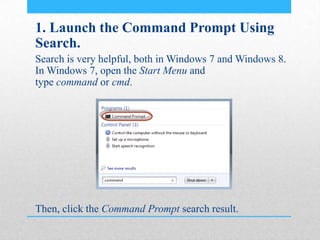
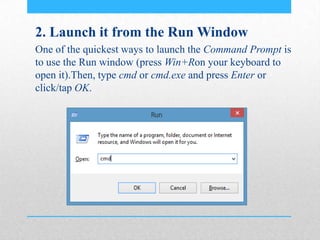
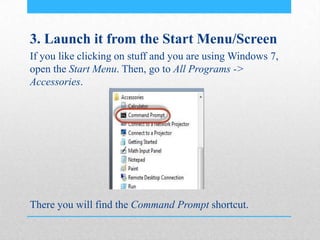
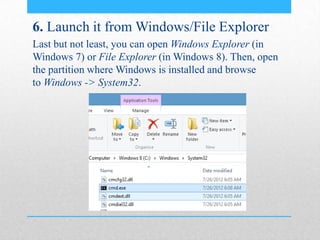
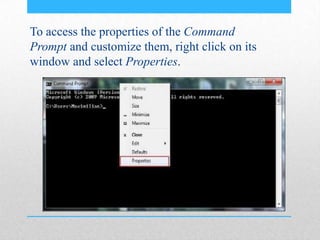
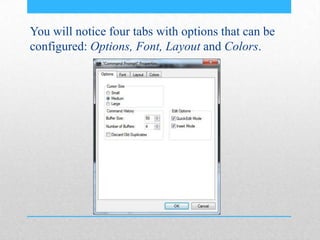
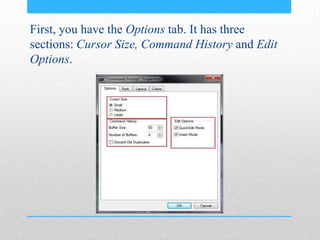
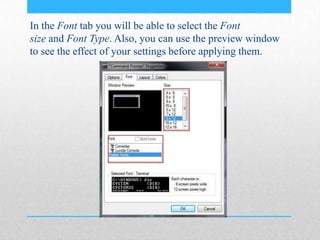
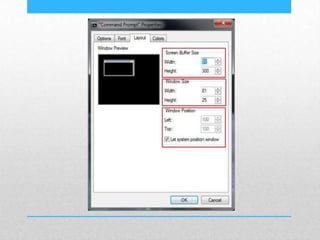
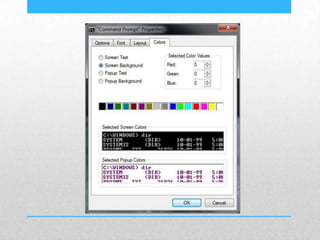
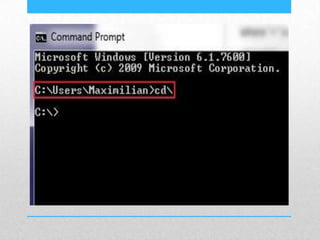
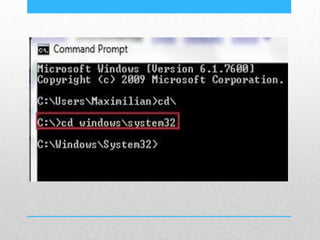
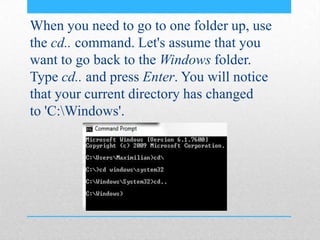
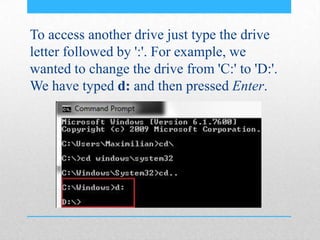
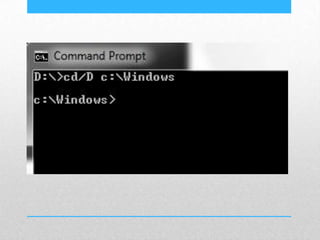
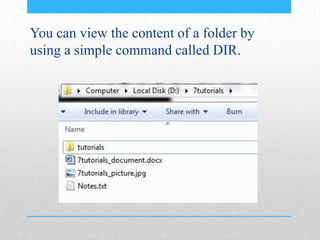
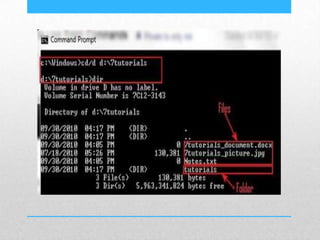
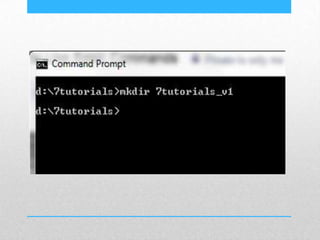
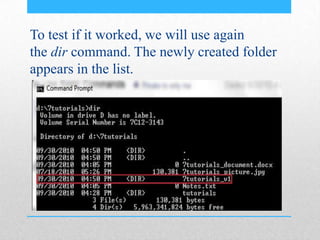
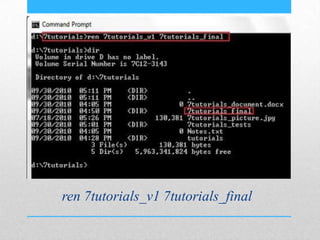
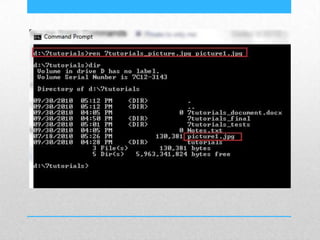
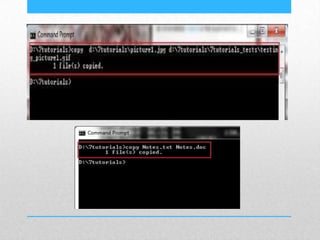
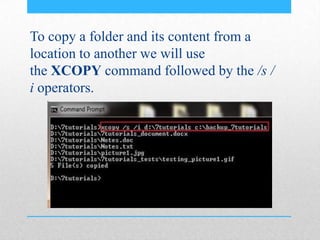
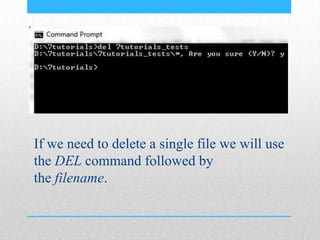
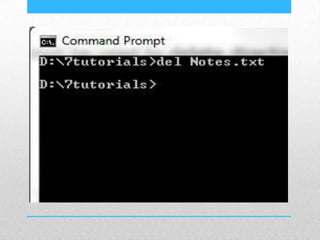
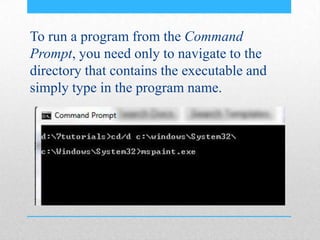
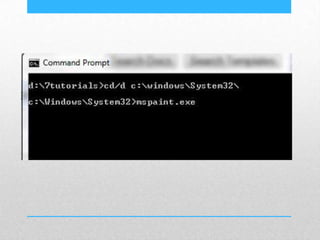
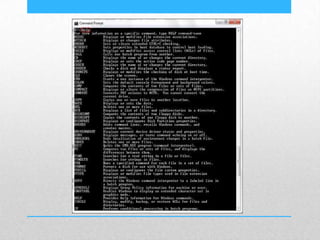
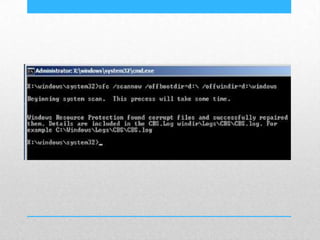
This document provides an introduction and overview of MS-DOS commands and how to use the Windows command line interface. It discusses what MS-DOS is, how to open the command prompt in Windows 7 and 8, and provides examples of basic commands like navigating directories, viewing folder contents, creating and deleting files and folders, copying and moving files, launching applications, and getting help. The document also describes how to customize properties of the command prompt like fonts, colors, window size and buffers.