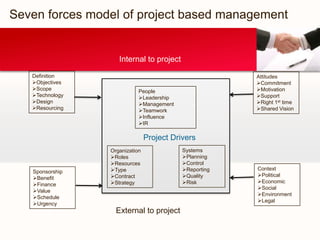
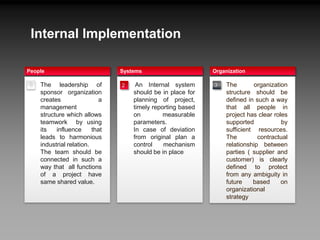
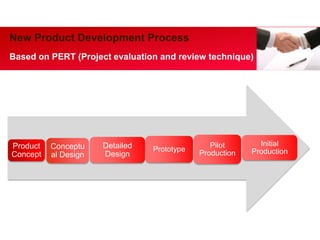
This document outlines key aspects of project management, including the seven forces of project-based management, the internal and external implementation processes, and the new product development process. It emphasizes the importance of leadership in ensuring project success through clear objectives, team motivation, and effective communication. The document also details the structured approach to product development using techniques such as PERT and phases from concept to market launch.