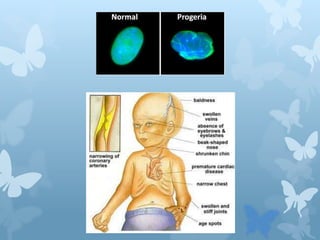
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome is a rare genetic condition caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene. This mutation prevents the normal processing of prelamin A protein, leaving it permanently anchored to the nuclear membrane. As a result, children with progeria exhibit rapid aging effects, including limited growth, hair loss, stiff joints, wrinkled skin, heart disease, and usually pass away from heart attacks or strokes at an average age of 14 years old.