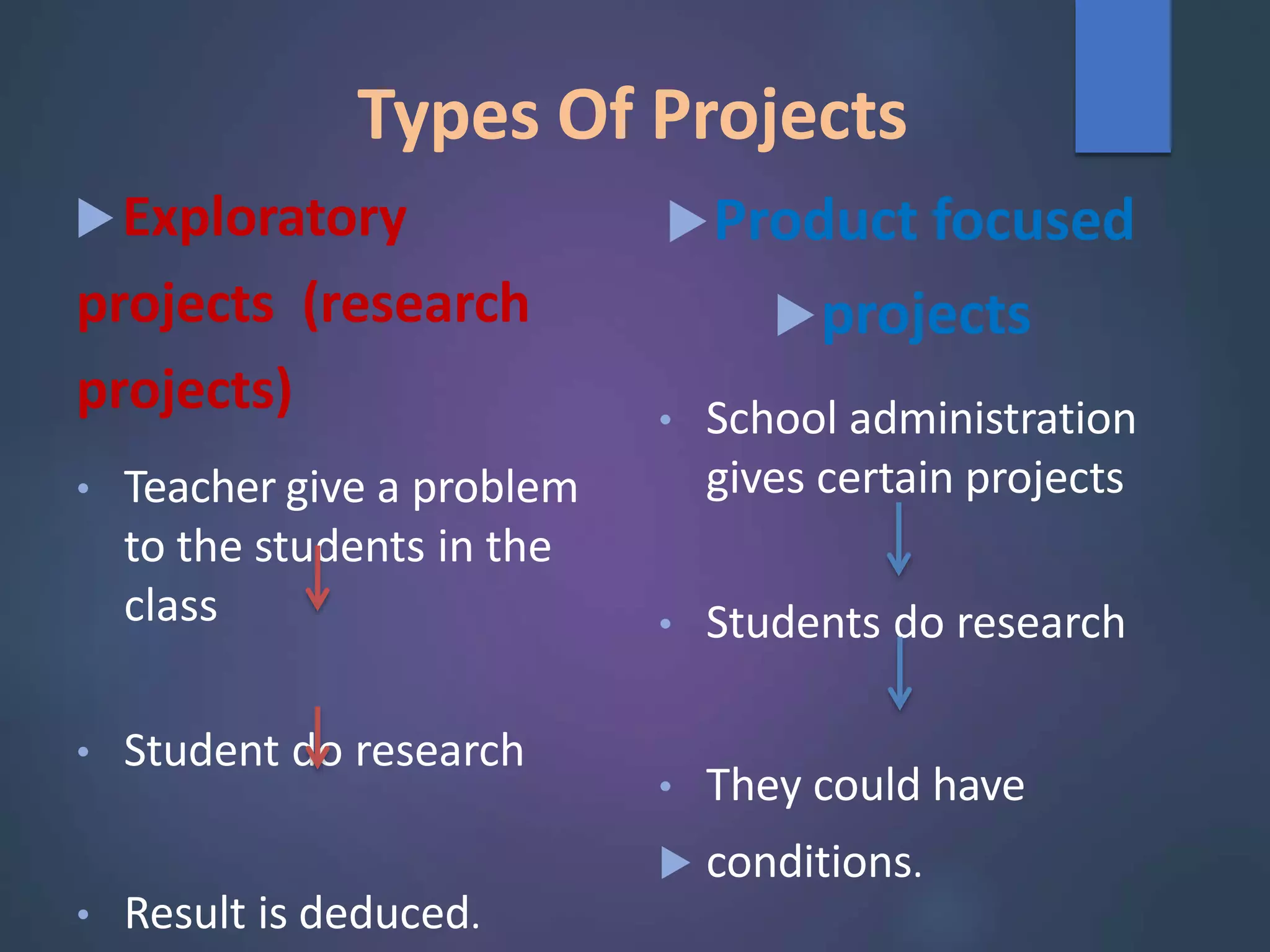
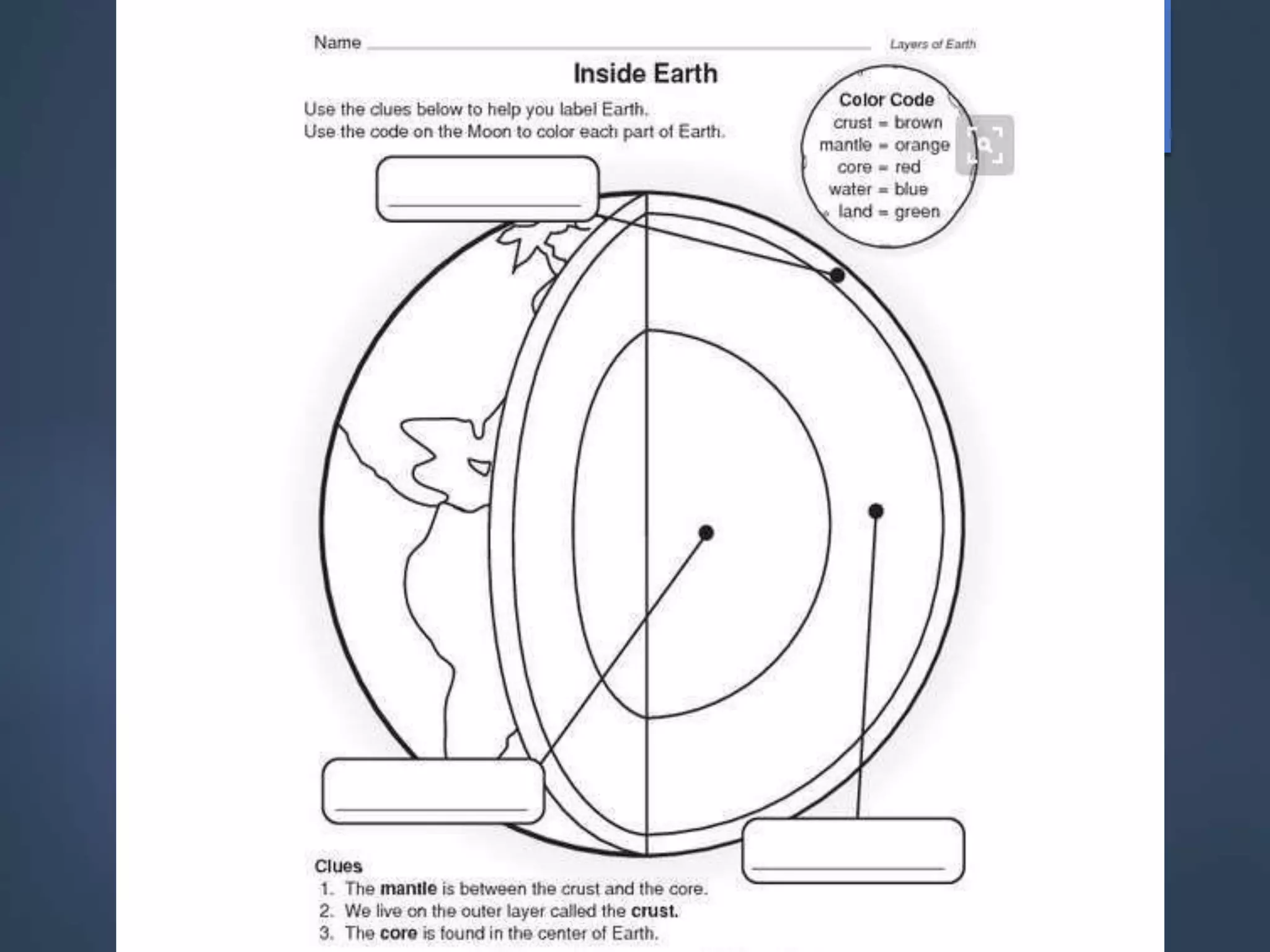
This document provides information about project based learning (PBL). It begins by quoting John Dewey about the role of the teacher being to select influences that affect students and help them respond appropriately. PBL is then defined as a teaching method where students gain knowledge and skills by investigating and responding to engaging, complex questions or challenges over an extended period. Key elements of PBL include role playing, real-world scenarios, blended writing genres, and authentic assessments. PBL is said to develop skills like information processing, reasoning, inquiry, creation and evaluation. Potential drawbacks include lack of resources and need for more staff involvement. The document also provides an example of a lesson plan on layers of the Earth incorporating a PBL approach.