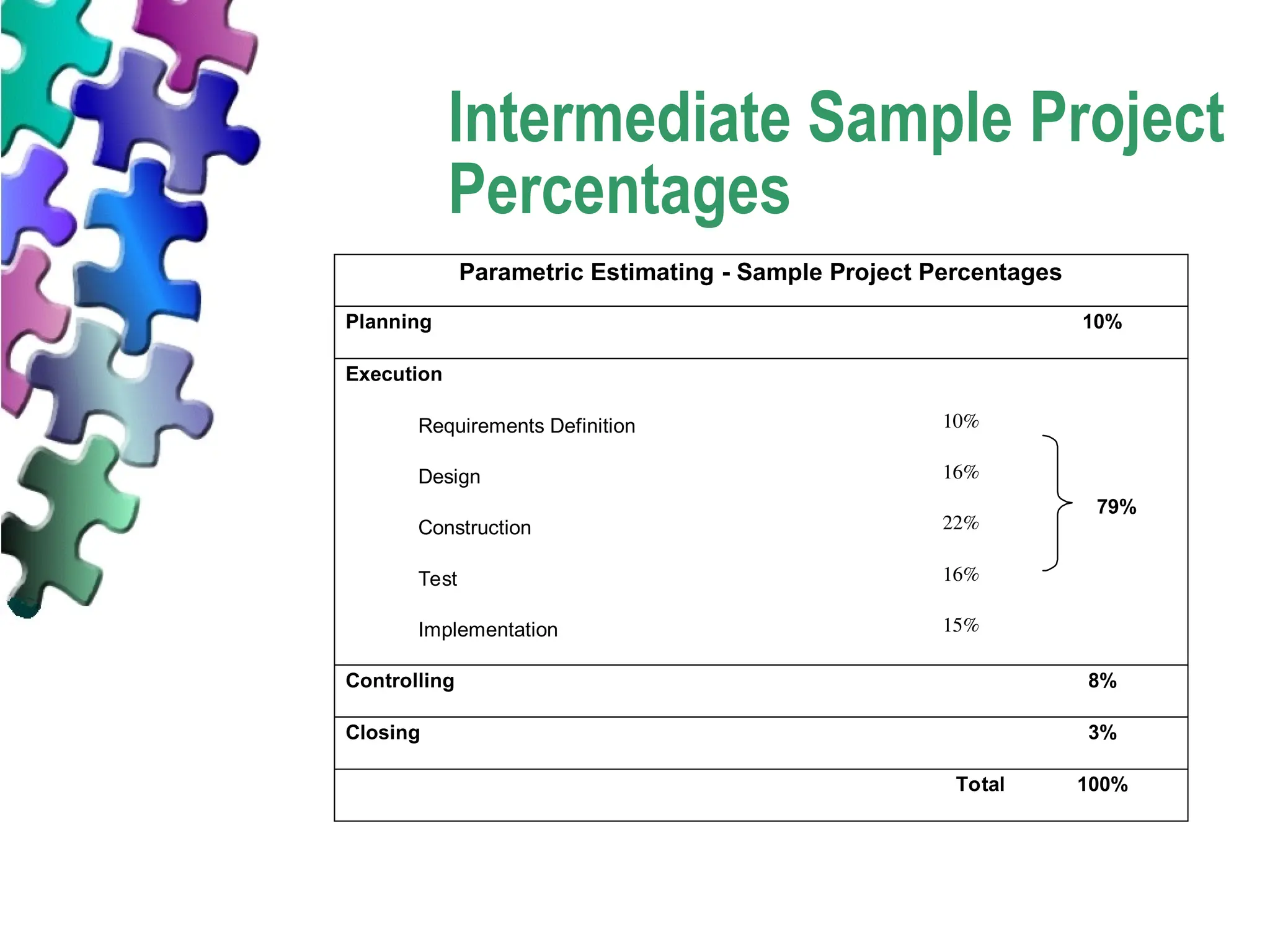
The document outlines various estimating techniques used in project management, including rough-order-of-magnitude (ROM), intermediate, and definitive estimates, each with specified accuracy ranges. It describes methodologies such as parametric and analogous estimating, emphasizing the importance of selecting the appropriate technique based on project requirements and available data. Additionally, it provides practical steps and references for utilizing these estimating tools effectively.