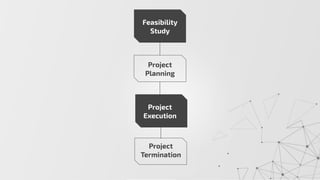
The document outlines the project management process including its phases: feasibility study, project planning, project execution, and project termination. It emphasizes the importance of defining project goals, evaluating feasibility, following a structured planning approach, and understanding factors influencing execution and closure. Additionally, it discusses the reasons for project termination and the necessity of post-performance analysis.