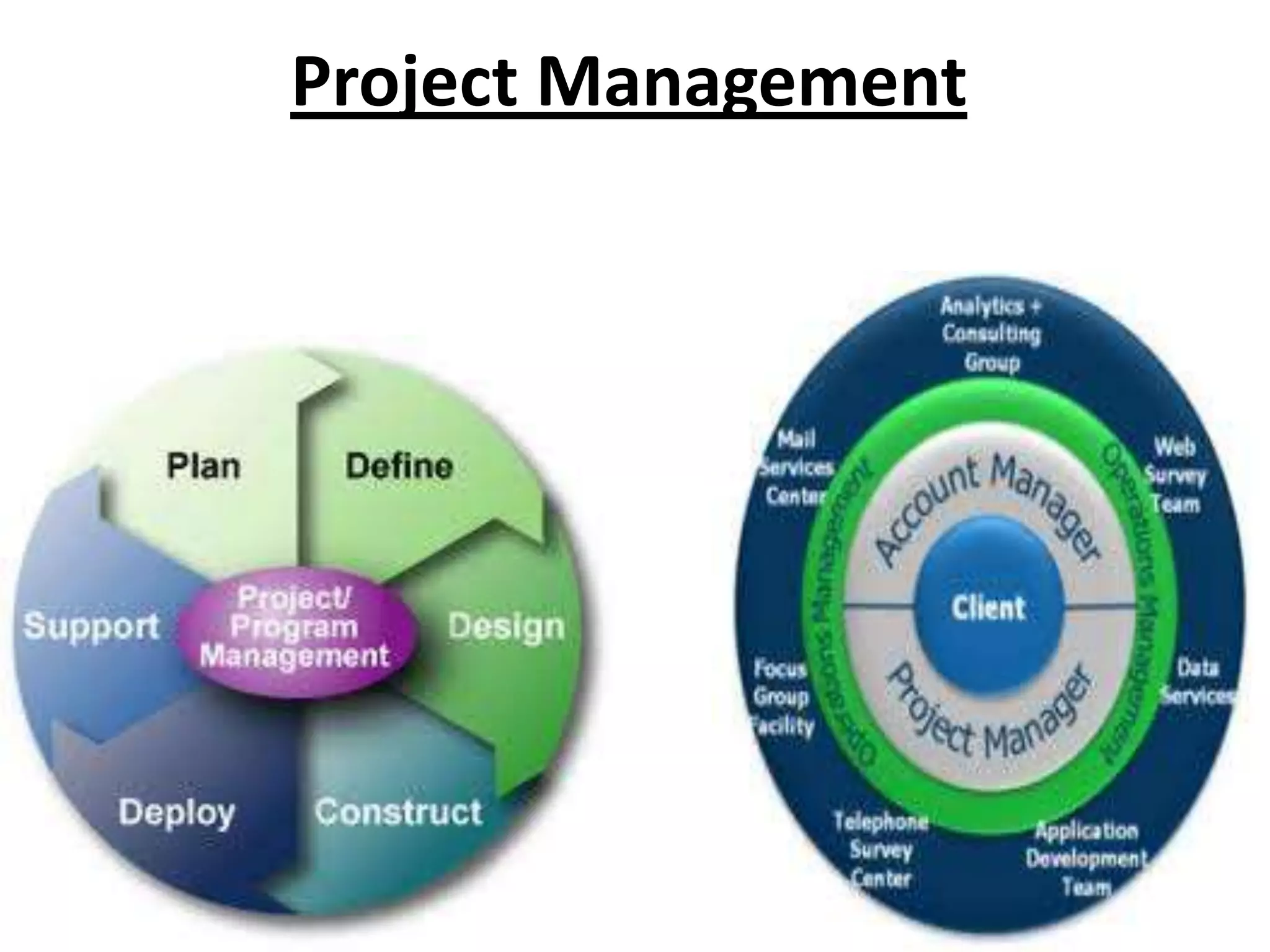
Project management involves planning, organizing, and managing resources to achieve goals within constraints of time, funding, and scope. A project has a defined start and end, and is undertaken to create beneficial change. Project management classifications include sector, scale, financial institution type, and purpose. The importance, features, and phases of project management are also outlined, including identification, formulation, appraisal, selection, implementation, and ongoing management.