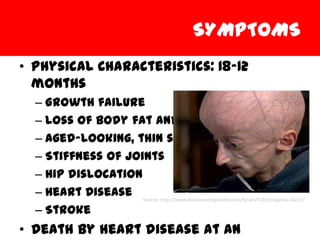
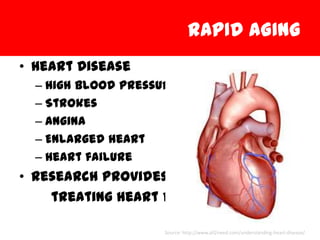
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome (HGPS) is a rare, fatal genetic condition where children experience rapid and premature aging. It affects about 1 in 8 million births. Children with HGPS show physical signs of aging like hair loss, aged-looking skin, stiff joints, and heart disease. They typically die of heart attacks or strokes at an average age of 14 years old. HGPS is caused by a mutation in the LMNA gene which produces abnormal lamin A proteins that cause aging defects in the cell nucleus. There is no cure for HGPS currently, but research aims to find treatments to correct the underlying genetic defects and extend patients' lives.