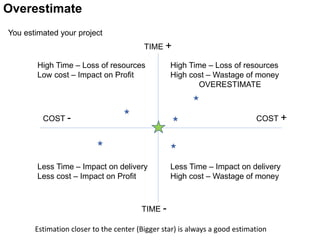
This document discusses various techniques for project estimation including expert opinion, analogous estimation, parametric estimation, three point estimation, and bottom-up estimation. It emphasizes that additional estimation efforts yield diminishing returns and that more detailed plans are not always better. While overestimation can waste money and resources, underestimation risks missing deadlines and reducing project effectiveness. The key is balancing estimation efforts with accuracy to develop reasonable plans.