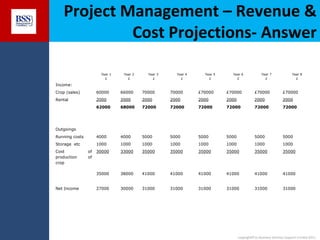
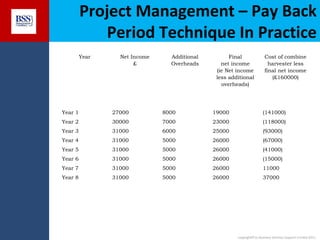
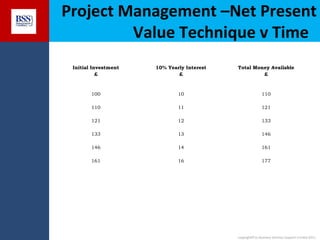
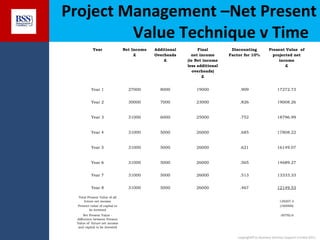
The document outlines project financial appraisal techniques as part of a finance training program for non-financial managers, focusing on the importance of financial evaluation and risk assessment for project viability. It provides methods such as payback period, return on investment, and net present value for effective project management, alongside practical examples illustrating revenue and cost projections in a farming scenario. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of understanding financial risks and provides a conclusive invitation for further course information.