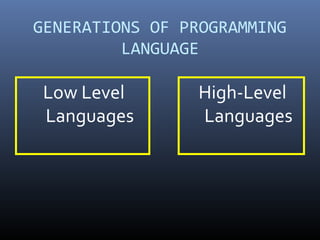
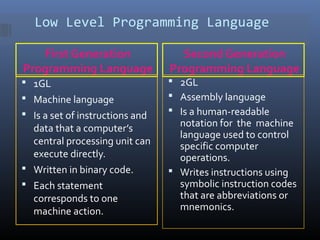
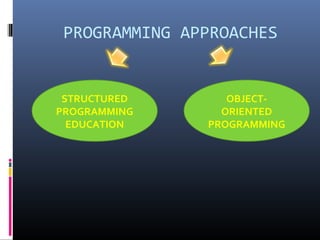
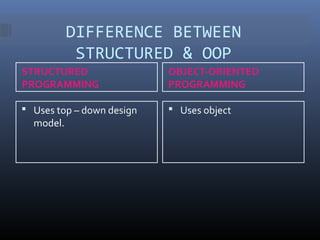
This document discusses computer programming and programming languages. It defines a computer program and programming language. It describes the different generations of programming languages from low-level machine languages and assembly languages to modern high-level languages like C++. It discusses programming approaches like structured programming which breaks programs into modules and object-oriented programming which combines data and functions into objects.