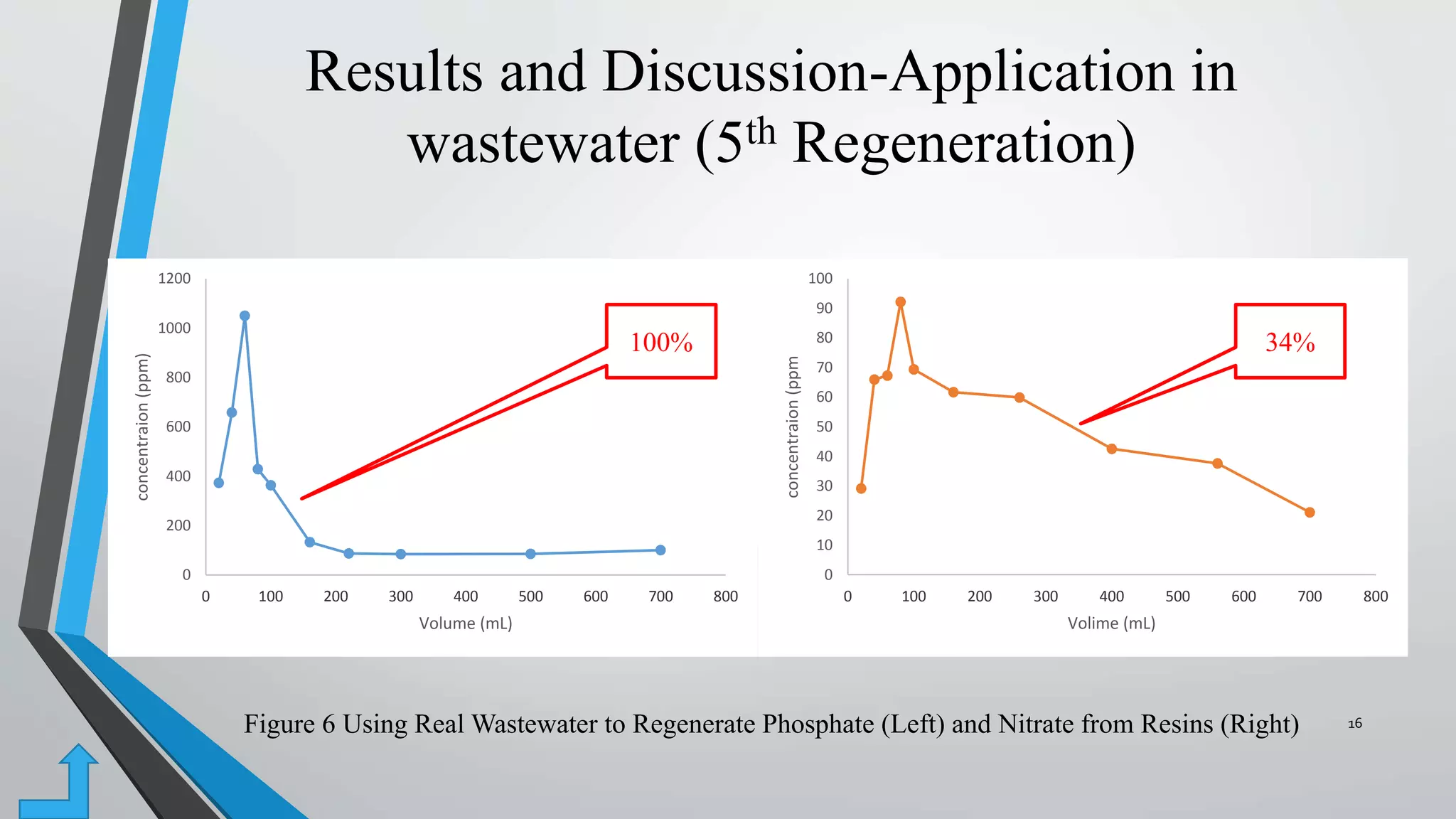
- The resins were then regenerated using salt solutions, achieving regeneration rates of 78-100% for phosphate and 34-95% for nitrate over multiple cycles.
- In a final test, the resins were able to regenerate 100% of phosphate and 34% of nitrate when exposed to real wastewater, demonstrating the potential