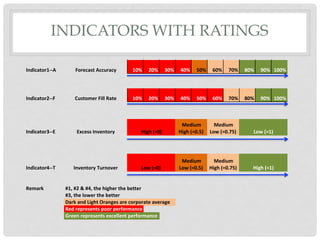
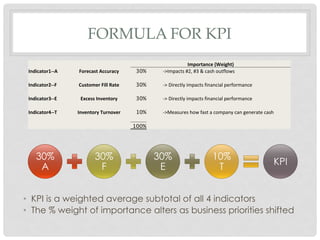
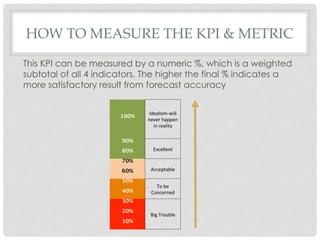
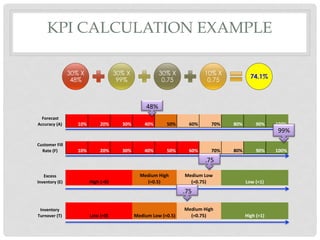
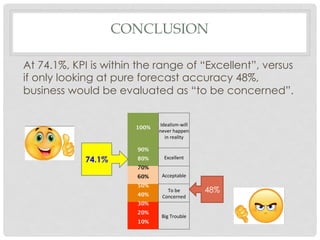
This document proposes a key performance indicator (KPI) for evaluating forecast accuracy that takes into account multiple factors. A KPI is calculated as a weighted average of four indicators: forecast accuracy, customer fill rate, excess inventory, and inventory turnover. Each indicator is rated on a scale and given an importance weight. The KPI is then calculated using a formula that averages the weighted ratings. This provides a more holistic view than only looking at raw forecast accuracy. An example calculation shows a scenario where the KPI evaluates as "excellent" while forecast accuracy alone would be "concerning." Considering multiple factors gives a fuller picture of forecast and business performance.