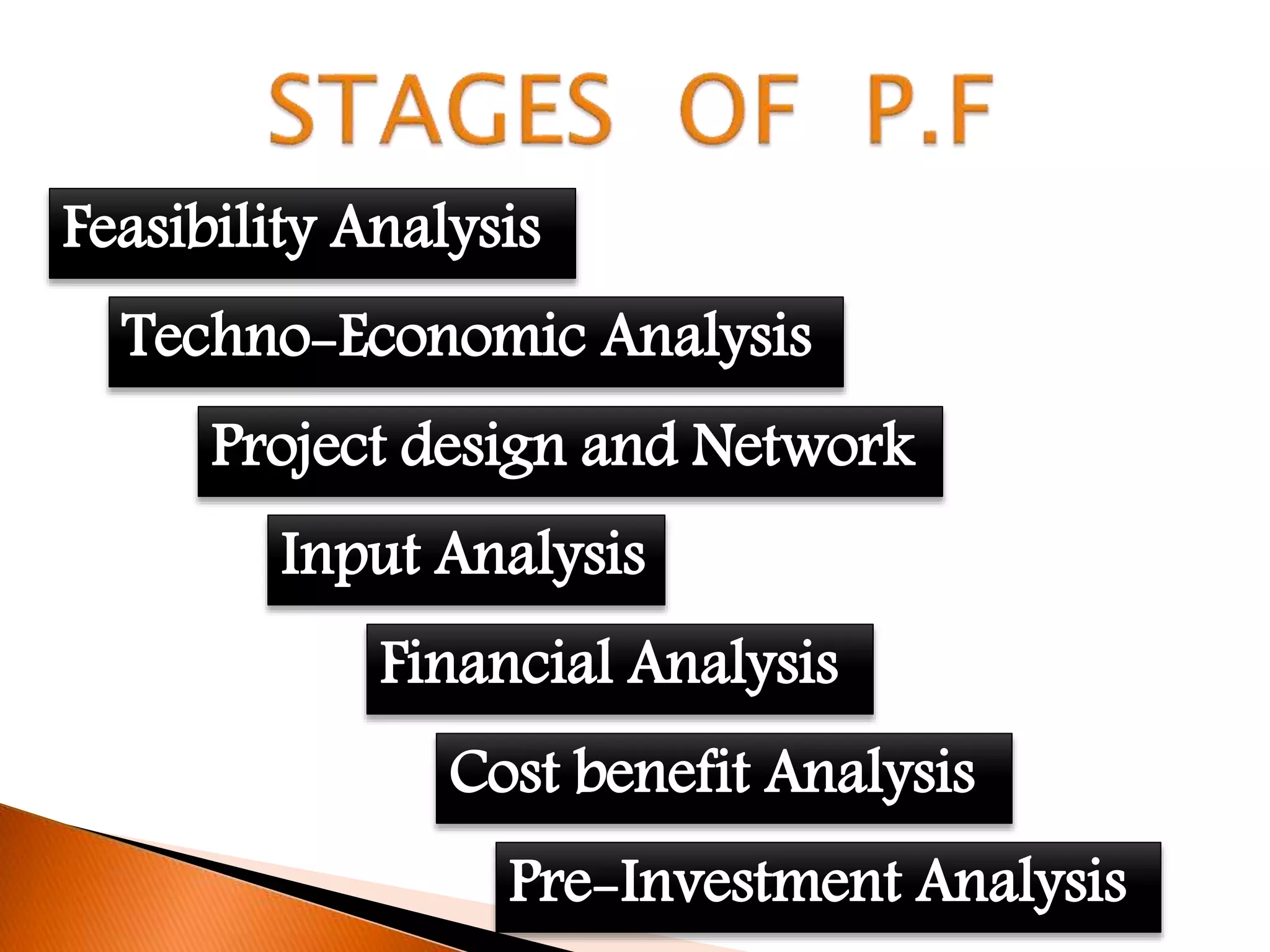
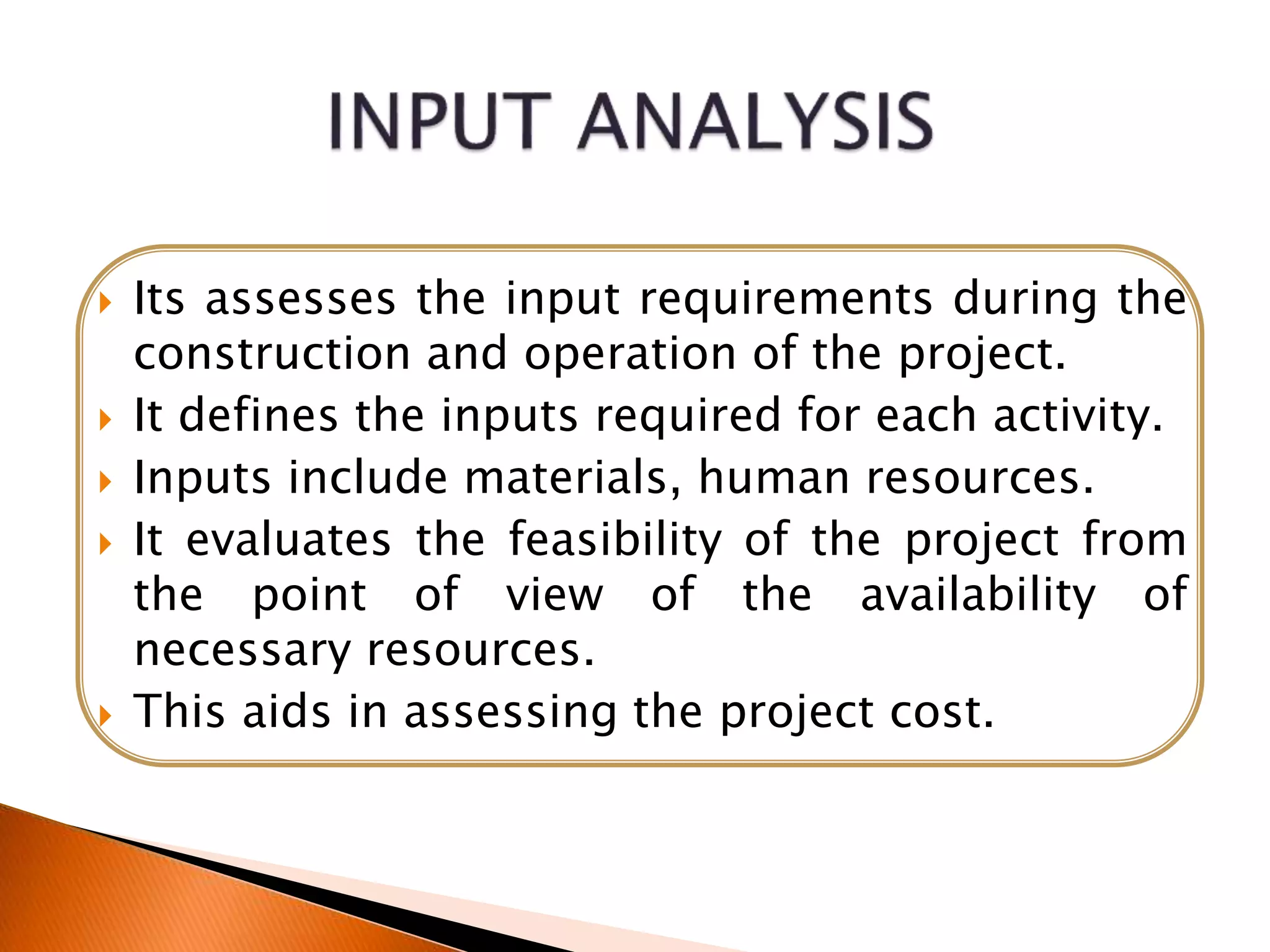
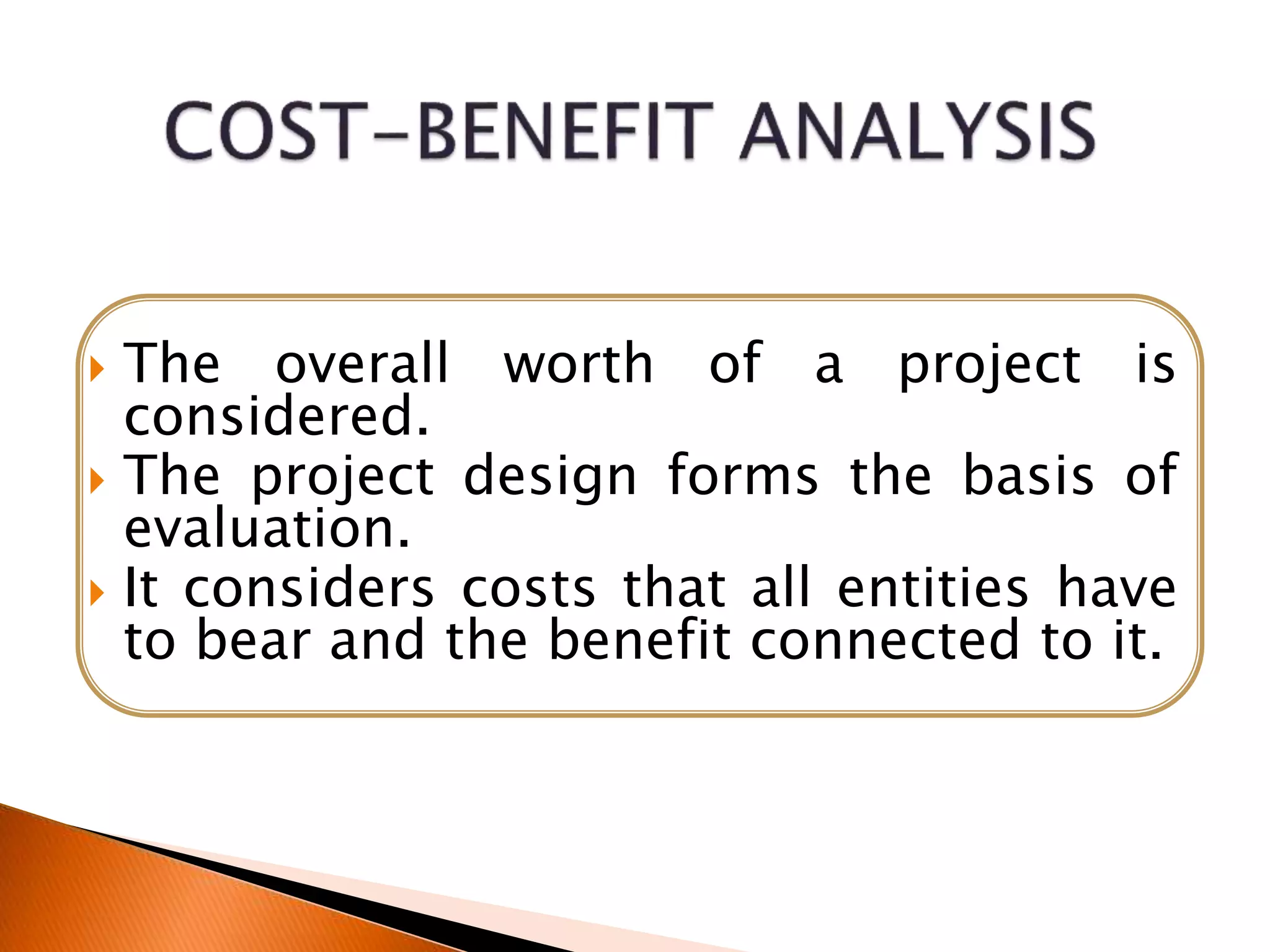
This document outlines the stages of project formulation, which is a systematic process involving a team of experts to develop a project idea and arrive at an investment decision. The key stages discussed are feasibility analysis, input analysis, financial analysis, cost-benefit analysis, pre-investment analysis, techno-economic analysis, and project design and network analysis. Feasibility analysis examines if a detailed proposal is warranted. Input analysis determines resource requirements. Financial analysis estimates costs and profits. Cost-benefit analysis evaluates overall project worth. Pre-investment analysis assesses external constraints. Techno-economic analysis chooses optimal technology. The project network defines activities and timelines. The final project report assesses demand, costs, and profitability to convince investors.